RXF PLUS MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL PANELS70-401 IOM
Page 16
through all menus, entering setpoints as required for the
system. Note that on initial power-up or simply on a loss of
setpoints the micro will display a NEW annunciation mes-
sage “FACTORY DEFAULTS SET”. If you need assistance
in optimizing setpoints, contact the FRICK Service Dept.
Since the lead lag version does not incorporate Auto-Cycle, it
is best to use standard programs on the compressors that the
RXF Plus controller sequences. This allows those compres-
sors to automatically switch to their respective Auto-Cycle
modes upon a 5 minute period of communications loss.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Most problems encountered with lead lag controls concern
two main areas:
1. Communications problems
2. Optimizing control sequencing
The RXF Plus lead lag control program has a new feature
that can be used to help diagnose communications prob-
lems. This feature may be accessed on a new display by
pressing the [F1] key, then pressing the [ * ] key once. This
new menu is actually the last menu in the program.
COM.IN:
## OUT:
The period after the word COM will blink for each character
received. While this may not be much help during normal
data exchanges, it will help the operator notice when the
micro is receiving abnormal single character hits. The ##
shows actual number of characters received since the last
pound # code was encountered, which will also reset this
counter to zero. Should the micro not receive a valid com-
mand sequence (most commands are less than 14 charac-
ters long) starting with a pound character, this counter will
count excessively high, up to 99 and stop, only resetting
upon receiving a pound code. The shaded area to the right
of IN: will show actual reception of data flow from right to
left. This information should be the normal data responses
from the compressors that the RXF Plus lead lag controller
is requesting data from. The shaded area to the right of OUT:
displays the actual command that the RXF Plus lead lag
controller is sending. This does not represent a feedback
loop verifying actual data sent; it only verifies what the mi-
cro is attempting to send.
The RXF Plus lead lag program has additional communica-
tions failure annunciation which will, on communication fail-
ure to a given compressor, report a message such as “COMP.
