E-16
Examples
sin 30°= 0.5 bv s 30 )= 0.5
sin
−1
0.5 = 30° bv 1s(sin
−1
) 0.5 )= 30
sinh 1 = 1.175201194 wb(sinh) 1 )= 1.175201194
cosh
–1
1 = 0 wf(cosh
−1
) 1 )= 0
π /2 radians = 90°, 50 grads = 45° v
(15( π ) / 2 )1G(DRG ') c(
r
) = 90
50 1G(DRG ') d(
g
) = 45
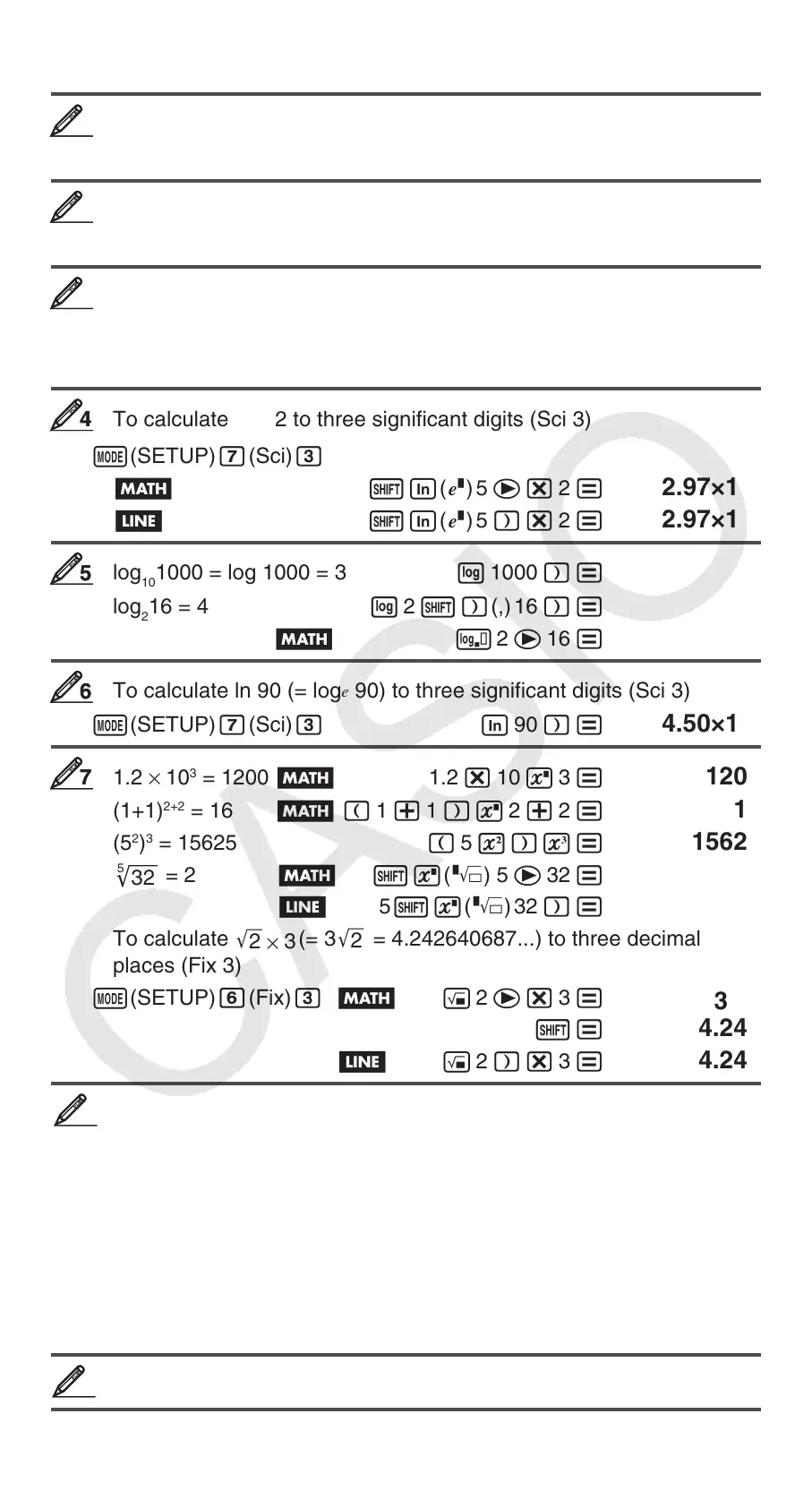
To calculate e
5
× 2 to three significant digits (Sci 3)
1N(SETUP) 7(Sci) 3
B 1i( %) 5 e* 2 =
2.97×10
2
b 1i( %) 5 )* 2 = 2.97×10
2
log
10
1000 = log 1000 = 3 l 1000 )= 3
log
2
16 = 4 l 2 1)(,) 16 )= 4
B & 2 e 16 = 4
To calculate ln 90 (= log
e
90) to three significant digits (Sci 3)
1N(SETUP) 7(Sci) 3 i 90 )= 4.50×10
0
1.2 × 10
3
= 1200 B 1.2 * 10 6 3 = 1200
(1+1)
2+2
= 16 B ( 1 + 1 )6 2 + 2 = 16
(5
2
)
3
= 15625 ( 5 x)W= 15625
32
5
= 2 B 16(") 5 e 32 = 2
b 5 16(") 32 )= 2
To calculate
'
2
×
3
(= 3
'
2
= 4.242640687...) to three decimal
places (Fix 3)
1N(SETUP) 6(Fix) 3 B ! 2 e* 3 =
3
'
2
1= 4.243
b ! 2 )* 3 = 4.243
To convert rectangular coordinates (
'
2
,
'
2
) to polar coordinates
v
B 1+(Pol) ! 2 e1)(,) ! 2 e)= r=2, =45
b 1+(Pol) ! 2 )1)(,) ! 2 ))= r= 2
= 45
To convert polar coordinates (
'
2
, 45°) to rectangular coordinates
v
B 1-(Rec) ! 2 e1)(,) 45 )=
X=1, Y=1
(5 + 3) ! = 40320 ( 5 + 3 )1E( x !) = 40320
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
88
99

 Loading...
Loading...