Column
Tube voltage
and
tube
current
The intensity
of
characteristic X-rays is proportional to
then-th
power
of
the difference between tube voltage and
excitation voltage (minimum voltage required
fo
r obtaining characteristic X-rays). It is also proportional to tube
current. When the tube voltage is low, the value
ofn
approaches 2. As the tube voltage increases, the value
of
n
becomes smaller.
On
the other hand, the intensity
of
continuous X-rays that appear as a background in the
KP
filter
method is proportional to the square
of
the tube voltage and is also proportional to the tube current.
Th
is means that
an optimum tube voltage value
exists for measurements with each target. The
fo
llowing table gives the optimum
voltages for different target types. For measurements using the
KfJ
filter method, it is a good way to set the tube
voltage so that the
P/8
ratio (peak-to
-b
ackground ratio) will become the largest.
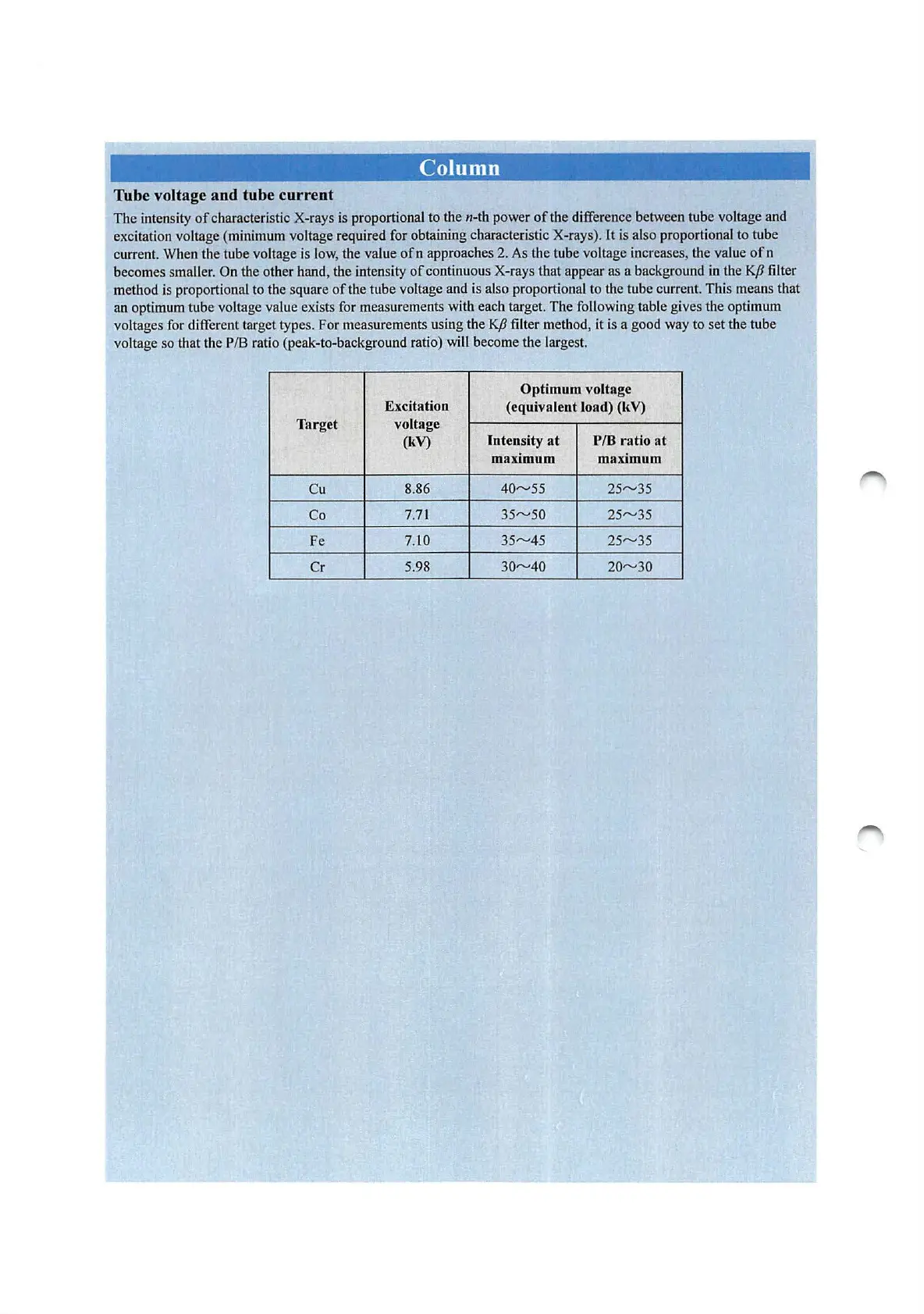
Optimum
voltage
Excitation
(equivalent
lo
ad)
(kV)
Target
voltage
(kV)
Intensity
at
P/8
rati
o
at
maximum maximum
Cu
8.86
40"-'55 25"-'35
Co
7.71
35"-'50 25"-'35
Fe
7.
10
35"-'45 25"-'35
Cr
5.
98
30"-'40 20"-'30
 Loading...
Loading...