6
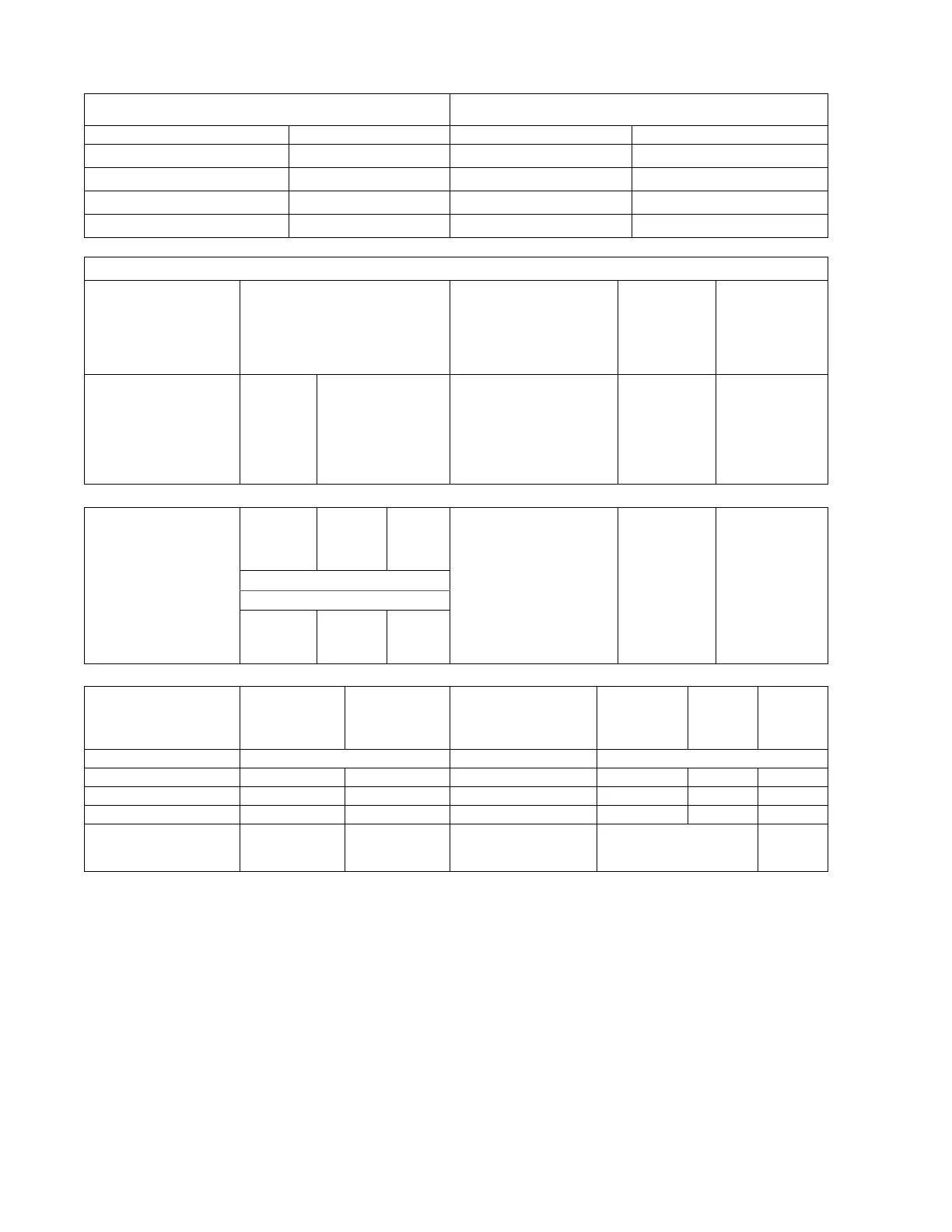
Specifications
Tissue Mimicking Material
Tissue Mimicking Material
Material Diameter
Monofilamennt Nylon
.12 mm
Dead Zone Groups
Lateral Displacement
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Vertical Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Depth
Horizontal Linear
Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Axial-Lateral
Resolution Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Horizontal Sector
Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Axial-Lateral
Resolution Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Horizontal Sector
Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Axial-Lateral
Resolution Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Horizontal Sector
Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Axial-Lateral
Resolution Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Horizontal Sector
Groups
Number of Targets
Interval Spacing
Scan Surface Depth
Standard
Endoscopic
Anechoic Target
Structures
Gray Scale Target
Structures
Non-echogenic, cylindrical
Non-echogenic, cylindrical
Contrast relative to
background material
(dB)
*Nominal dimensions
DEAD ZONE (A1 & A2)
Description and Reason For Testing
The dead zone is the distance from the front face of the transducer to the first identifiable echo at the phantom/
patient interface. The dead zone occurs because an imaging system cannot send and receive data at the same
time. Therefore, no clinical data can be collected in this region. However if artifacts are noted within the dead
zone, they may indicate fluctuations in the input power to the system. The depth of the dead zone depends upon
the frequency and performance of the transducer and the pulsing/receiving section of the system.
Testing Procedure
 Loading...
Loading...