A Series Diesel Engine Air System 101
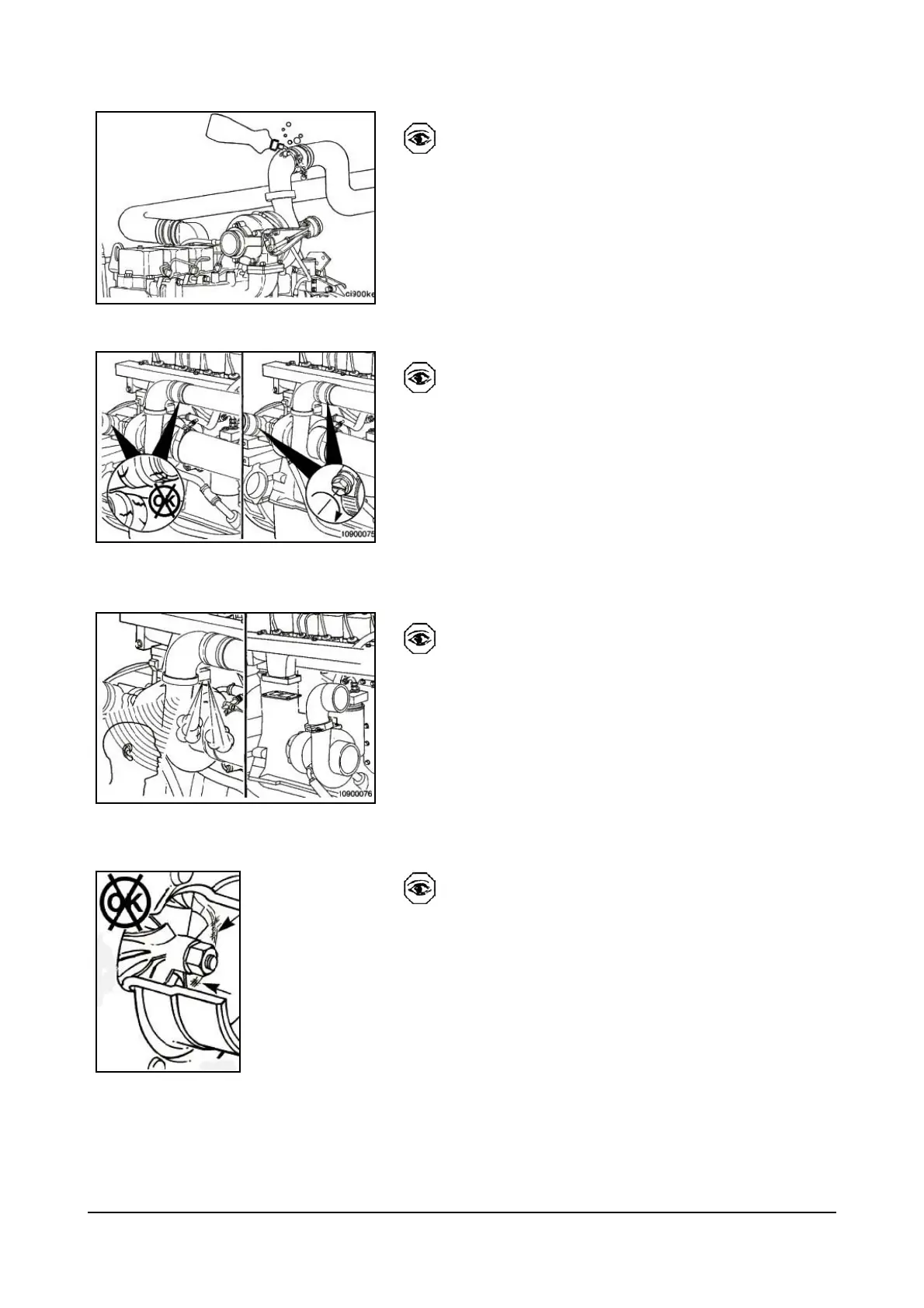
In addition to the visual inspection for cracks and loose
fittings, liquid soap can be applied to the crossover
tube, connections and the manifold cover sealing
surfaces to find the leaks.
The leaks will create bubbles that are easier to detect.
Measurement of manifold pressure is described in this
Section.
Exhaust Leaks (Turbocharged
Engines)
Inspect for exhaust leaks at the exhaust manifold and
turbocharger, gasket leaks, or exhaust pipe
restrictions.
Leaks or restrictions will cause the turbine and impeller
to operate at a lower speed and reduce the amount of
air being forced into the cylinders. Again, the symptom
will be excess smoke, low manifold pressure and low
power.
Exhaust leaks can usually be detected audibly or
visually by a discoloration caused by the escaping hot
gases.
Don’t overlook exhaust restrictions as a cause of low
power. If the exhaust gasses can not flow freely, the
turbocharger will not operate efficiently.
Malfunctioning Turbocharger
Failure of the internal components of the turbocharger
can reduce its effectiveness and also cause excess
smoke and low power. A bearing failure can produce
friction which will slow the speed of the rotor assembly.
Failed bearings can also allow the blades of the rotor
assembly to rub the housings, thus reducing the rotor
assembly speed.

 Loading...
Loading...