XP Transponders User Guide Rev 1.3
The antenna should be outed o the outside of the aiaft aodig to the aufatue’s
installation instructions. The ideal location is a vertical orientation, mounted on the underside of the
aircraft, near the wing root.
Try to minimize the distance between the transponder and the antenna. Take care to locate the antenna
away from any objects that may disrupt the ground plane for the antenna, such as doors and landing
gea. Do ot plae the atea lose to egie ehaust. T to keep the atea loated at least
away from other antennas on the aircraft. The antenna should be located as close to the centerline of
the fuselage as space allows, while trying to keep the antenna on a flat surface.
A ground plane is required for most transponder antennas (including examples listed above). Failure to
provide a good ground plane can result in degradation of antenna performance.
Also, take care not to over-torque the antenna in an attempt to reduce a gap between the antenna and
the mounting surface; torque the antenna to the manufacture’s instructions.
GPS Antenna
The XPG-TR uses an active GPS, and if an external antenna is required it should meet with the following
requirements.
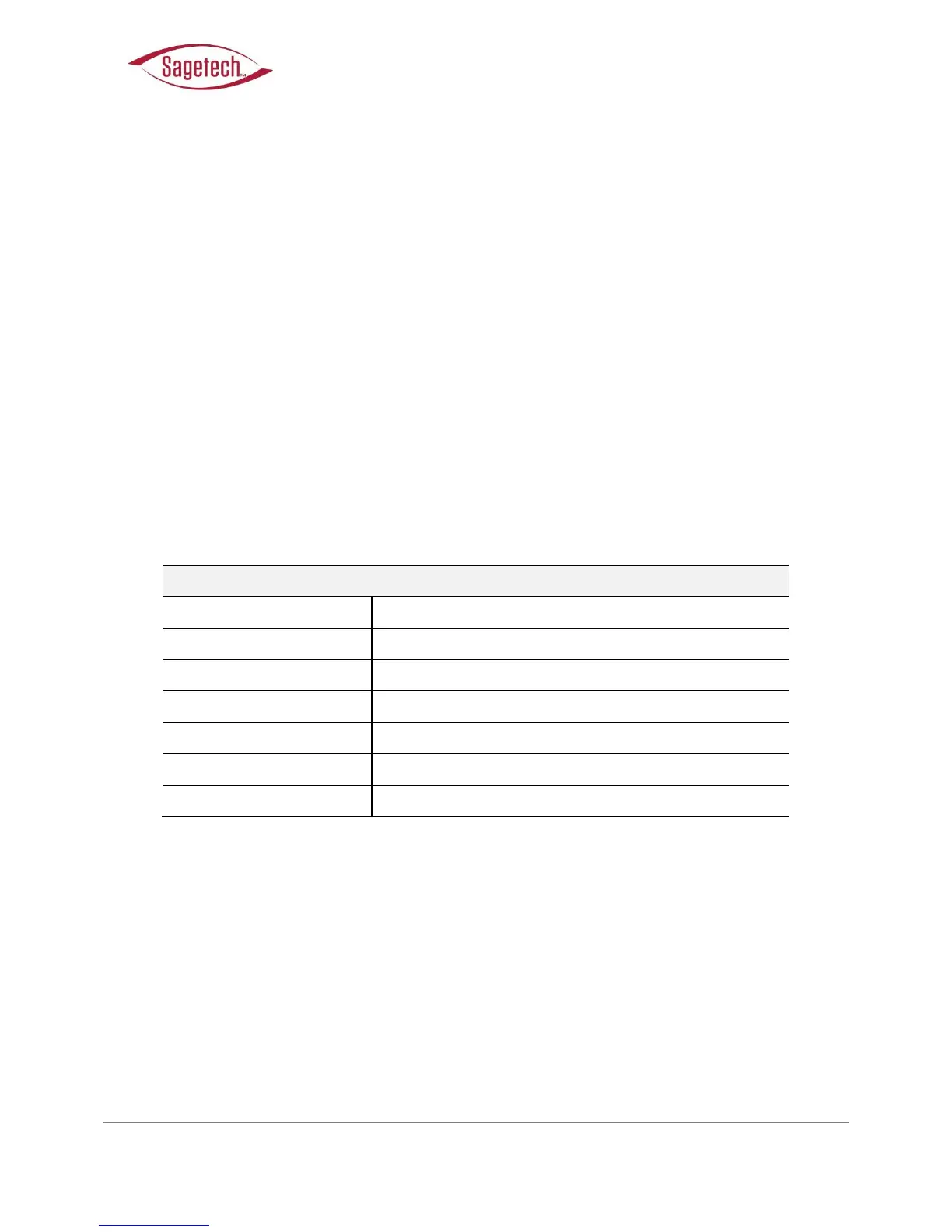
Table 5: GPS Antenna Specifications
Topside of aircraft fuselage, with clear view of sky.
Sagetech offers an external GPS antenna GPS-ANT-001 (GPS active antenna module with cable) that
meets these requirements, as well as XP-AT-002 (GPS active antenna module, bulkhead) and XP-CBL-
005, a cable to connect the antenna to the XPG-TR unit.
Antenna Cable
A suitable antenna cable consists of a male SMA connector, a length of co-axial cable, and a suitable
connector for your antenna. For example, if you are using a simple monopole antenna (as shown in
Table 4) with a BNC female connector, your antenna cable will need a BNC male connector.
 Loading...
Loading...