304 Chapter 5
Concepts
Audio Measurement Concepts
Audio SINAD Measurement Concepts
Purpose
Audio SINAD measures the amount of Audio SINAD contained in an Audio
signal by determining the ratio of fundamental power to harmonic and noise
power. Audio SINAD is the reciprocal of value provided for audio distortion by
the Audio Distortion measurement.
The SINAD measurement is identical to the Audio distortion measurement; but the
result is expressed differently. SINAD is often measured as part of receiver
sensitivity testing.
SINAD can also be measured on an external audio signal applied to the AUDIO
INPUT.
Measurement Technique
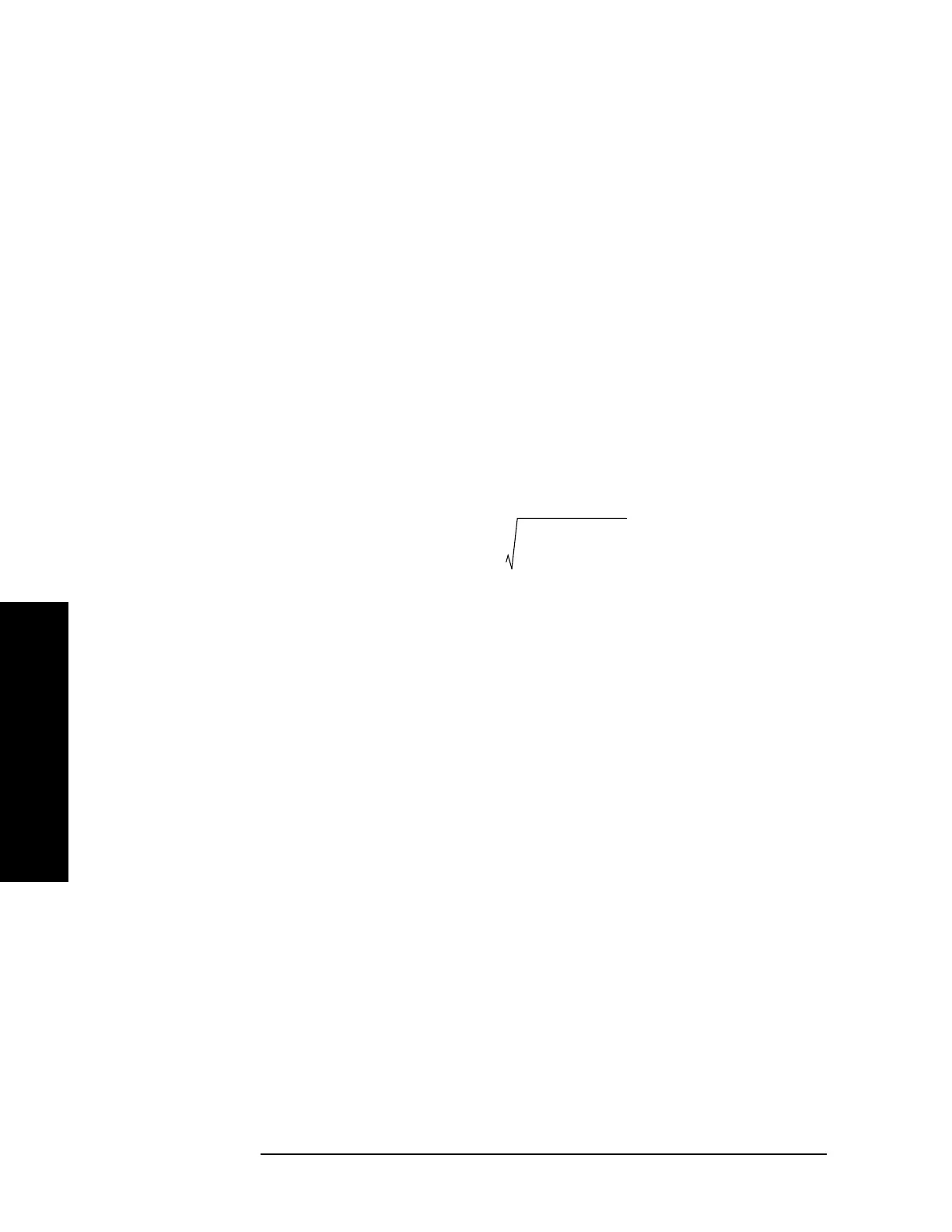
Audio SINAD is defined as:
Equation 5-6
where: P
total
= the power of the total signal,
P
signal
= the power of the wanted signal, and
P
total
− P
signal
= the total unwanted signals which include harmonic distortion
and noise.
To measure SINAD, the instrument compares the input signal level measurement
made with a true RMS detector to the same measurement made with the
fundamental component removed. SINAD is then calculated as the ratio of the
unfiltered signal to the signal with its fundamental removed. See Figure 5-12 on
page 302.
The received Audio signal is filtered to remove DC, then the filtered audio signal
is transformed by an FFT into frequency domain. Next, total power in the total
filter band is measured as P
total
, the peak power of modulated signal is computed
as P
signal
, the square root of the ratio of P
total
against P
total
− P
signal
is calculated.
The result is signal’s Audio SINAD. It can be expressed as dB or %.
dB
AudioSINAD
20
P
total
P
total
P
signal
–
-----------------------------------log×=

 Loading...
Loading...