Conguring IPSec Settings
0W20-04K
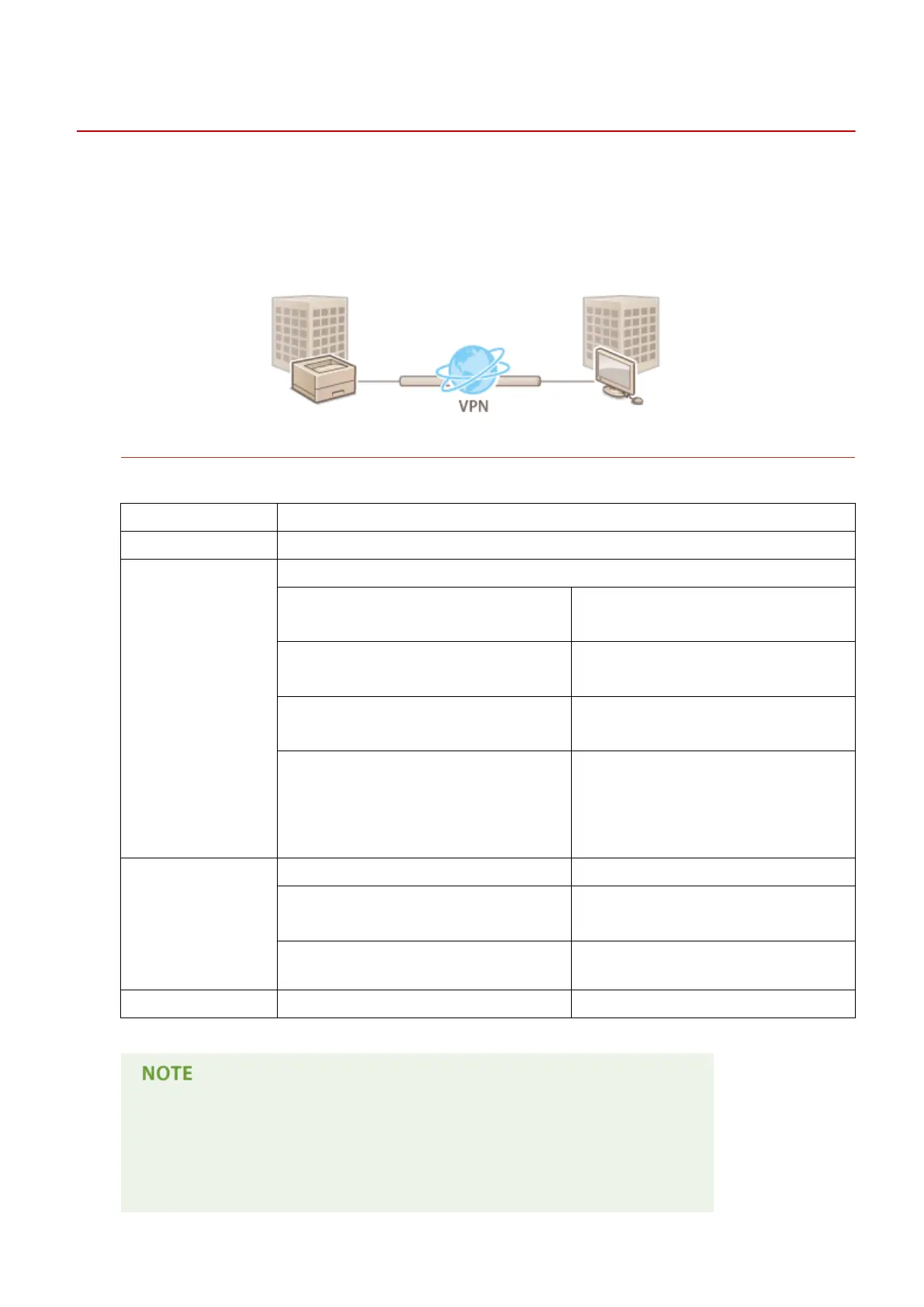
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec or IPsec) is a protocol suite for encrypting data transported over a network, including
Internet networks. While SSL only encrypts data used on a specic application, such as a Web browser or an e-mail
application, IPSec encrypts either whole IP packets or the payloads of IP packets, offering a more versatile security
system. The IPSec of the machine works in transport mode, in which the payloads of IP packets are encrypted. With
this feature, the machine can connect directly to a computer that is in the same virtual private network (VPN). Check
the system requirements and set the necessary conguration on the computer before you congure the machine.
System Requirements
IPSec that is supported by the machine conforms to RFC2401, RFC2402, RFC2406, and RFC4305.
Operating system Windows Vista/7/8/Server 2003/Server 2008/Server 2012
Connection mode Transport mode
Key exchange protocol
IKEv1 (main mode)
Authentication method
● Pre-shared key
● Digital signature
Hash algorithm
(and key length)
● HMAC-SHA1-96
● HMAC-SHA2 (256 bits or 384 bits)
Encryption algorithm
(and key length)
● 3DES-CBC
● AES-CBC (128 bits, 192 bits, or 256 bits)
Key exchange algorithm/group (and key
length)
Die-Hellman (DH)
● Group 1 (768 bits)
● Group 2 (1024 bits)
● Group 14 (2048 bits)
ESP
Hash algorithm HMAC-SHA1-96
Encryption algorithm
(and key length)
● 3DES-CBC
● AES-CBC (128 bits, 192 bits, or 256 bits)
Hash algorithm/encryption algorithm (and
key length)
AES-GCM (128 bits, 192 bits, or 256 bits)
AH Hash algorithm HMAC-SHA1-96
IPSec functional restrictions
● IPSec supports communication to a unicast address (or a single device).
● The machine cannot use both IPSec and DHCPv6 at the same time.
● IPSec is unavailable in networks in which NAT or IP masquerade is implemented.
Security
239

 Loading...
Loading...











