9
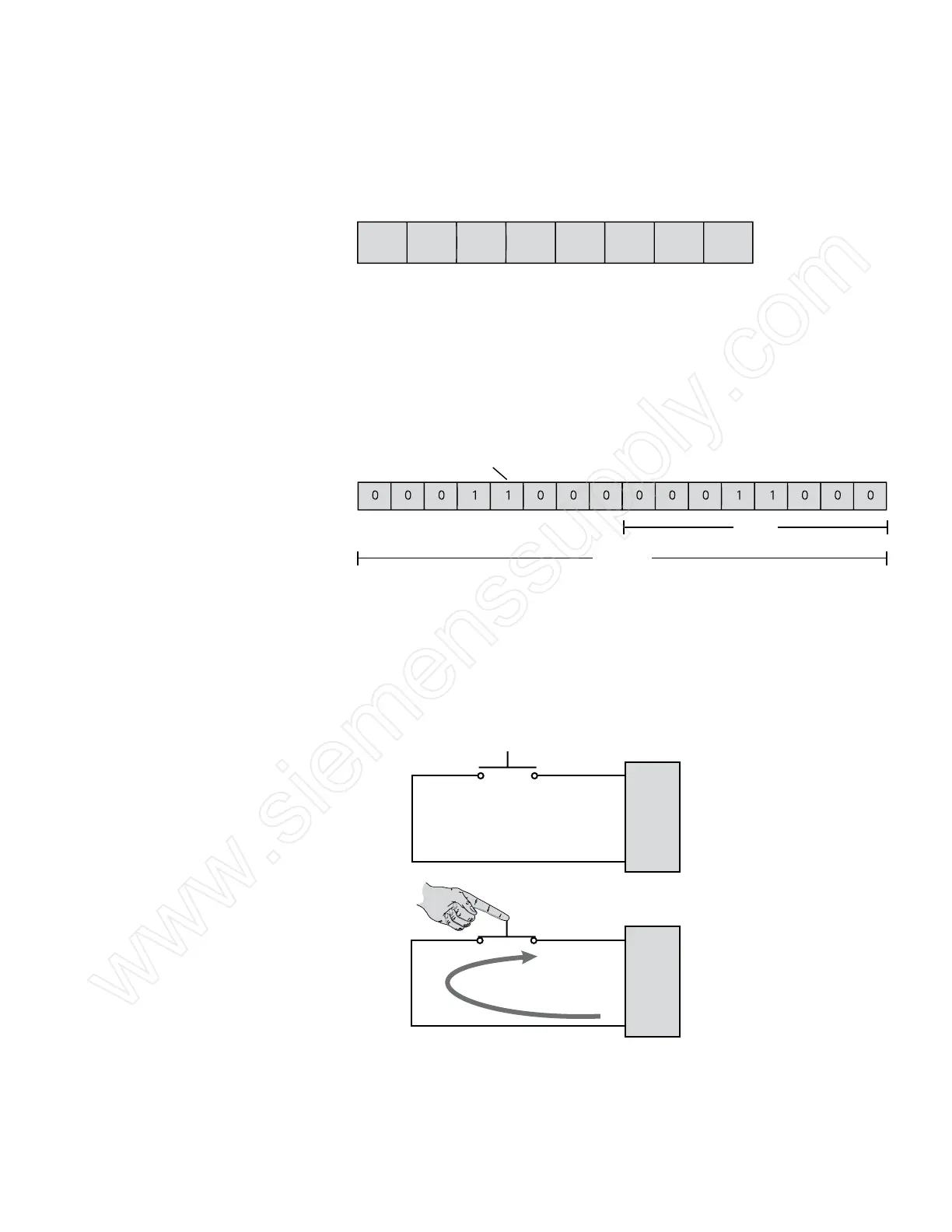
The process of converting a binary number to an equal decimal
value is as simple as adding the equivalent decimal value
for each position in the binary number where a 1 is shown.
Positions with a 0 do not add to the number value.
128 64 32 16 8 4
2 1
0 0 11 0 0
2
7
2
6
2
5
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
1 0
Decimal Value = 32 + 8 + 1 = 41
Bits, Bytes, and Words Each position in a binary number is called a bit. The number
of bits used to represent numbers varies with the device.
However, instructions and data are usually grouped in bytes and
eight bits make up one byte. Two bytes, or 16 bits, make up one
word.
Logic 0, Logic 1 While PLCs are capable of sensing and generating analog
values, programmable controllers internally use signals that are
on or off. These on and off conditions correspond to the binary
values 1 and 0. For example, a binary 0, also called logic 0, can
be used to indicate that a switch is off, and a binary 1 (logic 1)
can be used to indicate that a switch is on.
PLC
Input 1
24 VDC
Off
Logic 0
On
Logic 1
PLC
Input 1
24 VDC
 Loading...
Loading...











