Addressing Reference
1785 PLC-5
12
This word of
the status file:
Stores:
S:77 Communication time slice for communication housekeeping functions (in ms)
S:78 MCP I/O update disable bits
Bit 0 for MCP A
Bit 1 for MCP B
etc.
S:79 MCP inhibit bits
Bit 0 for MCP A
Bit 1 for MCP B
etc.
S:80-S:127 MCP file number
MCP scan time (in ms)
MCP max scan time (in ms)
The above sequence applies to each MCP; therefore, each MCP has 3 status
words.
For example, word 80: file number for MCP A
word 81: scan time for MCP A
word 82: maximum scan time for MCP A
word 83: file number for MCP B
word 84: scan time for MCP B
etc.
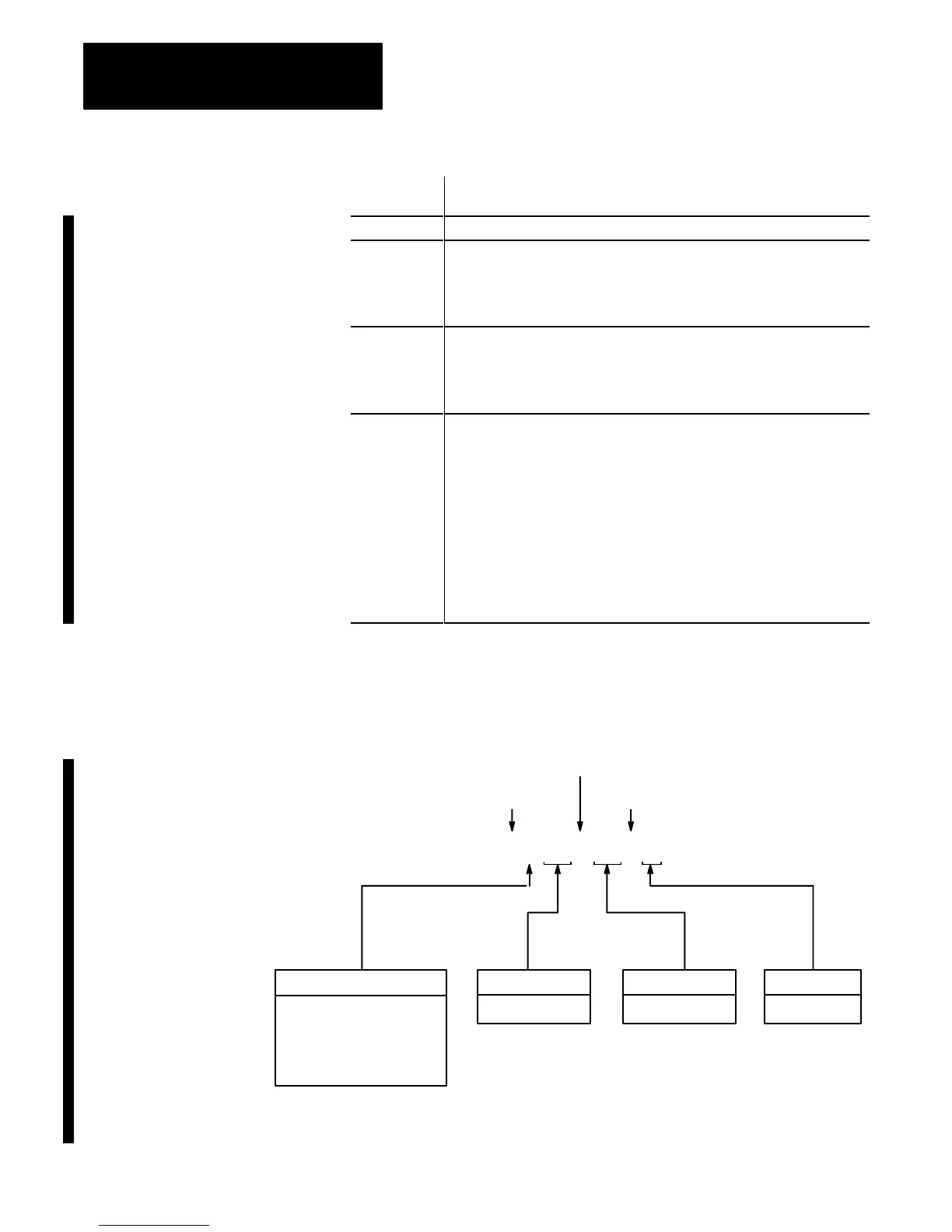
Figure 7
Format
for Logical Addressing of ASCII, Binary
, BCD, Floating-Point, and
Integer Files
File
Type
A = ASCII display (default)
B = Binary
D = BCD display (defalut)
F = Floating-point
N = Integer
Bit Number
0 – 15 Decimal
W
ord Number
0 – 999 Decimal
Logical
Address Identifier
File Separator
Bit Separator (if addressing a bit)
$ B 123 : 123 / 15
File Number
3 – 999 Decimal
Note: Except for data entry and display, all values in A, B, D, and N files
are processed as integer values stored in natural binary format.
Logical Addressing for ASCII,
Binary, BCD, Floating-Point,
and Integer Files

 Loading...
Loading...