E-14
Prime Factorization
In the COMP Mode, you can factor a positive integer up to 10 digits into
prime factors up to three digits.
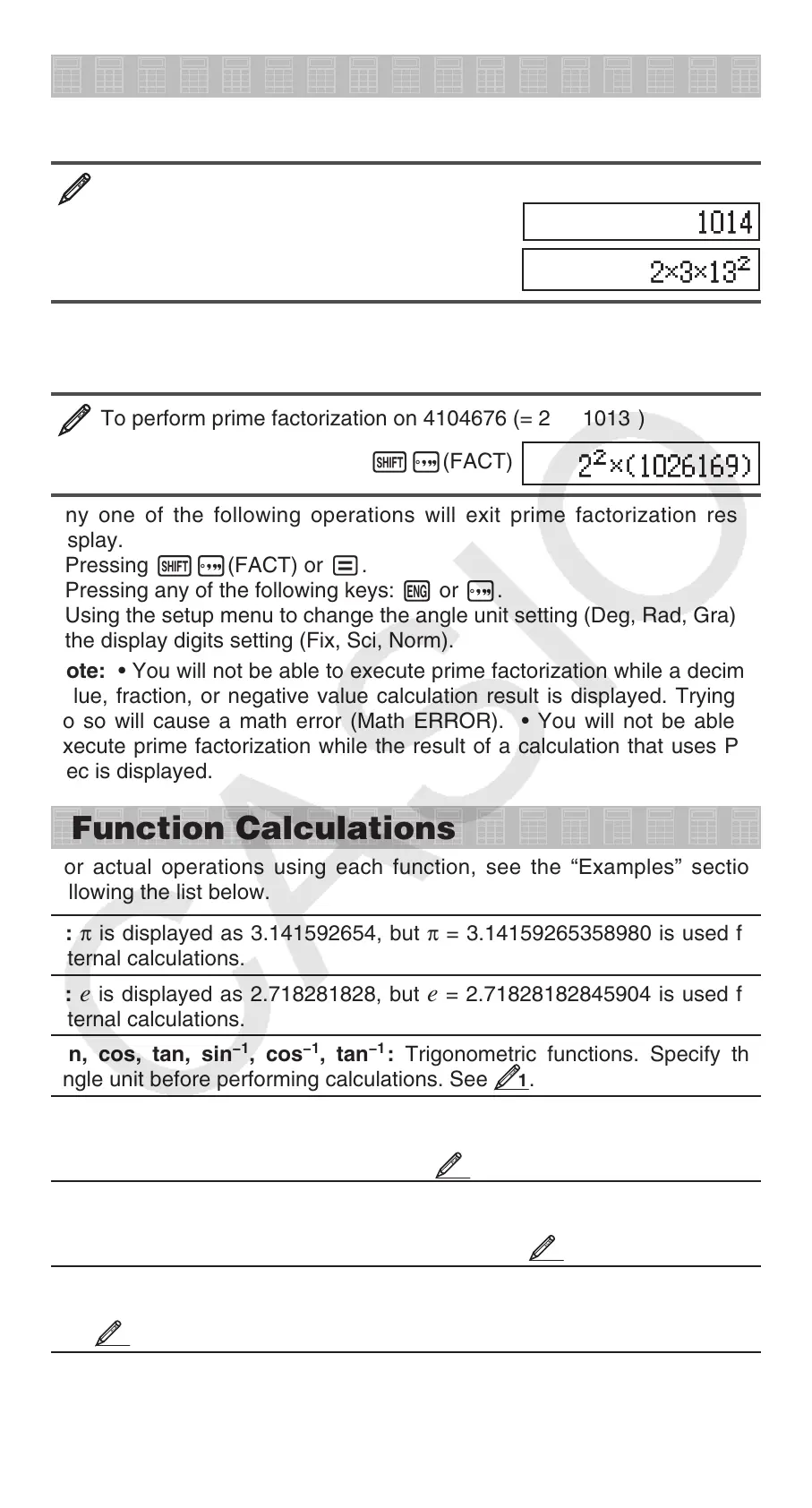
To perform prime factorization on 1014
1014 =
!e(FACT)
When you perform prime factorization on a value that includes a factor that
is prime number with more than three digits, the part that cannot be factored
will be enclosed in parentheses on the display.
To perform prime factorization on 4104676 (= 2
2
× 1013
2
)
!e(FACT)
Any one of the following operations will exit prime factorization result
display.
• Pressing !e(FACT) or =.
• Pressing any of the following keys: . or e.
• Using the setup menu to change the angle unit setting (Deg, Rad, Gra) or
the display digits setting (Fix, Sci, Norm).
Note: • You will not be able to execute prime factorization while a decimal
value, fraction, or negative value calculation result is displayed. Trying to
do so will cause a math error (Math ERROR). • You will not be able to
execute prime factorization while the result of a calculation that uses Pol,
Rec is displayed.
Function Calculations
For actual operations using each function, see the “Examples” section
following the list below.
π
: π is displayed as 3.141592654, but π = 3.14159265358980 is used for
internal calculations.
e : e is displayed as 2.718281828, but e = 2.71828182845904 is used for
internal calculations.
sin, cos, tan, sin
−1
, cos
−1
, tan
−1
: Trigonometric functions. Specify the
angle unit before performing calculations. See
1
.
sinh, cosh, tanh, sinh
−1
, cosh
−1
, tanh
−1
: Hyperbolic functions. Input a
function from the menu that appears when you press w. The angle unit
setting does not affect calculations. See
2
.
°,
r
,
g
: These functions specify the angle unit. ° specifies degrees,
r
radians,
and
g
grads. Input a function from the menu that appears when you perform
the following key operation: 1G(DRG '). See
3
.
$, %
: Exponential functions. Note that the input method is different
depending upon whether you are using Natural Display or Linear Display.
See
4
.
 Loading...
Loading...