.L_
.- . . .L
.;‘.&<a
More About Blood
Pressure
Measurements
WHO Blood Pressure Classifications
Standards for assessment of high or low blood pressure, without
regard to age, have been established
by
the World Health
Organiza-
tion (WHO), as shown in this chart.
%
mmHg
$2
95
2
1
9:
90
2
cl
Systolic Blood
Pressure
Reference
Material
Investigation
into
Adult
Diseases
Report
by
the
Ministry
of
Health
and Social
Security
1971.
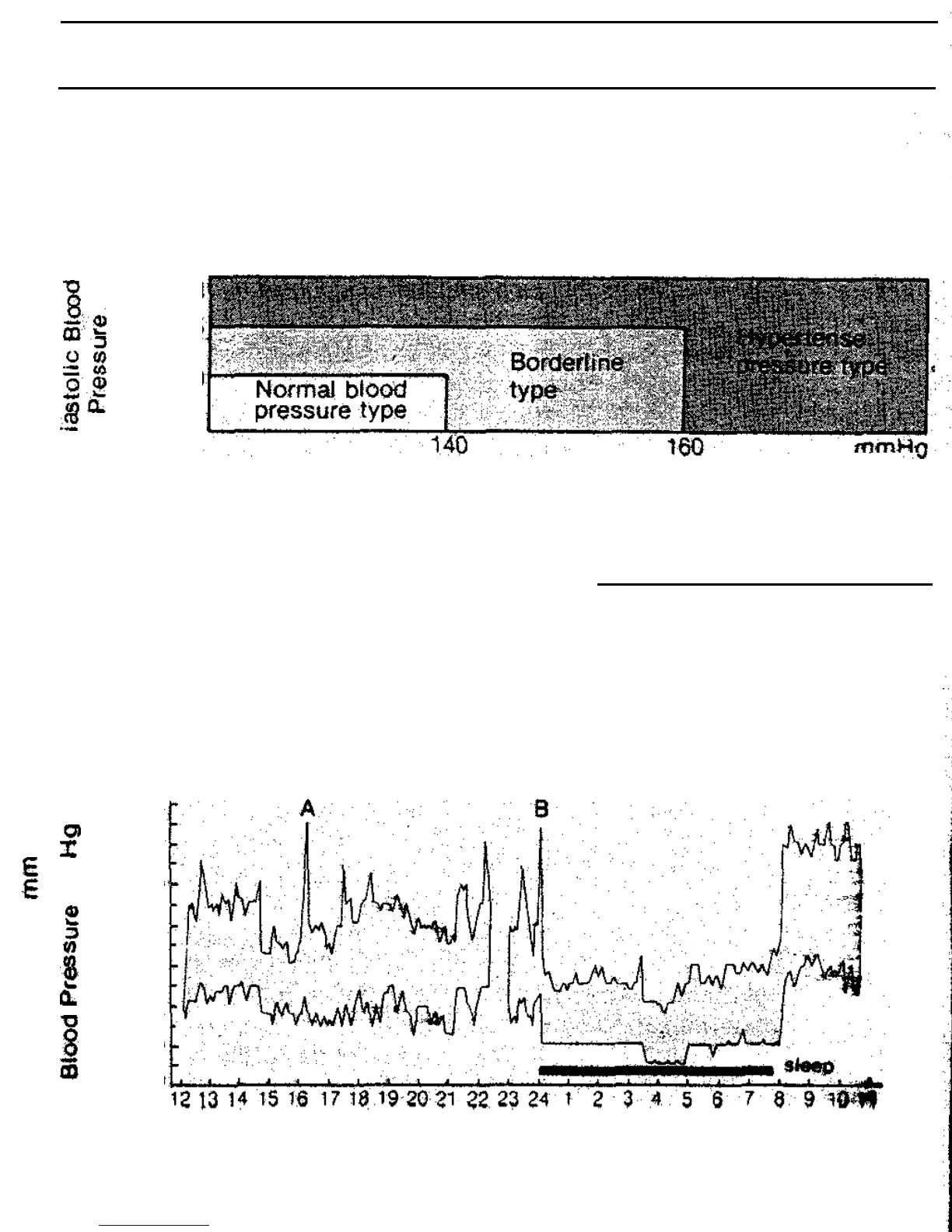
Variations in Blood Pressure
Individual blood pressures vary greatly both on a daily and a seasonal
basis. These variations are even more pronounced in
hypertense pa-
tients. Normally the blood pressure rises while at work and is at
its
lowest during the sleeping period. The graph below illustrates the
variations in blood pressure over a whole day with measurement
taken every five minutes.
160
r”
140
E 120
f
100
I
%
80
60
i
40
20
PM
Time
AM
Shown is data
for
measurement taken
every
5 minutes
The thick
line
represents sleep.
The
rises
in blood pressure
at 4 PM (A in We graph)
and
12 PM
(B
in
the
graph) correspond to an at-
tack
Of pain and
sexual
intercourse
(Beven,
Honour
&
Stott:
Clin. Sci. 36:329.
1969)

 Loading...
Loading...