Chapter 7 Optional AccessoriesMS300
79
The Motor Cable Length
1. Consequence of leakage current on the motor
If the cable length is too long, the stray capacitance between cables increases and may cause
leakage current. In this case, It activates the over-current protection, increases leakage current, or
may affect the current display. The worst case is that it may damage the AC motor drive. If more
than one motor is connected to one AC motor drive, the total wiring length should be the sum of the
wiring length from AC motor drive to each motor.
For the 460V models AC motor drive, when you install an overload thermal relay between the drive
and the motor to protect the motor from overheating, the connecting cable must be shorter than 50
m; however, an overload thermal relay malfunction may still occur. To prevent the malfunction,
install an output reactor (optional) to the drive or lower the carrier frequency setting (see Pr.00-17
Carrier Frequency).
2. Consequence of the surge voltage on the motor
When a motor is driven by a PWM-type AC motor drive, the motor terminals experience surge
voltages (dv/dt) due to power transistor conversion of AC motor drive. When the motor cable is very
long (especially for the 460V models), surge voltages (dv/dt) may damage the motor insulation and
bearing. To prevent this, follow these rules:
a. Use a motor with enhanced insulation.
b. Reduce the cable length between the AC motor drive and motor to suggested values.
c. Connect an output reactor (optional) to the output terminals of the AC motor drive.
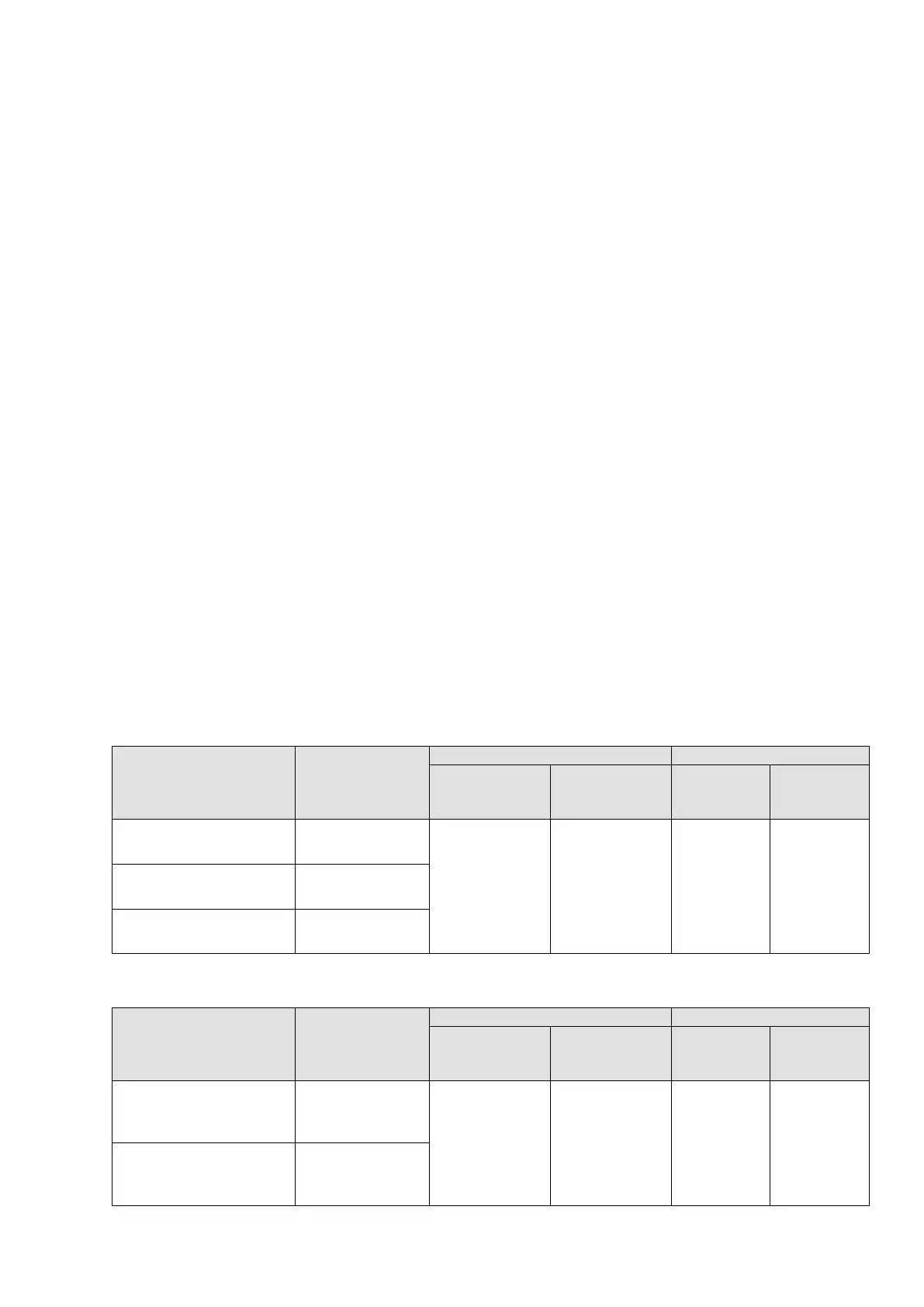
Refer to the following tables for the suggested motor shielded cable length. For drive models <
480V, use a motor with a rated voltage ≤ 500 V
AC
and an insulation level ≥ 1.35 kV
p-p
in accordance
with IEC 60034-17. For the 575V drive model, use a motor with a rated voltage ≤ 600 V
AC
and an
insulation level ≥ 1.79 kV
p-p
in accordance with IEC 60034-25.
 Loading...
Loading...











