TD 92685EN
28 June 2012 / Ver. A
Troubleshooting Guide
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
22
3. The VoWiFi Handset as
Port 5061 is typically used for traffic encrypted with Transport Layer Security (TLS).
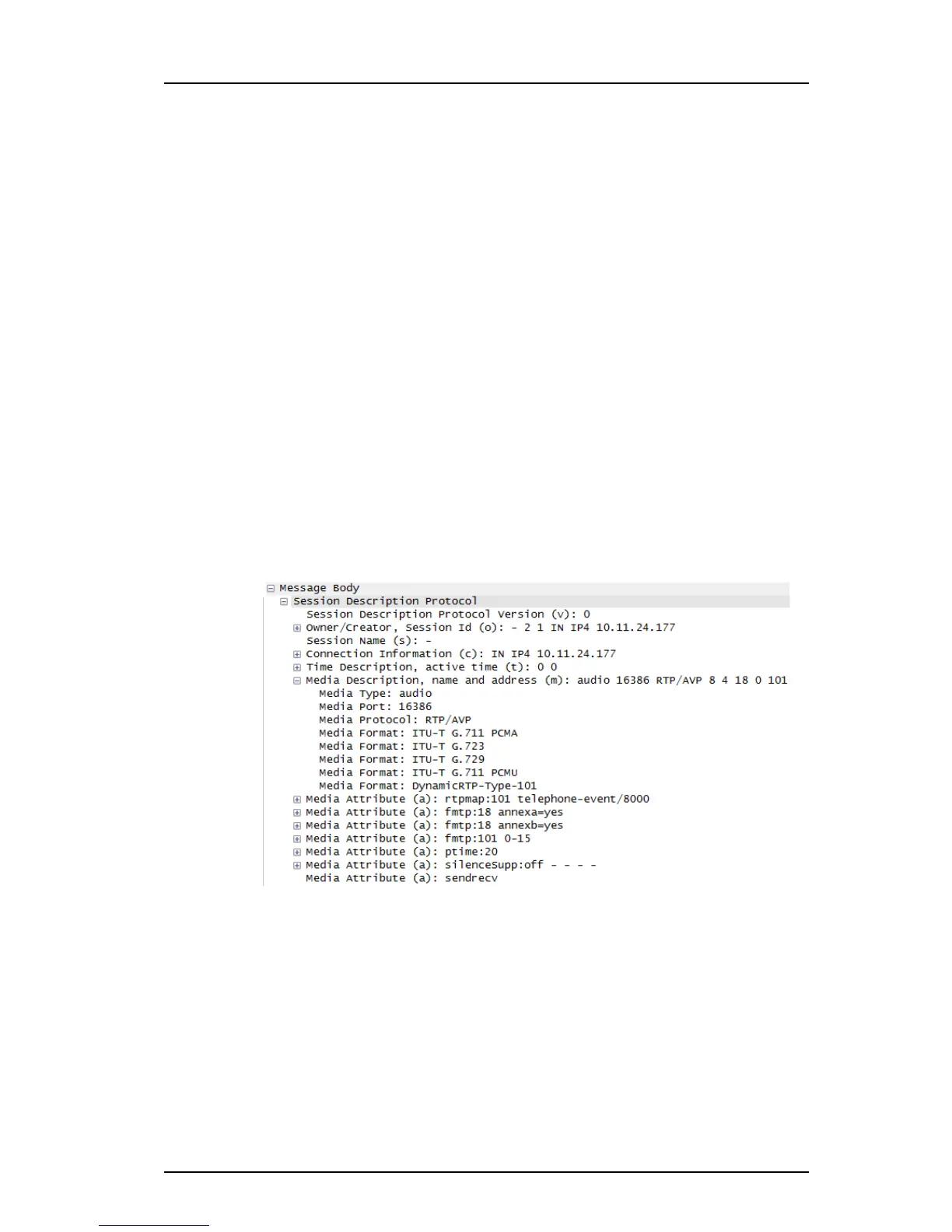
Session Description Protocol
The Session Description Protocol (SDP) is used to initiat
e a media session and support the
flow of RTP packets between SIP endpoints. An SDP message contains information about
the SIP entity, such as an INVITE message, that created it. Such information describes the
codecs that may be negotiated between the SIP endpoints, the transport protocol to be
used, and the ports and IP addresses that RTP packets are to be sent to.
Codec negotiation is about selecting which codec to use on each leg of a call and SDP
supports this negotiation. A ha
ndset tha
t initiates a call announces to the called party
handset the codec that it wishes to use for the media session. The called party confirms
whether or not the desired codec is supported. In practice most SIP endpoints support
multiple codecs, so the SDP codec negotiation process sifts through the choices and settles
on a single codec to use.
To check the codecs supported by a handset, expand the mes
s
age body associated with the
SIP entity specifying the call invitation and then expand SDP and Media Description. The
supported codecs are listed as Media Attributes followed by an ITU-T standard speech codec
extension.
As SDP is a text-based protocol embedded into SIP Messages it is relatively easy to display
and inspect the content of SDPs using a protocol analyzer such as WireShark. For example,
the SDP part of a SIP INVITE request viewable from a WireShark trace is shown in figure 4:
Figure 4. SDP Part of SIP Invite
The supported codecs and their respective properties are listed under the Media Description
and Media Attribute followed by ITU-T standard speech codec extensions.
Media Description
The Media Description part of the SDP for audio contains:
• The RTP port number
• The RTP/AVP profile for the use of the RTP
•Payload types.
 Loading...
Loading...