TD 92685EN
28 June 2012 / Ver. A
Troubleshooting Guide
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
15
3. The VoWiFi Handset as
elapsed time based on a number of beacons. Normally the DTIM set to 5 beacons, which
means the handset wakes up every 512ms, that is, approximately twice a second. If, at that
point, the beacon Traffic Indicator Map (TIM) announces it contains buffered data, the
handset transmits a QoS Null data frame as a polling frame to the AP. The QoS Null frame
releases the buffered frame and the AP proceeds to transmit the frame. The handset keeps
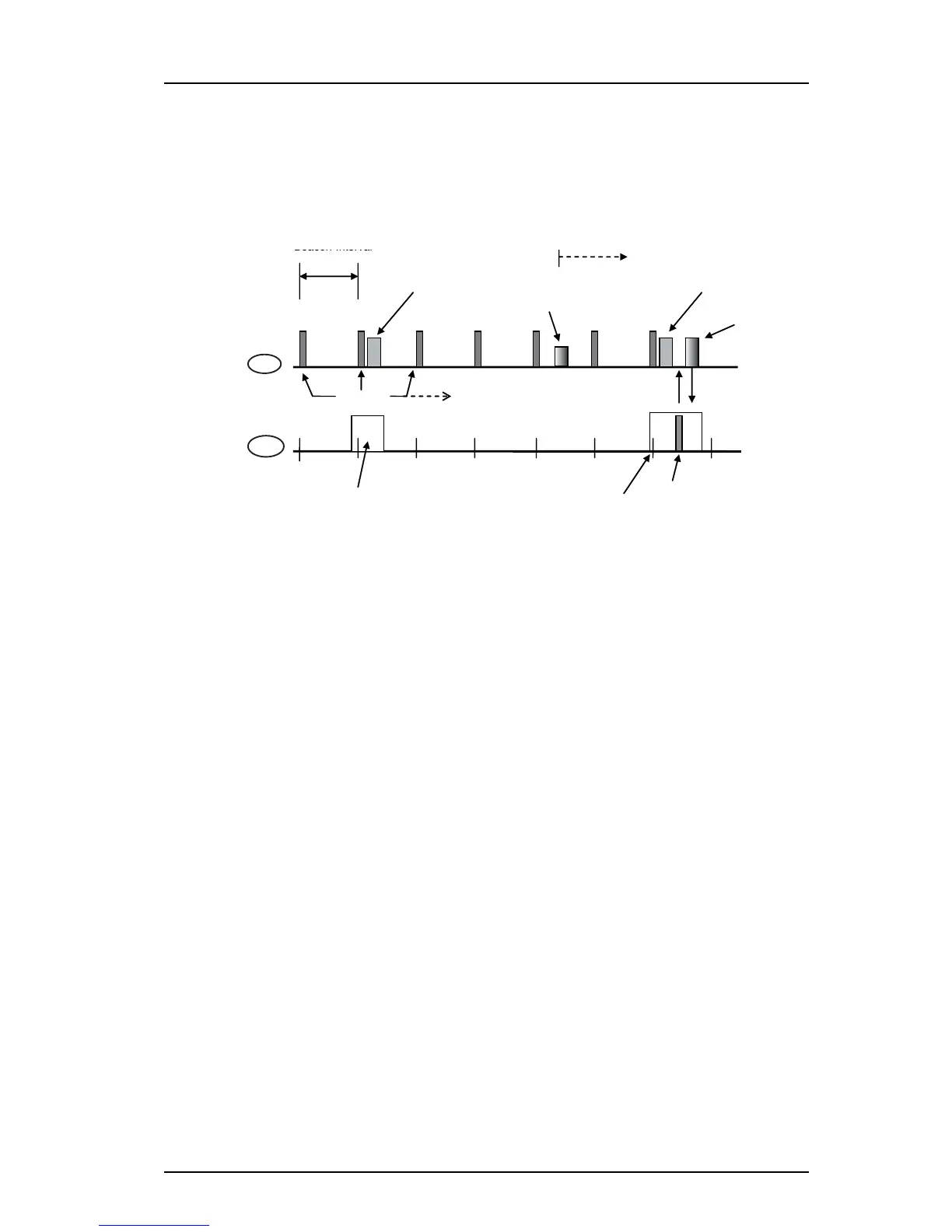
it’s receiver turned on until the frame is received. These concepts are illustrated in figure 2:
Figure 2. Handset Operating in PS-mode.
TIM
AP
DTIM
Broadcasts
DTIM
Beacons
QoS Null Data
Battery Life
The implication for battery power consumption of a handset in PS-mode is that by
decreasing the beacon interval or increasing t
he DTIM parameter, or both, the handset uses
more power and shortens the battery time. However, the handset response time to any
pending TIM will be faster.
Roaming Implications
When the handset hears a beacon and the signal level i
s
below -70dBm, roaming is initiated
and the scanning process starts. The handset will continue the scan process every 4 seconds
as long as the RSSI value is less than -70dBm. For additional information about roaming
periods and thresholds, see the section 3.6 Roaming on
pa
ge 17.
3.5.2 U-APSD PS Mode Operation
The handset may be configured for U-APSD if the VoWiFi system manufactured by a product
partner supp
orts Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (U-APSD). The two power
management modes are valid also in U-APSD mode and the AP buffers downlink frames
only if the station is in PS-mode.
U-APSD is basically a polling scheme, like 802.11e PS
management, but in U-APSD mode,
QoS Null data frame acts as a polling frame and is called a “trigger frame”.
An AP capable of supporting U-APSD indicates this capabi
lity through the QoS parameters
found in the WLAN management system. If the supported U-APSD capability is only present
in the type of WMM Power Save used, the capability is indicated in the QoS information field
in the WMM parameter or information elements.
This information is present in Beacon, Probe Response
, and (Re) Association Response
management frames.
 Loading...
Loading...