cSolve()
Catalog >
You should also use var_ for any other
variables in Equation that might have
unreal values. Otherwise, you may receive
unexpected results.
cSolve(Eqn1andEqn2 [and…],
VarOrGuess1, VarOrGuess2 [, … ]) ⇒
Booleanexpression
cSolve(SystemOfEqns, VarOrGuess1,
VarOrGuess2 [, …]) ⇒
Booleanexpression
Returns candidate complex solutions to the
simultaneous algebraic equations, where
each varOrGuess specifies a variable that
you want to solve for.
Optionally, you can specify an initial guess
for a variable. Each varOrGuess must have
the form:
variable
– or –
variable = real or non-real number
For example, x is valid and so is x=3+i.
If all of the equations are polynomials and
if you do NOT specify any initial guesses,
cSolve() uses the lexical
Gröbner/Buchberger elimination method to
attempt to determine all complex solutions.
Note: The following examples use an
underscore (press /_) so that the
variables will be treated as complex.
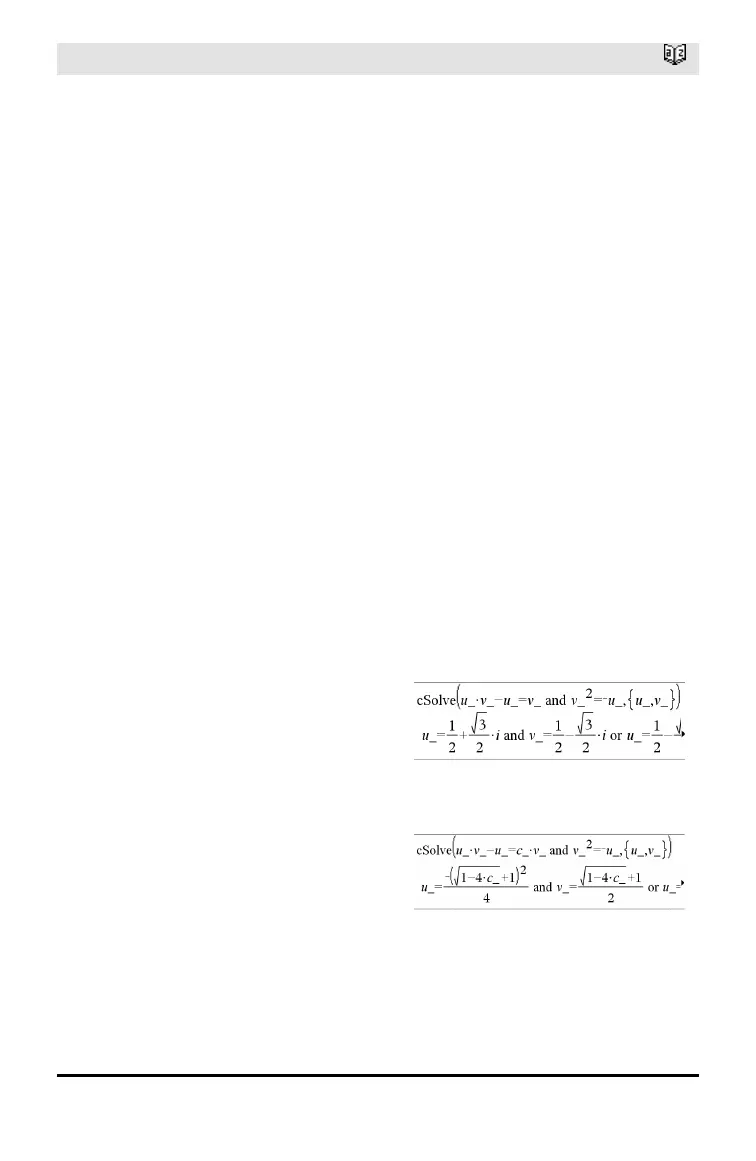
Complex solutions can include both real and
non-real solutions, as in the example to the
right.
To see the entire result, press £ and then
use ¡and¢ to move the cursor.
Simultaneous polynomial equations can
have extra variables that have no values,
but represent given numeric values that
could be substituted later.
To see the entire result, press £ and then
use ¡and¢ to move the cursor.
Alphabetical Listing 43

 Loading...
Loading...