5
CROSBY STYLE JOS-E, JBS-E, JLT*-JBS-E, JLT*-JOS-E VALVES
InstallatIon and MaIntenance InstructIons
3.4 Outlet piping
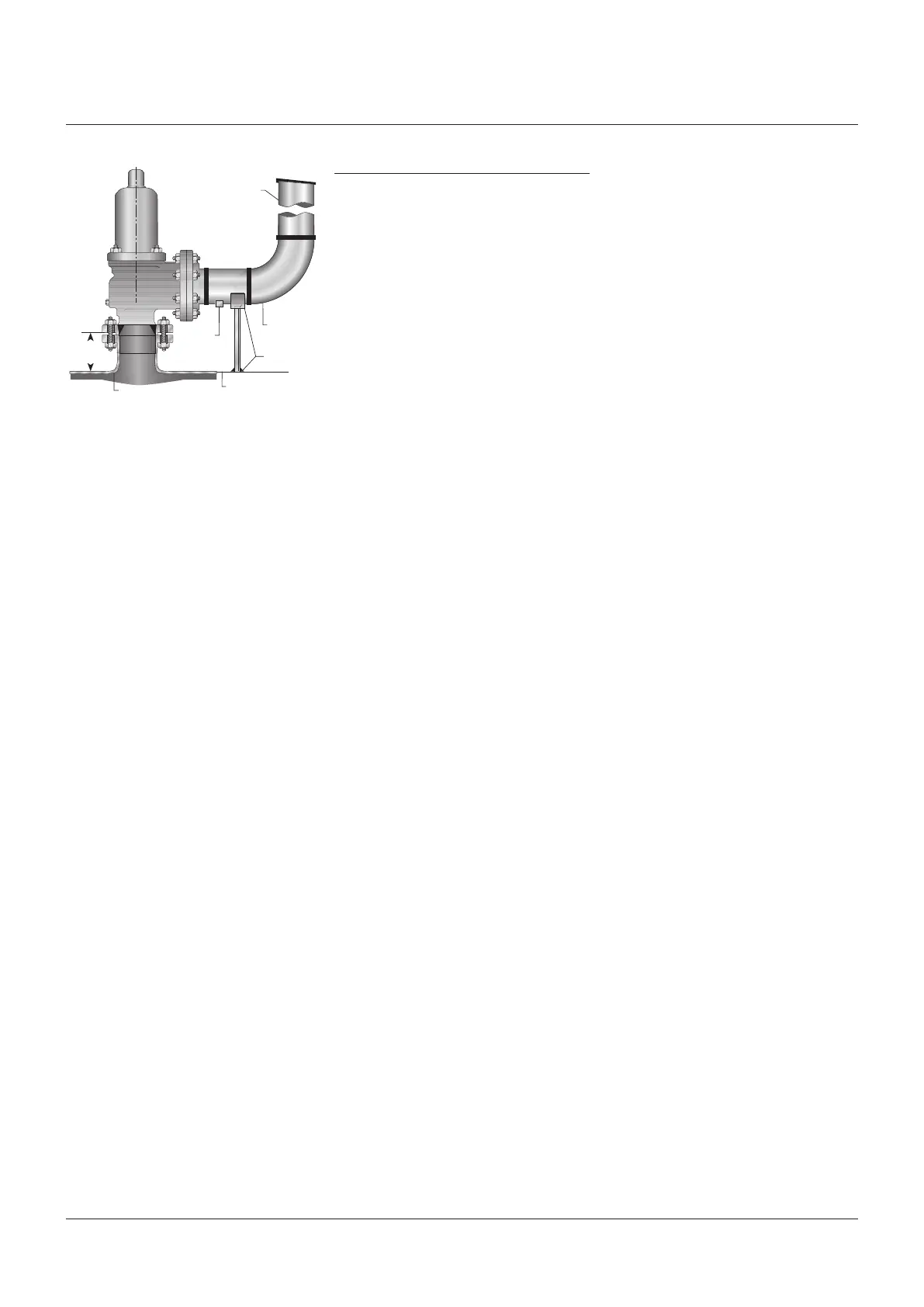
Outlet piping should be simple and direct.
Where possible, for non-hazardous fluids, a
short discharge pipe or vertical riser connected
through a long radius elbow venting directly to
atmosphere is recommended. Such discharge
piping should be at least the same size as the
valve outlet.
All discharge piping should be run as direct as
is practicable to the point of final release for
disposal. Valve effluent must discharge to a
safe disposal area.
Where discharge piping is long, due
consideration shall be given to the use of long
radius elbows, and the reduction of excessive
line strains through the use of expansion joints
and proper means of support to minimize
line sway and vibration under operating
conditions. Adequate drainage is required
to prevent corrosive media from collecting
in the discharge side of the pressure relief
valve. When required, low point drains shall be
provided in the discharge pipe. Particular care
must be observed to ensure that the drains
are directed or piped to a safe disposal area.
In installations where the pressure relief valve
discharges into a closed system, care must be
taken to ensure that built up and superimposed
back pressure has been calculated properly,
specified and accounted for when sizing and
selecting the valve.
Where built up back pressure is expected to
exceed 10% of set pressure or if superimposed
back pressure is variable, a bellows valve is
required.
4 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE TESTS
4.1 Hydrostatic test of vessel or system
When a pressure vessel or system is to be
hydrostatically tested, it is recommended
that the pressure relief valve be removed
and a blank flange be installed in its place.
This practice precludes the possibility of
any damage to the pressure relief valve.
Bent spindles and damaged valve seats are
problems that can be caused by improper
hydrostatic test procedures.
Blank flanges must be removed and the
pressure relief valve reinstalled before the
vessel is placed in service.
When the hydrostatic test must be performed
with the valve in place, a test gag may be used.
Crosby Style JOS-E/JBS-E valves are designed
to accommodate test gags for use with each
type of cap. In the case of the Type C cap with
lifting lever, the lifting lever assembly must be
replaced with a hydrostatic test cap and test
rod prior to hydrostatic testing. When test rods
are used, care must be exercised to prevent
overtightening that could damage the valve
spindle and valve seats. Generally, a test rod
which is hand tight will provide sufficient force
to hold the valve closed.
After the hydrostatic test, the test rod (gag)
must be removed and replaced by either a cap
plug or a cap not fitted with a test rod.
FIGURE 3 - Recommended installation
discharging to atmosphere
Discharge pipe
Low
pointdrain
Long
radius
elbow
Free
support
Top of vessel
Rounded approach
Short
aspossible
Lid
4.2 Hydrostatic test of outlet system
When a hydrostatic test must be conducted
on the outlet piping system, with the valve in
place, special consideration must be given
not to exceed the design pressure limits of
the downstream side of the pressure relief
valve. The outlet side of a pressure relief valve
is known as the secondary pressure zone.
Thiszone is normally designed to a lower
pressure rating than the inlet and frequently is
designed to a lower pressure rating than the
outlet flange. This is true particularly in the
case of balanced bellows designs and in the
larger valve sizes.
Consult relevant product specifications
for the back pressure design limits of
the Style JOS-E/JBS-E or JLT-E valves.

 Loading...
Loading...











