Agilent N518xA, E8663B, E44x8C, and E82x7D Signal Generators Programming Guide 299
Creating and Downloading User-Data Files
User File Data (Bit/Binary) Downloads (E4438C and E8267D)
Command for Bit File Downloads
Because the signal generator adds a 10- byte file header during a bit file download, you must use the
SCPI command shown in Table 8- 3. If you FTP or copy the file for the initial download, the signal
generator does not add the 10- byte file header, and it does recognize the data in the file (no data in
the transmitted signal).
Bit files enable you to control how many bits in the file the signal generator modulates onto the
signal. Even with this file type, the signal generator requires that all data be contained within bytes.
For more information on bit files, see “Bit File Type Data” on page 288.
8 Send the user file data stored in the array (databuffer) to the signal generator.
• iwrite() sends the data specified in databuffer to the signal generator (session identifier
specified in id).
• The third argument of iwrite(), bytesToSend, contains the length of the databuffer in bytes.
In this example, it is 2000.
• The fourth argument of iwrite(), 0, means there is no END of file indicator in the data.
In many programming languages, there are two methods to send SCPI commands and data:
— Method 1 where the program stops the data download when it encounters the first zero
(END indicator) in the data.
— Method 2 where the program sends a fixed number of bytes and ignores any zeros in
the data. This is the method used in our program.
For your programming language, you must find and use the equivalent of method two.
Otherwise you may only achieve a partial download of the user file data.
9 Send the terminating carriage (\n) as the last byte of the waveform data.
• iwrite() writes the data “\n” to the signal generator (session identifier specified in id).
• The third argument of iwrite(), 1, sends one byte to the signal generator.
• The fourth argument of iwrite(), 1, is the END of file indicator, which the program uses to
terminate the data download.
To verify the user file data download, see “Command for Bit File Downloads” on page 299 and
“Commands for Binary File Downloads” on page 300.
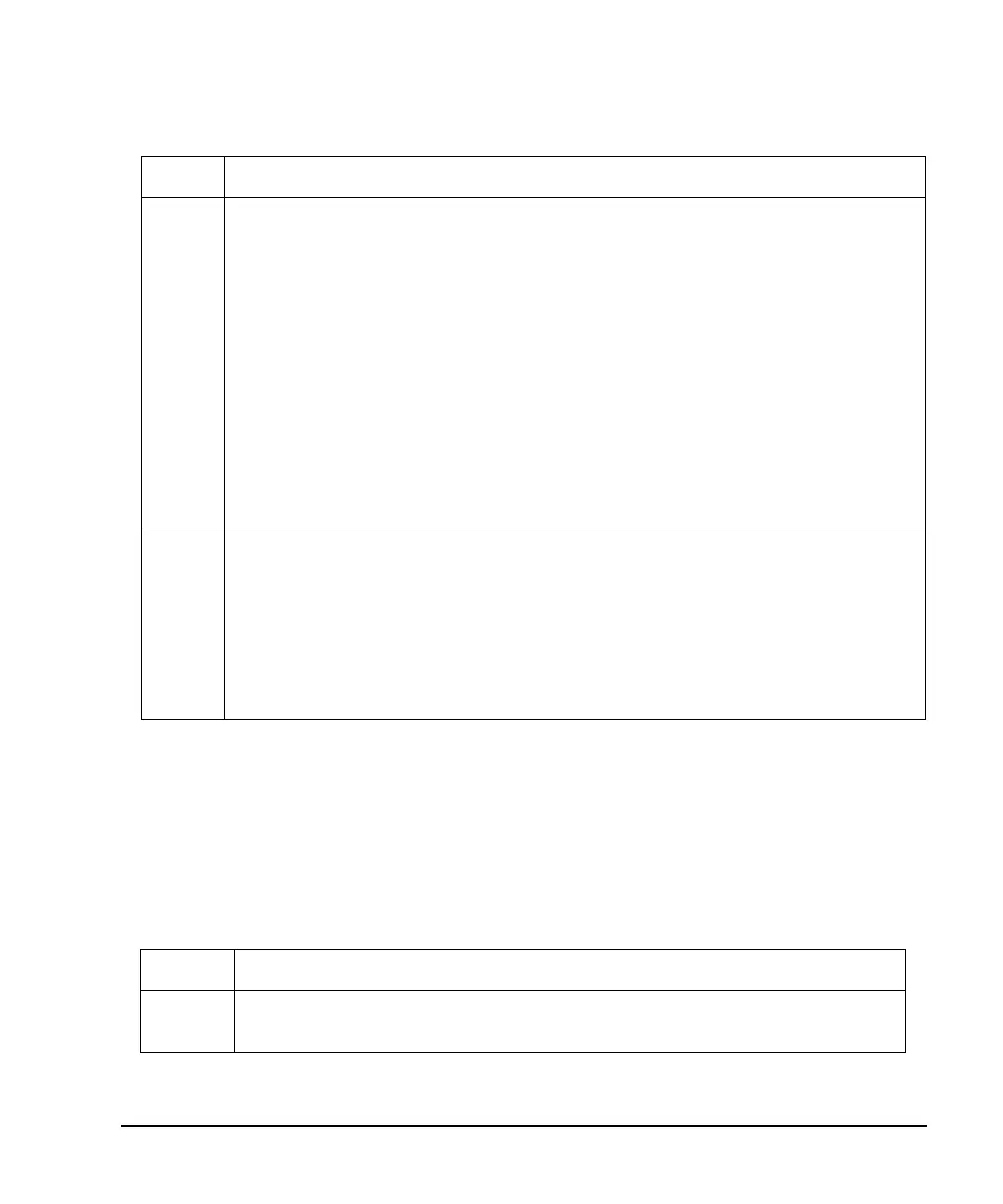
Table 8-3 Bit File Type SCPI Commands
Type Command Syntax
Command :MEM:DATA:BIT <"file_name">,<bit_count>,<block_data>
This downloads the file to the signal generator.
Line Code Description—Download User File Data

 Loading...
Loading...