191
The T-1 Notebook : Reference & Guide
190
The T-1 Notebook : Reference & Guide
NOTES
Analog Connectivity
9
Analog Connectivity
9
9.1 General Trig & CV Concepts
Analog control with audio gear is typically based on a voltage signal. There
are several applications of voltage control depending on manufacturer
preference and standards. In Eurorack, the most common modular format,
a 0-5V signal is usually used for triggering events i.e. Note, On, Off and for
modulation, pitch and velocity. Other Voltage ranges of -5V to +5V bi-polar,
0-8V or 0-10V can also be found in Eurorack format.
Trigger & Gate
A trigger is a short pulse that activates an event. Typically a note is
activated by a trigger. In T-1 Triggers have a 0-5V range although most
gear will recognise the switch is triggered below the 5V threshold. Formats
may differ in whether the increase voltage from 0 to 5V triggers an event or
whether the trigger operates on a falling edge 5V to 0. These are V-Trig and
S-Trig formats respectively. A trigger differs from a gate in that it consists of
shorter pulses. A gate would normally be controlled to be held high or low
for longer periods.
T-1 triggers are 0-5V although the input voltage tolerance is up to 10V.
Control Voltage
Control Voltage or CV is used to control absolute or relative values. A
typical application is to control Pitch of an oscillator. The most common
format being 1V / Octave although Hz/Volt is an alternative. A trigger would
activate a note and the note value set by CV. Other modulation destinations
such as affecting parameters for effects and modules are also controlled by
CV. T-1 CV can also be congured as gates.
T-1 operates with a 0-5V CV range.
Clock
A clock is used to synchronise timing between devices. Pulses are
generated typically by a nominated primary lead and other secondary
devices will synchronise to this clock. The format is based on PPQN -
Pulses per Quarter Note with 24PPQN being most common. Other options
are available but the most important consideration is to match up the clock
with devices in the conguration. A reset is also available in T-1.
T-1 Clock Hierarchy - 1. Analog Clock 2. MIDI Clock 3. Link
T-1 has clock 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 24 PPQN Options. Reset level 5V.
1
Pitch
V/Oct - 1 Volt per Octave
Note: Frequency to the perception of pitch is logarithmic
Volts
4
3
2
5
0
Velocity
Modulation
Voltage ranges may vary between devices and formats
Volts
3.75
2.5
1.25
5
A1
55Hz
0
A2
110Hz
32
A3
220Hz
64
A4
440Hz
95
A5
880Hz
127
V-Trig
0 to +5V
S-Trig
+5V to 0V
Time
Time
0
Volts
+5
0
Volts
+5
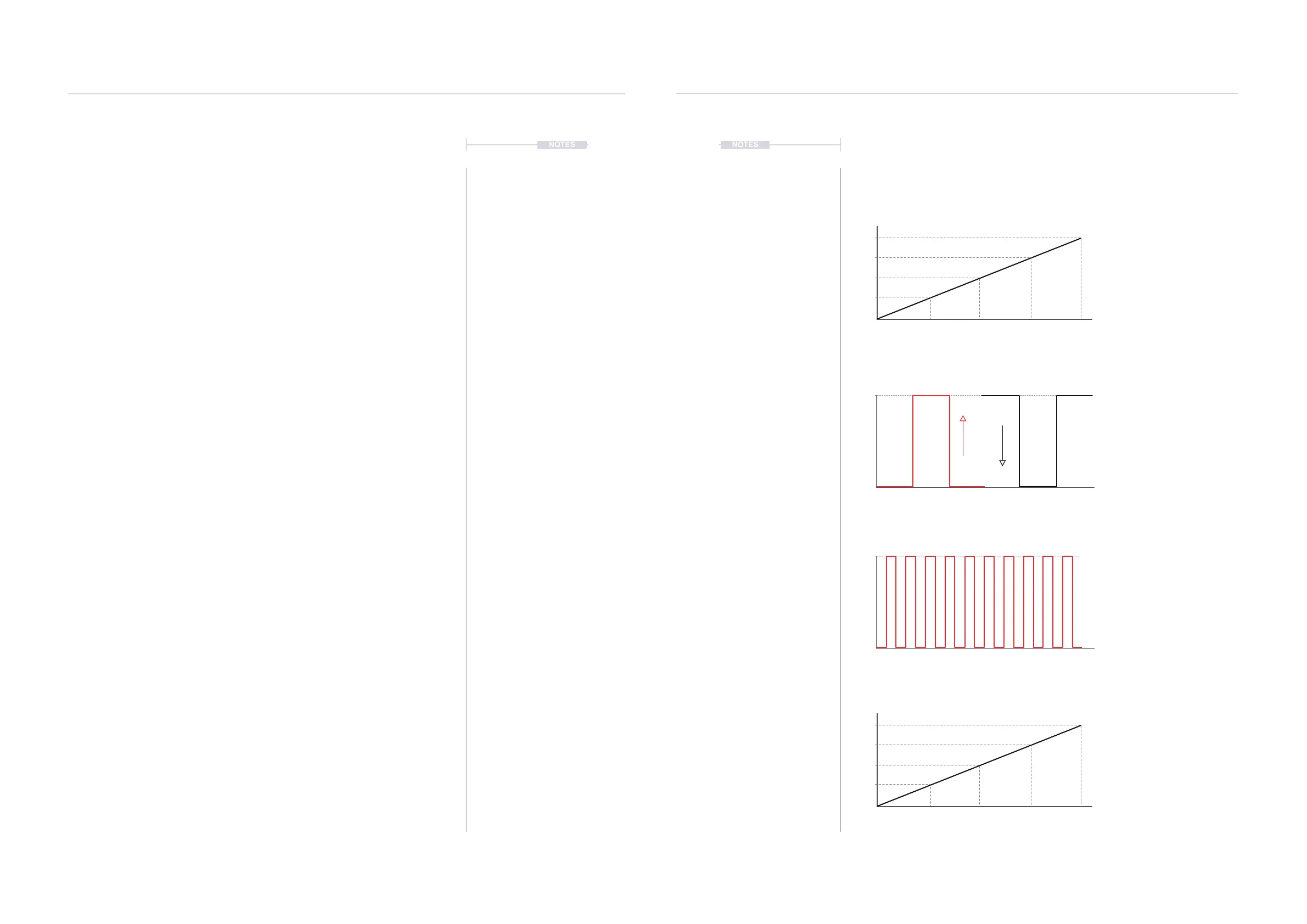
Example CV Concepts and Applications.
Diagrams and values for Illustrative purposes only. Actual behaviour will be based on specic devices.
Pitch
Volts per Octave is a common
approach to controlling pitch of an
analog device, especially in Eurorack.
Occasionally this may also follow an
alternative Hz / Volt format, used by
Korg and Yamaha.
Range
Control Voltages can also modulate
various parameters. These may be %
ranges, absolute values, offsets etc. T-
1 has a conguration option for
velocity. While this is based on the
velocity of notes it can be used to
modulate any analog parameter.
Trig
A trigger is a short voltage pulse that
activates an event. A gate is similar but
usually a longer, controlled length. A
trigger is often used for note on, off
and switch functions. V-Trig is the most
common, 0-5 rise to trigger. S-Trig
activates on a falling 5-0 voltage level.
Clock
An analog clock operates on a series
of pulses to synchronise devices.
Pulses are normally measured Pulses
per Quarter Note - PPQN. T-1 has
adjustable settings for analog clock
rates and pulse width to help match up
to devices. Analog clock is the highest
order in the clock hierarchy.
Trigger
Clock
NOTES
 Loading...
Loading...