Chapter 16 PLC Function Applications│CP2000
16-27
16-5-1 Introduction to device functions
Input/output contact functions
Input contact X functions: Input contact X is connected with an input device, and reads input
signals entering the PLC. The number of times that contact a or b of input contact X used in the
program is not subject to restrictions. The ON/OFF state of input contact X will change as the input
device switches ON and OFF; a peripheral device (WPLSoft) cannot be used to force contact X On or
Off.
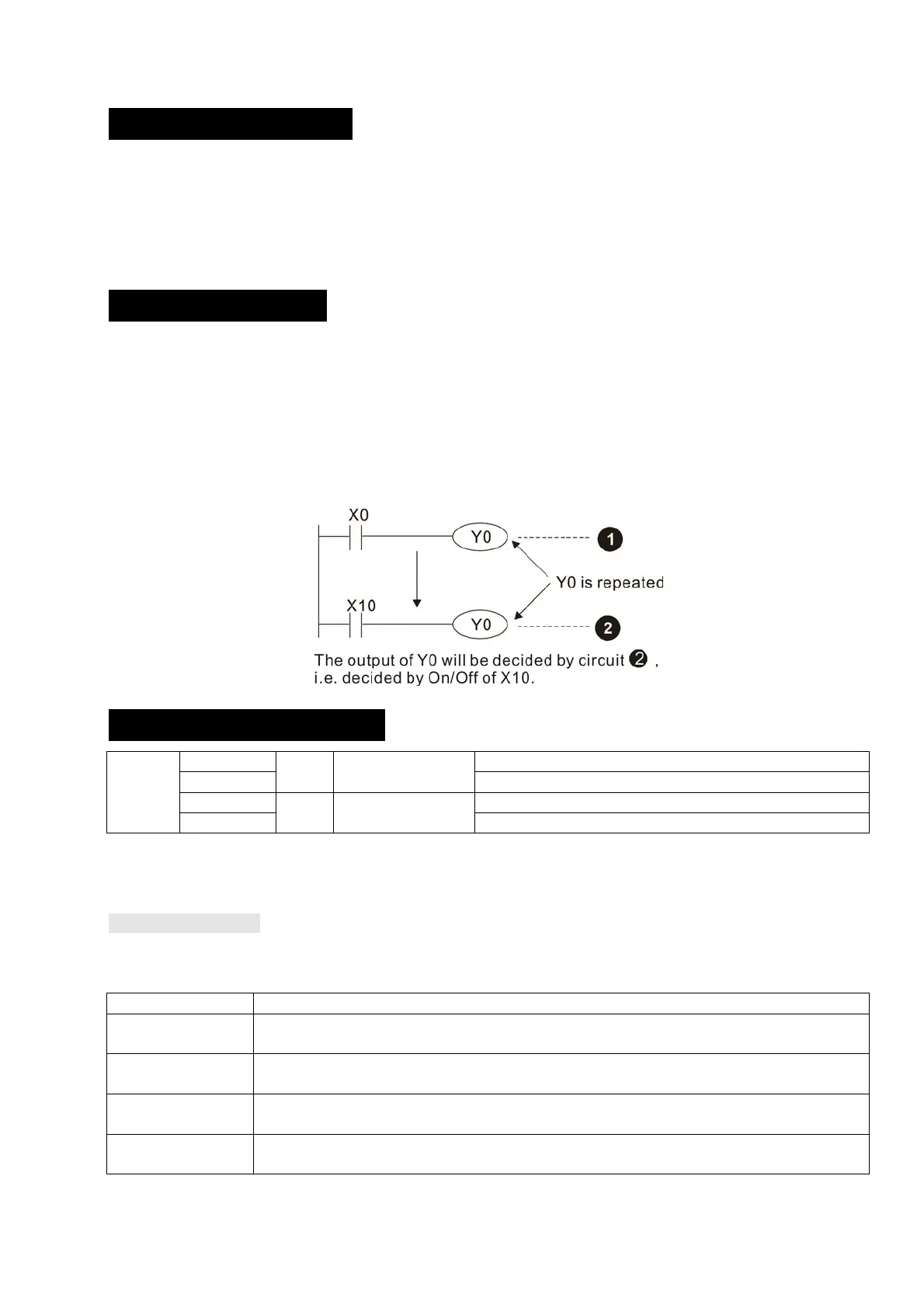
Output contact Y functions
The job of output contact Y is to send an ON/OFF signal to drive the load connected with output
contact Y. Output contacts consist of two types: relays and transistors. While number of times that
contact a or b of each output contact Y used in the program is not subject to restrictions, it is
recommended that the number of output coil Y be used only once in a program, otherwise the right to
determine the output state when the PLC performs program scanning will be assigned to the
program's final output Y circuit.
Numerical value, constant [K]/ [H]
Constant
Single-byte
K Decimal
K-32,768–K32,767
Double-byte K-2,147,483,648–K2,147,483,647
Single-byte
H Hexadecimal
H0000–HFFFF
Double-byte H00000000–HFFFFFFFF
The PLC can use five types of numerical values to implement calculations based on its control tasks;
the following is an explanation of the missions and functions of different numerical values.
Binary Number, BIN
The PLC's numerical operations and memory employ binary numbers. Binary nibbles and relevant
terms are explained as follows:
bit bits are the fundamental units of binary values, and have a state of either 1 or 0
Nibble
Comprised of a series of 4 bits (such as b3–b0); can be used to express a
one-nibble decimal number 0–9 or hexadecimal number: 0–F.
Byte
Comprised of a series of two nibbles (i.e. 8 bits, b7–b0); can express a
hexadecimal number: 00–FF.
Word
Comprised of a series of two bytes (i.e. 16 bits, b15–b0); can express a
hexadecimal number with four nibbles: 0000–FFFF.
Double Word
Comprised of a series of two words (i.e. 32 bits, b31–b0); can express a
hexadecimal number with eight nibbles: 00000000–FFFFFFFF
 Loading...
Loading...