1-5
Introduction to GR228X Test Systems
A dedicated functional test system is often used for functional testing. Alternatively, you can move
many of the functional tests to the GR228X Test System which has many of the necessary hybrid
test capabilities built-in. The ICA systems contain instruments for testing groups of analog
components, groups of ICs using the system’s parallel Driver/Sensors, and groups of hybrid
components using the AWG, DMM, and ACM in addition to the other instruments. Functional testing
may require the addition of optional power supplies. The Hybrid Test Library (HTL) enables you to
develop a library of functional tests that can be automatically generated. Functional testing enables
you to collect additional test statistics using the system’s data logging feature.
In-circuit testing individually checks the performance of each component on the board with little or
no operator probing. Occasionally a fault such as an open connection needs to be localized further.
The GR228X systems offer a scratchprobing technique that can discriminate between a poor test
probe contact, a bent IC pin that was not inserted correctly, or a broken track.
Performing a combination of in-circuit and functional tests provides the most thorough fault
coverage. The GR228X software and hardware are optimized for in-circuit component testing,
therefore, the test development process focuses on in-circuit testing. GR228X systems can also
perform “clusters” of functional tests using the same test fixture. By grouping the UUT into
functional clusters, you can simplify test development and improve the diagnostic accuracy of
failing cluster tests.
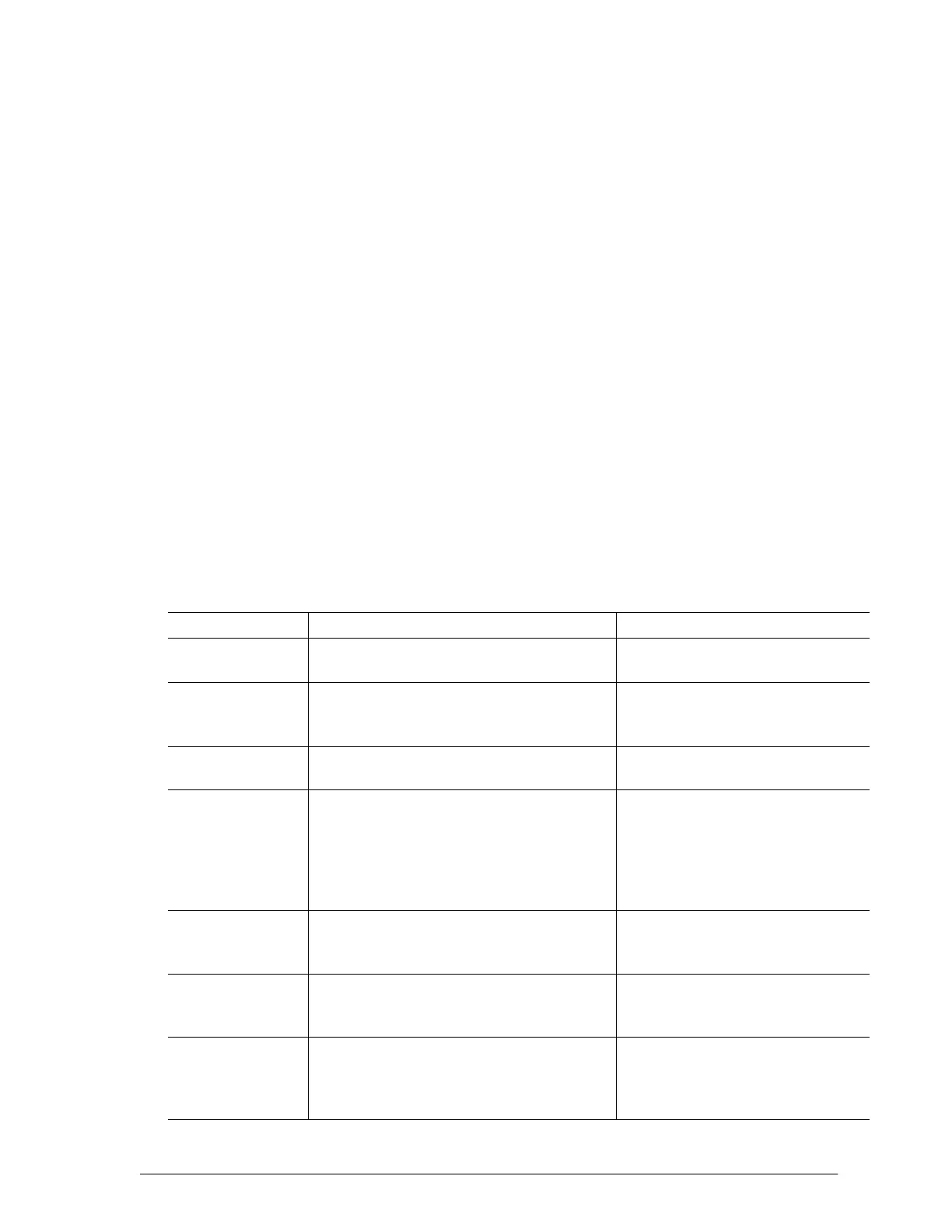
Table 1–2 identifies and contrasts the major characteristics of functional and in-circuit testing.
Table 1–2
Functional and In-Circuit Test Characteristics
Characteristic
Functional (Board-Edge) Test In-Circuit Test
What is tested Component inputs and outputs. Component connections, values,
and functions.
How is it tested Power is applied to the board. Component-by-component;
power is applied to UUT for digital
and hybrid tests.
Fixture
requirements
Board edge connector that may accept
many boards.
Bed-of-nails fixture for each
board design.
Software
requirements
Can use an optional circuit simulator as a
diagnostic aid to predict outputs and fault
coverage. Test development requires a
simulator library, and a programmer to
write part of the test. It requires a longer
test development cycle.
Automatic Test Generator (ATG)
writes the test using test libraries.
The hybrid library can generate
functional tests.
Component
library
Must contain complete transfer function or
truth table for each digital device.
Contains analog, digital, and
hybrid model tests, written for a
variety of circuit environments.
Fault diagnosis Provided by guided operator probing; fault
identification depends on adequate
simulation.
Probing is not required to obtain
good fault identification.
Fault coverage Excellent fault coverage, although both
the test development and debug time are
lengthy. Also, manufacturing faults may
not be detected.
Excellent fault coverage with fast
test development and debug
time.
 Loading...
Loading...