TD 92685EN
28 June 2012 / Ver. A
Troubleshooting Guide
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
11
3. The VoWiFi Handset as
Link Layer - MAC and Physical Sub Layers
The physical sub layer and MAC sub layer
, in the context of the TCP/IP model, replaces the
data link and physical layers of the OSI model with a single link layer. This means that the
link layer:
• Controls how data in the form of bit stream
s, is transmitted through the network on
standard RF channels. The layer is about the interfaces between the RF channel and
network devices such as the APs, controllers, if used, and handsets. The notion of the
physical layer also defines the protocols that define the characteristics of the channels
conveying data. The handset uses the standard RF channel on either the 2.4 GHZ band or
the 5GHz band as defined by the 802.11a/b/g/n amendments.
• Manages the raw bit stream data received by the AP or controller from the handset
radio,
and packages the bits into 802.11 frames. 802.11 defines three kinds of frame for
WLANS, one for management, one for control and one for data. The handset uses
management and control frames for AP association and authentication.
• The MAC sub layer manages the physical MAC addressi
ng scheme by encapsulating layer
2 PDUs in a MAC sub layer PDU. The MAC sub layer uses Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP
) to maintain logical IP to physical MAC address mapping of SIP servers in the call
path.
Internet Level
The Internet level responds to UDP and TCP service requests from
the transport layer and
provides network to network routing.
Transport Layer
The transport layer provides the TCP/IP
address used by network devices. TCP packets are
routed using the IP addresses of WLAN network devices that may interwork with other
networks such as the internet or Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). In the context
of the VoWiFi system this is likely to be a VoIP gateway or IP-PBX
The transport layer also provides congestion throttling to maximize da
ta throughput
without overwhelming the resources of the network.
Application Level
The application layer includes t
he functions of OSI Application, Presentation Layer and
Session Layer, which are often referred to as a user services. TCP/IP sockets and ports are
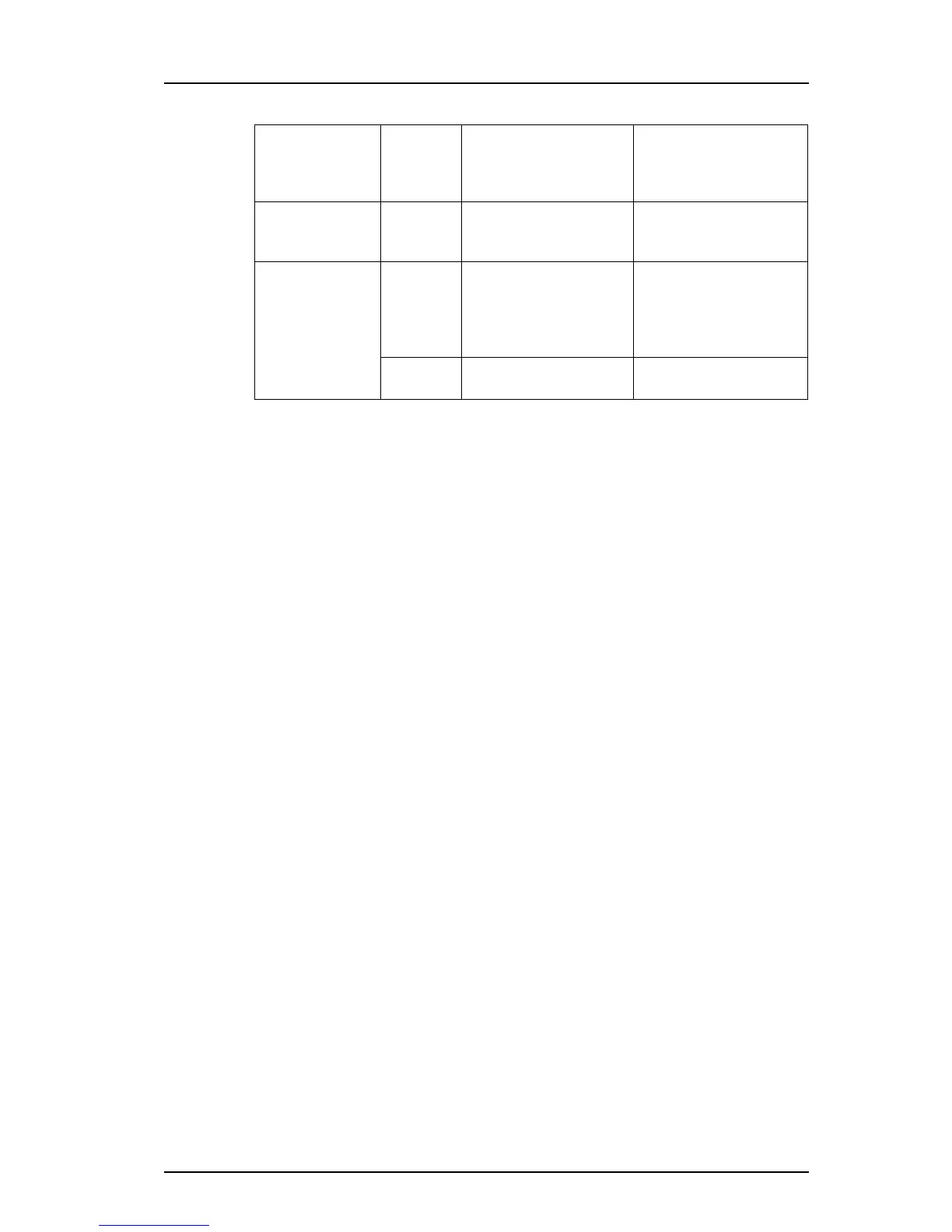
Transport layer TCP packets The handset uses TCP/IP as
the pro
tocol to address
packets to be delivered to
other devices like a SIP PBX
Internet layer IP packets IP addressing - APs,
co
ntrollers
Link layer MAC sub
layer
802.11 frames
(Man
agement, control and
data frames)
The handset uses the IEEE
802.11 WLAN standard
protocol suit to get access
to the media and to send
packets to the AP
Physical sub
layer
RF signals, digitized bit
strea
ms
 Loading...
Loading...