DL06 Micro PLC User Manual; 3rd Edition Rev. E
4–12
Chapter 4: System Design and Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
Network Slave Operation
This section describes how other devices on a network can communicate with a CPU port
that you have configured as a DirectNET slave or MODBUS slave (DL06). A MODBUS
host must use the MODBUS RTU protocol to communicate with the DL06 as a slave. The
host software must send a MODBUS function code and MODBUS address to specify a PLC
memory location the DL06 comprehends. The DirectNET host uses normal I/O addresses to
access applicable DL06 CPU and system. No CPU ladder logic is required to support either
MODBUS slave or DirectNET slave operation.
NOTE: For more intformation on DirectNET proprietary protocol, see the DirectNET reference
manual, DA-DNET-M, available on our website.
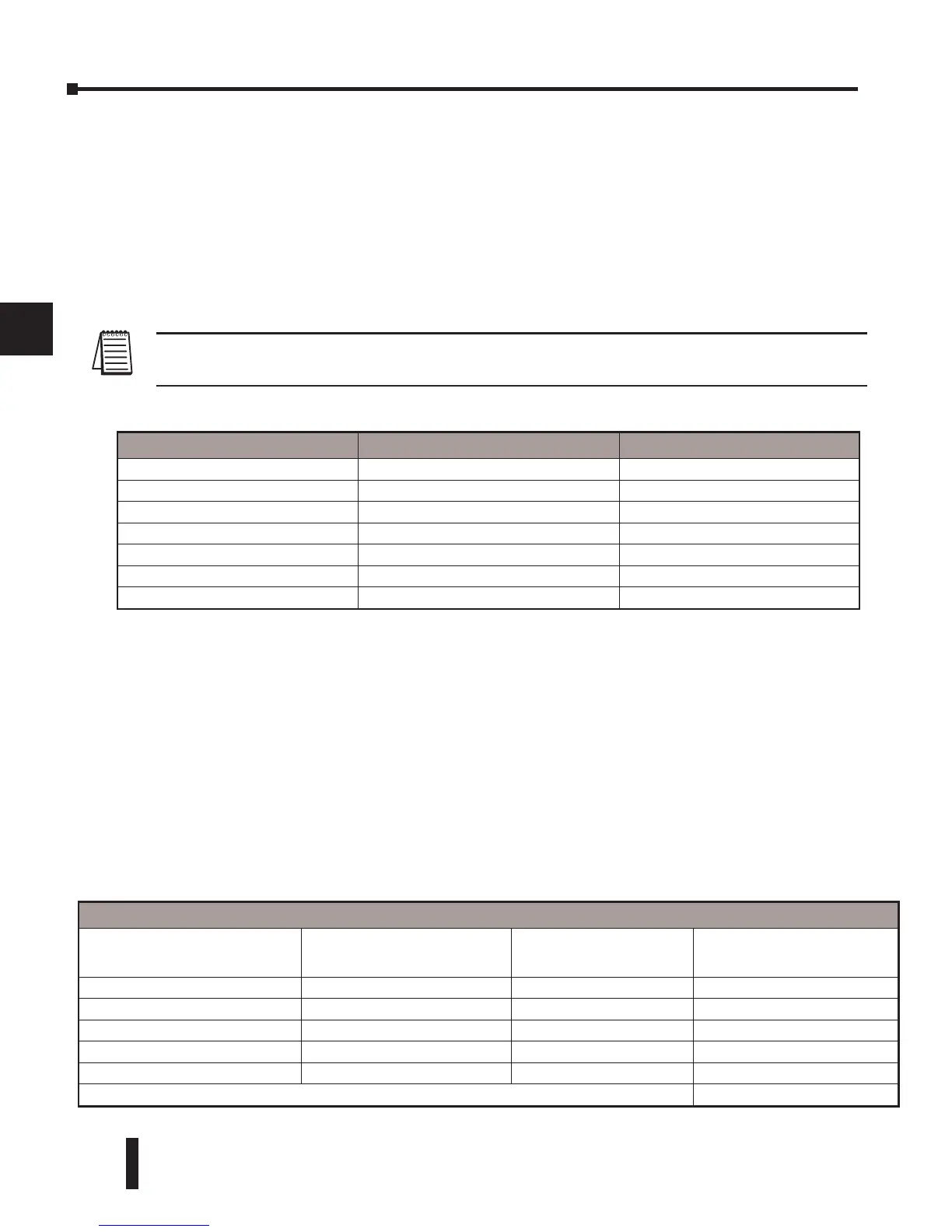
MODBUS Function Codes Supported
The MODBUS function code determines whether the access is a read or a write, and whether
to access a single data point or a group of them. The DL06 supports the MODBUS function
codes described below.
Determining the MODBUS Address
There are typically two ways that most host software conventions allow you to specify a PLC
memory location. These are:
• By specifying the MODBUS data type and address
• By specifying a MODBUS address only
MODBUS Function Code Function DL06 Data Types Available
01
Read a group of coils Y, CR, T, CT
02
Read a group of inputs X, SP
05
Set / Reset a single coil Y, CR, T, CT
15
Set / Reset a group of coils Y, CR, T, CT
03, 04
Read a value from one or more registers V
06
Write a value into a single register V
16
Write a value into a group of registers V
Word Data Types
Registers
PLC Range
(Octal)
Input/Holding
(484 Mode)*
Input/Holding
(584/984 Mode)*
V-Memory (Timers)
V0 - V377 3001 / 4001 30001 / 40001
V-Memory (Counters)
V1000 - V1177 3513 / 4513 30513 / 40513
V-Memory (Data Words)
V400 - V677 3257 / 4257 30257 / 40257
V1200 - V7377 3641 / 4641 30641 / 40641
V10000 - V17777 - 34097 / 44097
* Modbus: Function 04
 Loading...
Loading...