3.1 Accessing the System
You access the 4033A remotely by connecting to its Command-And-Response (CNR) Port
through the Ethernet connection. The CNR port (Port 10001), which uses TCP/IP, lets users input
commands, displays results of the commands, and publishes alarms as they occur.
When users Telnet to the CNR port, the system does not display a prompt.
3.2 Checking System Status
3.2.1 Checking Alarms and Input Frequency
The system can report current alarms, latched alarms, and the type of input signal.
To check system status:
Type: S (case sensitive)
You do not need to type a carriage return or line feed.
The system returns Scccc,llll,x\r\n where
cccc is current alarms.
llll is latched alarms since the last status request.
Both cccc and llll are hexadecimal numbers, with each binary bit position representing
one output. The MSB is the input signal status. The LSB (farthest right) is output 1 status.
A value of 1 in a bit position indicates an alarm condition.
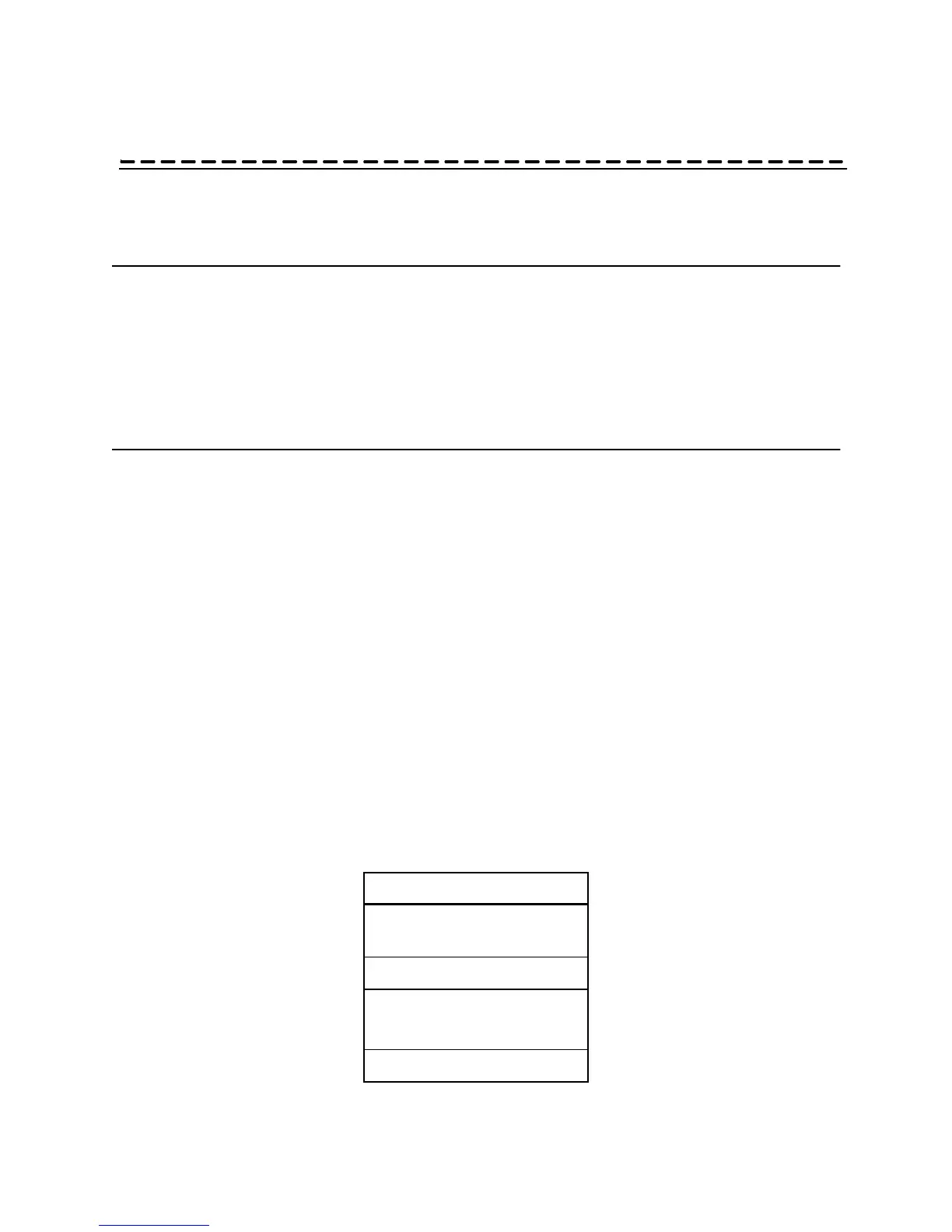
x is one of the values for inputs shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Input values
Value Input Frequency
0
Not 1 PPS, DC
IRIG, or Other
1
1 PPS
2
DC IRIG
(IRIG-B is 100 PPS)
(IRIG-A is 1 kPPS)
3
Other
3: Monitoring the 4033A
 Loading...
Loading...