PRON NA60-MB0
Version 3.50
PRON NA60-MB0 Remote Setting Manual
Page: 16 of 59
4.2 Example 2. How to read a BIT data type
Let’s read from the Slave address 1 the variable “I> Trip”.
From the Address Data Table (Appendix A) we find out the following information;
VAR REF IDX DIM TYPE UM Kv ENUM
I> Trip 1x 7 1 BIT 0=OFF, 1=ON
The REF field value specify a Discrete Input (1x), so the function 0x02 is used for reading. From the IDX the
Modbus address is derived: Modbus address = IDX -1 = 7 - 1 = 6. DIM specify the number of register to be read.
01 02 00 06 00 01 - -
TX
S F ADR DIM CRC
01 02 01 00 01 - -
RX
S F B VAL CRC
The TYPE field value is equal to BIT. Applying the rules described in the chapter 2.1, the following value is
obtained
VAL = 1.
The ENUM field specifies the meaning of the value. In this case, the value 1 corresponds to the “ON” state and it
means that a Trip has occurred on the first threshold of the 51 function.
4.3 Example 3. How to execute a command
Let’s execute the command “Reset events” on the Slave address 1.
From the Address Data Table (Appendix A) we find out the following information;
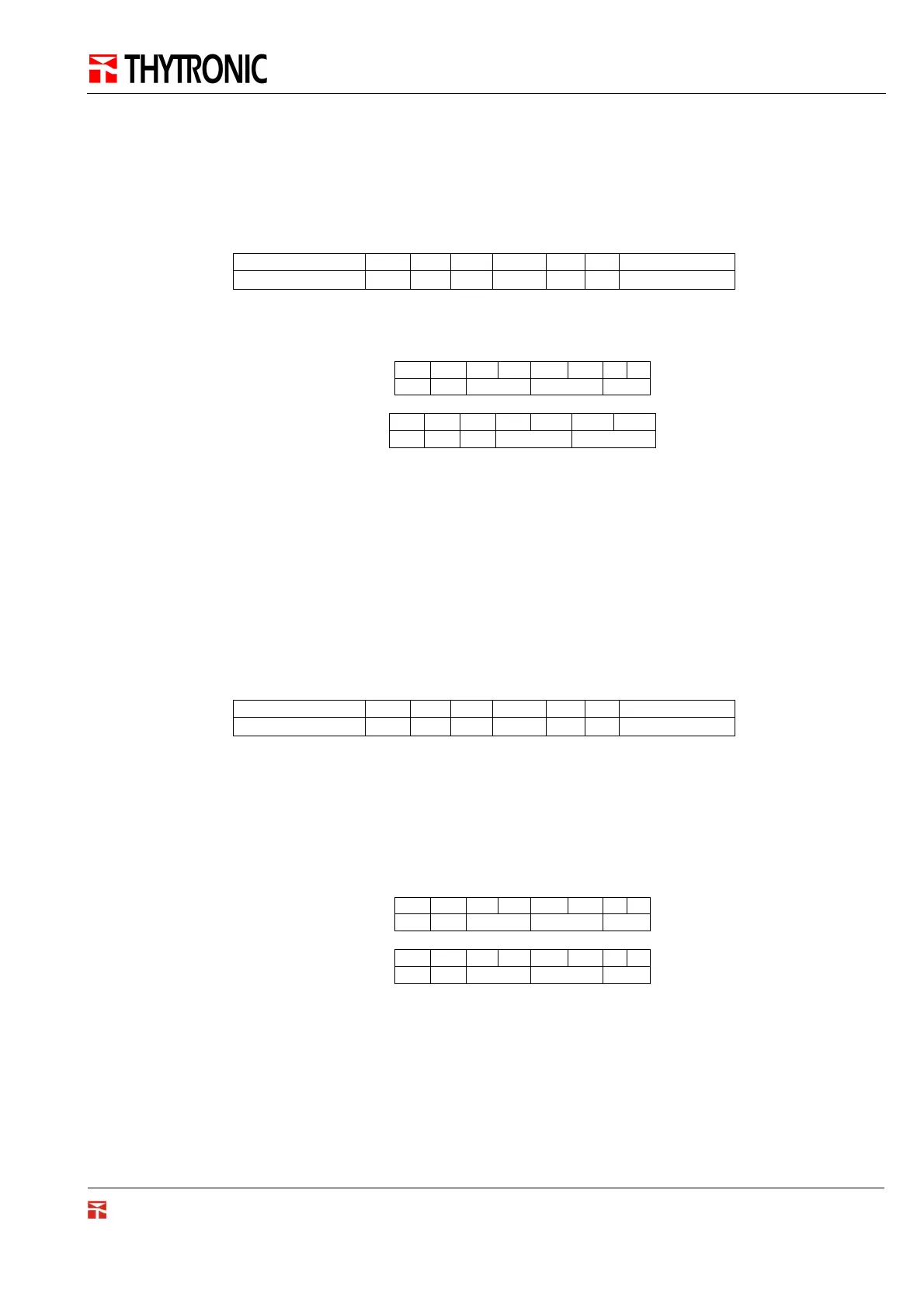
VAR REF IDX DIM TYPE UM Kv ENUM
Reset LEDs 0x 2 1 CMD 0=OFF, 1=ON
The TYPE field value specifies a Command (CMD). As described in chapter 2.1, to execute the command, it is
necessary to set its value to 1.
The REF field value specify a Coil (0x), so the function 0x05 is used for writing. From the IDX the Modbus address
is derived: Modbus address = IDX -1 = 2 - 1 = 1
The Response message is known as an “Acknowledge” because it’s an echo of the request, and it means that the
Coil has been set:
01 05 00 01 FF 00 - -
TX
S F ADR DATA CRC
01 05 00 01 FF 00 - -
RX
S F ADR DATA CRC

 Loading...
Loading...