Spark Plug Insulators
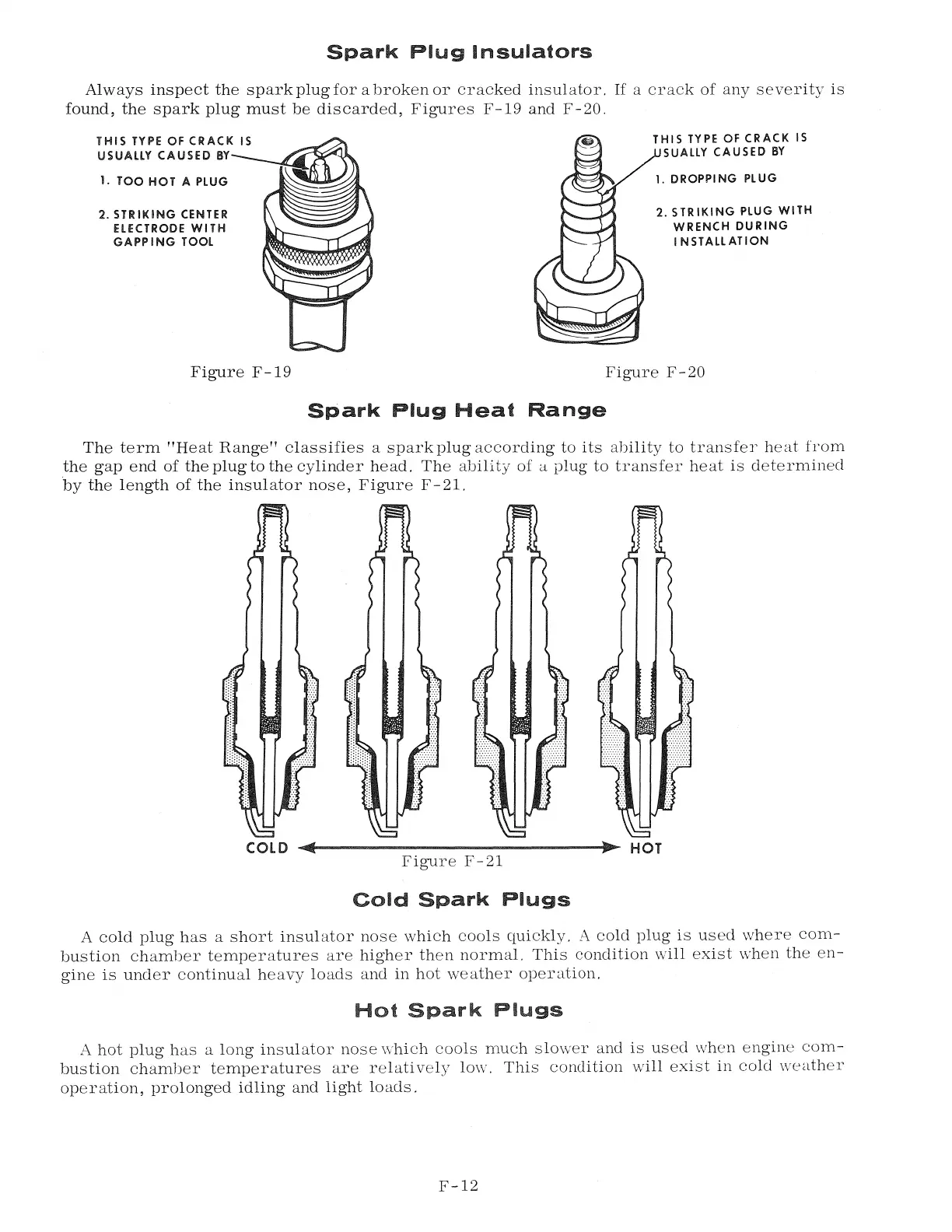
Always inspect the spark plug for a broken or cracked insulator. If a crack of any severity is
found, the spark plug must be discarded, Figures F-19 and F-20.
THIS TYPE OF CRACK IS
USUALLY CAUSED BY
1. TOO HOT A PLUG
2. STRIKING CENTER
ELECTRODE WITH
GAPPING TOOL
Figure F-19
THIS TYPE OF CRACK IS
SUALLY CAUSED BY
1. DR OPP I NG PLUG
2. STRIKING PLUG WITH
WRENCH DURING
INSTALLATION
Figure F-20
Spark Plug Heat Range
The term "Heat Range" classifies a spark plug according to its ability to transfer heat from
the gap end of the plug to the cylinder head. The ability of a plug to transfer heat is determined
by the length of the insulator nose, Figure F-21.
COLD
HOT
Figure F-21
Cold Spark Plugs
A cold plug has a short insulator nose which cools quickly. A cold plug is used where com-
bustion chamber temperatures are higher then normal. This condition will exist when the en-
gine is under continual heavy loads and in hot weather operation.
Hot Spark Plugs
A hot plug has a long insulator nose which cools much slower and is used when engine com-
bustion chamber temperatures are relatively low. This condition will exist in cold weather
operation, prolonged idling and light loads.
F-12
 Loading...
Loading...