#1 COMM. FAIL”, with its associated time of failure. This
feature is enabled once a nonzero ID code is entered to add
a compressor to the lead lag sequence and lead lag is en-
abled. The controller must get 3 successive communica-
tions failures to actually set the failure, which also will turn
on the RXF Plus controllers alarm output. Individual (single
hit) communications errors will actually display “NOT COM-
MUNICATING” in the LEAD LAG STATUS display. This mes-
sage will disappear once normal communications have re-
sumed.
Optimizing control sequence is combining an educated
guess with trial and error. Every system is to some degree
unique, either due to operating conditions, equipment cali-
bration, or simply the operators desired control. The RXF
Plus lead lag program, on initial power-up, defaults all
setpoints to known values, such as all minimum slide valve
settings will default to 50 %. Start / Stop setpoints are actu-
ally defaulted to values that will prevent actual sequencing
from occurring. Hence the need for an operator to work
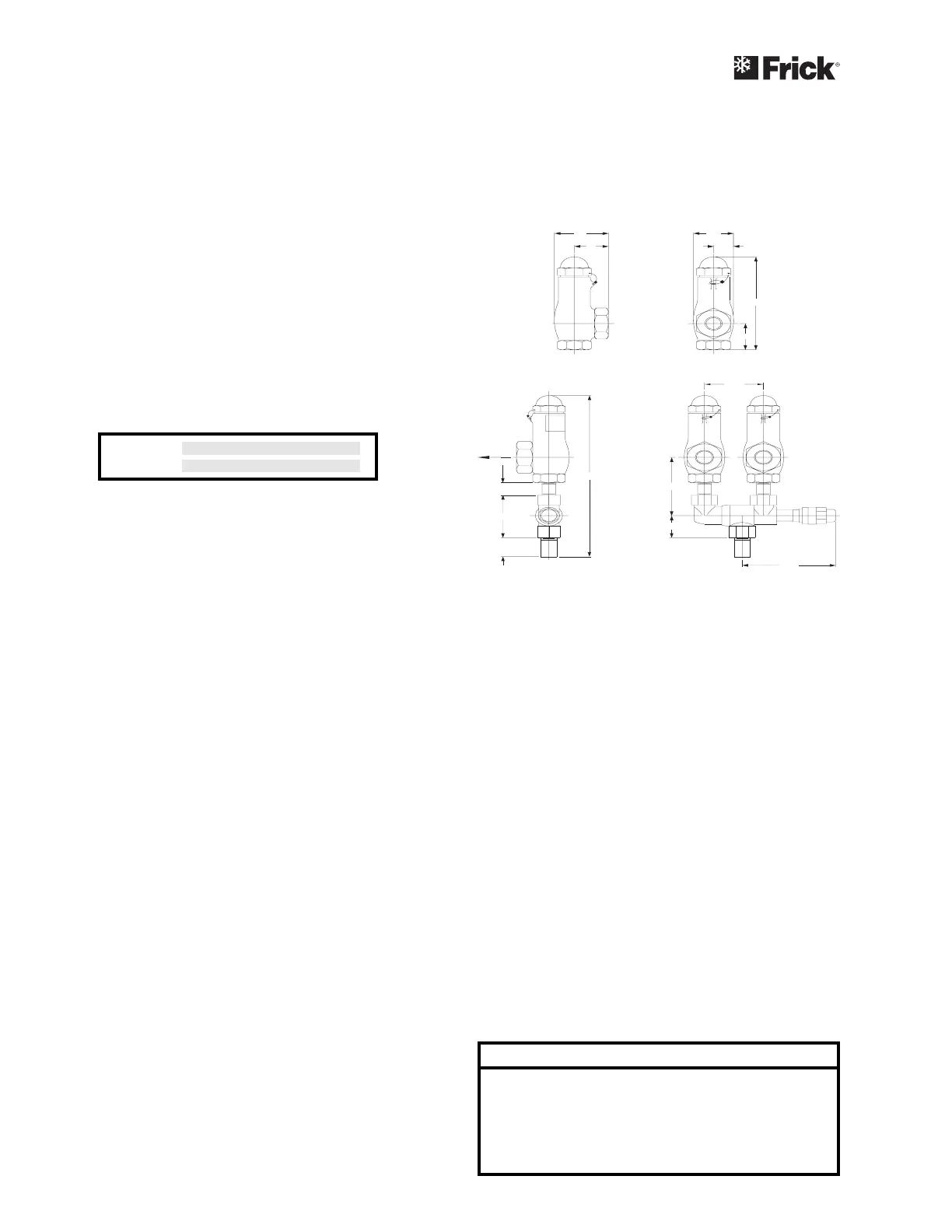
1 1/2" REF
13/4"
33/8"
1" REF
53/4"
3 5/8"
D
A
E
F
C
B
H
G
OUTLET
INLET
OUTLET
INLET
SRVSHNK1
MICROPROCESSOR
TELECOMMUNICATIONS
The Frick RXF Microprocessor comes with an onboard tele-
communications interface. The telecommunications feature
permits interfacing the microprocessor with a modem, re-
mote data communications terminal, or master computer via
RS-422 protocol. In the case of a modem, telephone lines
are used for the actual transmission of data permitting
communications from a remote location.
The components necessary to utilize the telecommunica-
tions feature will vary with the application. Information
concerning these items may be obtained from Frick Com-
pany, Waynesboro, Pa.
COMMUNICATIONS PROTOCOL
SPECIFICATIONS:
All commands must be in ASCII (CAPS) to be recognized. A
compressor with an ID code of [00] is considered disabled.
ID Codes from [01] thru [99] are valid and are recognized by
the microprocessor.
The following is a complete list of available command types:
COMMAND CODE and DESCRIPTION
I = Returns compressor status information.
R = Compressor start command.
S = Compressor stop command.
V = Compressor capacity control command.
P = Return Pressures information.
T = Return Temperatures information.
A = Return full load amps information.
C = Enter Change setpoints mode.
OPERATION
 Loading...
Loading...