30 | SAMLEX AMERICA INC. SAMLEX AMERICA INC. | 31
7.15.3 Series – Parallel Connection
6V
200 Ah
12V String 1 12V String 2
Battery 1 Battery 3Battery 2 Battery 4
6V
200 Ah
6V
200 Ah
6V
200 Ah
12V Inverter
or 12V Charger
Cable “A”
Cable “B”
Fig. 7.4 Series-Parallel Connection
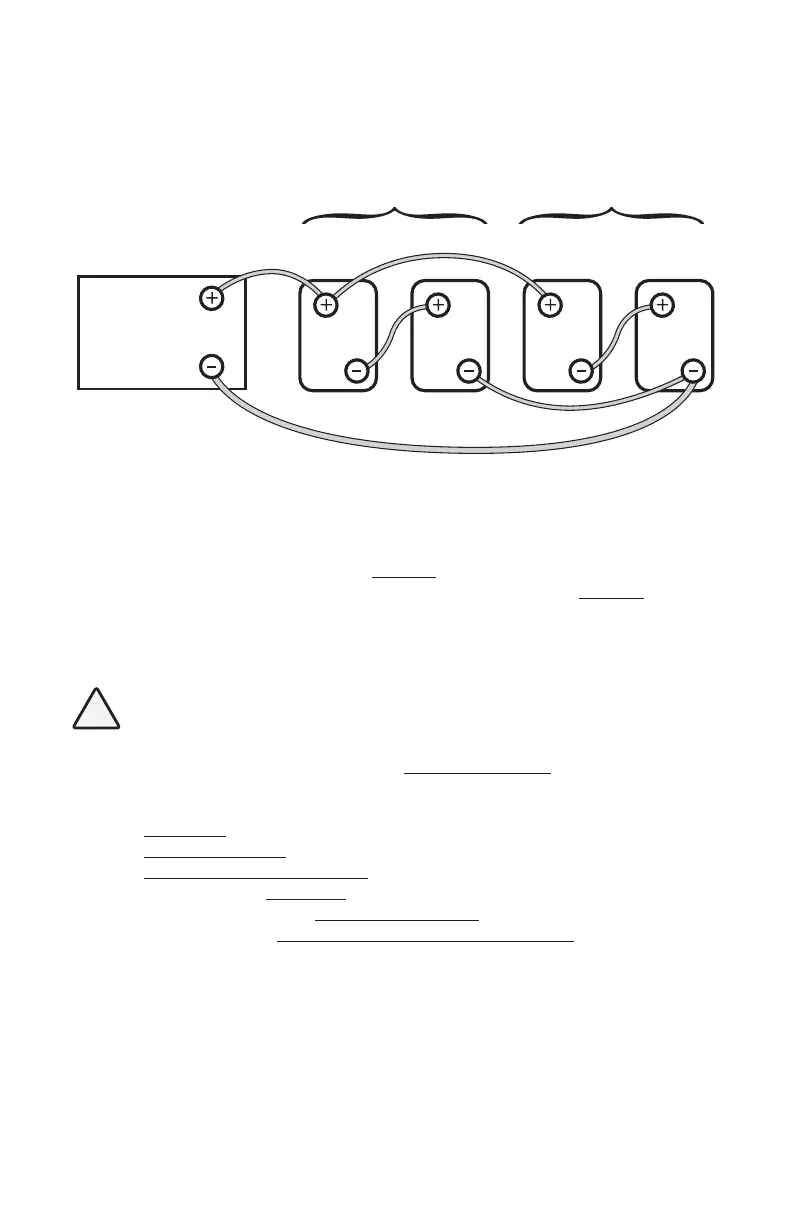
Figure 7.4 shows a series – parallel connection consisting of four 6V, 200 AH batteries to
form a 12V, 400 Ah battery bank. Two 6V, 200 Ah batteries, Batteries 1 and 2 are connect-
ed in series to form a 12V, 200 Ah battery (String 1). Similarly, two 6V, 200 Ah batteries,
Batteries 3 and 4 are connected in series to form a 12V, 200 Ah battery (String 2). These
two 12V, 200 Ah Strings 1 and 2 are connected in parallel to form a 12V, 400 Ah bank.
7.15.4 Wiring Order in Parallel Connection of Batteries
CAUTION!
When 2 or more batteries / battery strings are connected in parallel and are
then connected to inverter/charger (See Figs 7.3 and 7.4), attention should be
paid to the manner in which the inverter/charger is connected to the battery
bank. Please ensure that if the Positive output cable of the inverter/charger
(Cable “A”) is connected to the Positive battery post of the rst battery
(Battery 1 in Fig 7.3) or to the Positive battery post of the rst battery string
(Battery 1 of String 1 in Fig. 7.4), then the Negative output cable of the
inverter/charger (Cable “B”) should be connected to the Negative battery
post of the last battery (Battery 4 as in Fig. 7.3) or to the Negative Post of the
last battery string (Battery 4 of Battery String 2 as in Fig. 7.4). This connection
ensures the following:
- The resistances of the interconnecting cables will be balanced.
- All the individual batteries / battery strings will see the same series resistance.
- All the individual batteries will charge/discharge at the same charging/
discharging current and thus, will be charged/discharged to the same state at
the same time.
- None of the batteries will see an overcharge/overdischarge condition.
SECTION 7 | General Information - Battery Related
 Loading...
Loading...