Appendix
A.1 Information about upgrading to a CPU 31xC or CPU 31x
CPU 31xC and CPU 31x, Technical Data
A-6 Manual, 01/2006 Edition, A5E00105475-06
A.1.7 Replacing a CPU 31xC/31x
Replacing a CPU 31xC/31x
When supplied, the CPU 31xC/31x adds a connecting plug to the power supply connector.
You no longer need to disconnect the cables of the CPU when you replace a 31xC / 31x
CPU. Insert a screwdriver with 3.5 mm blade into the right side of the connector to open the
interlock mechanism, then unplug it from the CPU. Once you have replaced the CPU, simply
plug the connecting plug back into the power supply connector.
A.1.8 Using consistent data areas in the process image of a DP slave system
Consistent data
The table below illustrates the points to consider with respect to communication in a DP
master system if you want to transfer I/O areas with "Total length" consistency. You can
transfer a maximum of 128 bytes of consistent data.
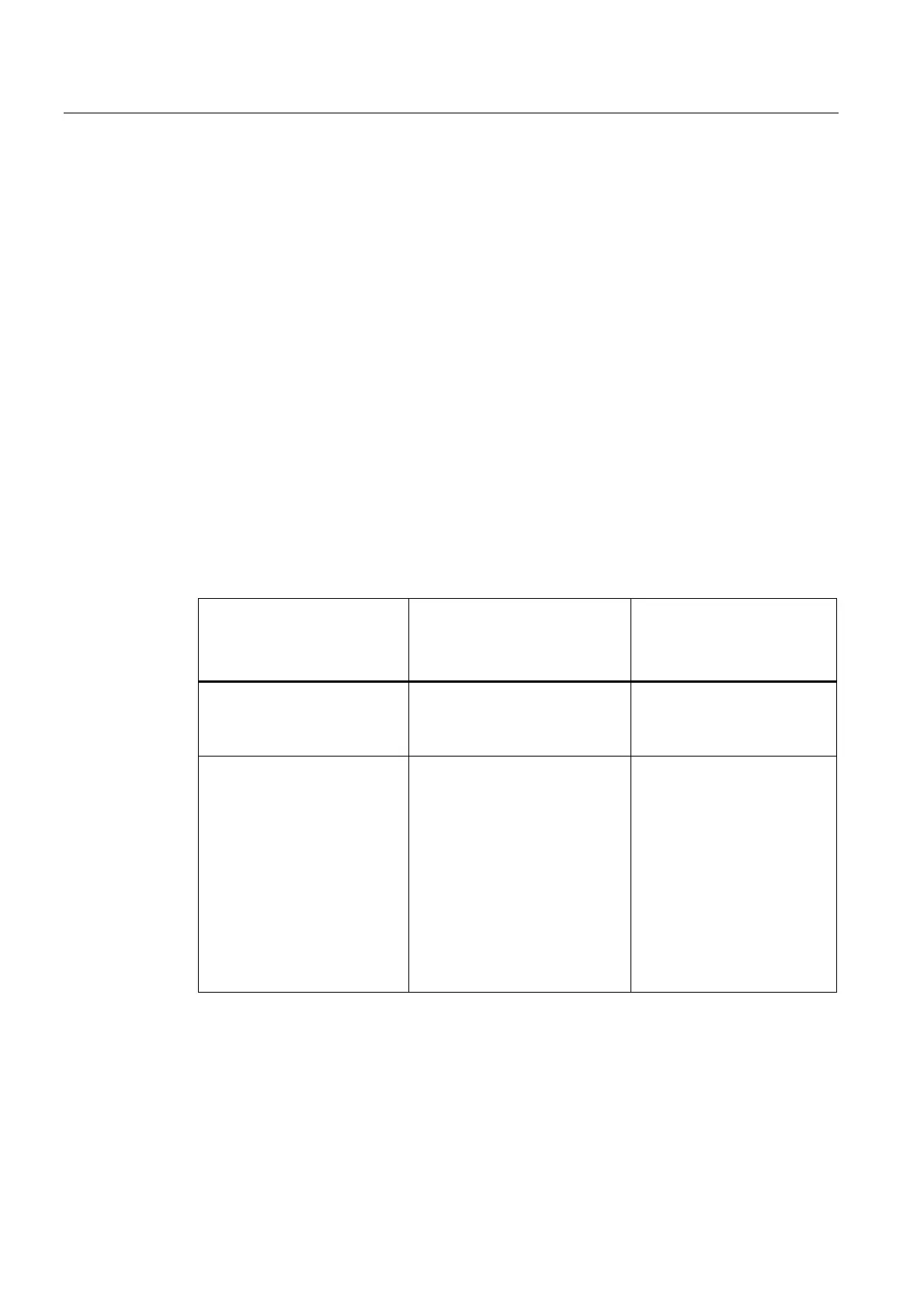
Table A-1 Consistent data
CPU 315-2 DP
(as of firmware 2.0.0),
CPU 317, CPU 319
CPU 31xC
CPU 315-2 DP
(as of firmware 1.0.0),
CPU 316-2 DP,
CPU 318-2 DP (firmware < 3.0)
CPU 318-2 DP
(firmware >= 3.0)
The address area of consistent
data in the process image is
automatically updated.
Even if they exist in the process
image, consistent data is not
automatically updated.
You can choose whether or not
to update the address area of
consistent data in the process
image.
In order to read and write
consistent data
you can also use the SFCs 14
and 15
If the address area of consistent
data is outside the process
image,
you have to use the SFCs 14
and 15 to read and write
consistent data.
Direct access to consistent
areas is also possible (e.g.
L PEW or T PAW).
To read and write consistent data,
you must use SFC14 and 15.
To read and write consistent
data, you can also use SFC 14
and SFC 15.
If the address area of
consistent data is not in the
process image, you must use
SFC 14 and SFC 15 to read
and write consistent data.
Direct access to consistent
areas is also possible (for
example, L PEW or T PAW).

 Loading...
Loading...











