VLT-MAN-ESO-14650-4942
P96
24.06.2015
47 of 161
ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany
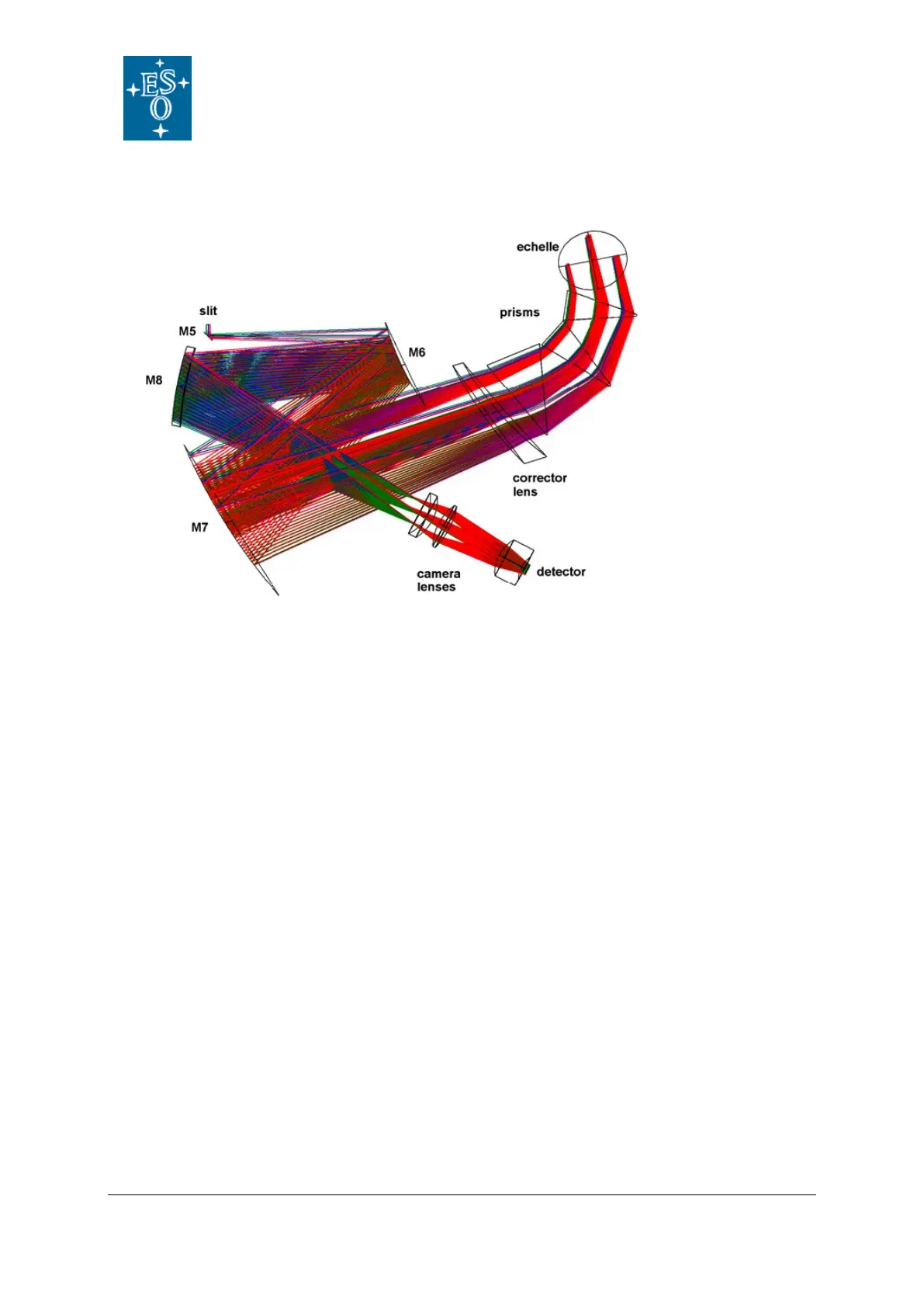
2.2.6.4 Optical layout
The optical layout of the NIR spectrograph is presented in Figure 8. The conceptual design is
the same than for the UVB and the VIS spectrographs. Light entering the spectrograph via
the entrance slit and folding mirror M5 feeds an off-axis Maksutov-inspired collimator. In this
case, the collimator is made of 2 spherical mirrors M6 and M7 plus an Infrasil corrector lens
(with only spherical surfaces). In order to get enough cross dispersion, three prisms are used
in double path. Prism 1 is a 35° top angle made of Infrasil; prisms 2 and 3 are two 22° top
angle ZnSe prisms. This design provides an almost constant order separation. Main
dispersion is provided by a 55 grooves/mm échelle grating with a blaze angle of 46.07˚. The
off-blaze angle is 0.0˚, while the off-plane angle is 1.8˚. After dispersion, the collimator
creates an intermediate spectrum near the entrance slit, where M8, a spherical mirror, acts
as a field mirror, relocating the pupil between L2 and L3, the last lenses of the camera. The
fixed focus camera re-images the échellogramme onto the detector at f/2.1 (plate scale
12.1”/mm).
Figure 8: The NIR spectrograph optical layout.
 Loading...
Loading...