6
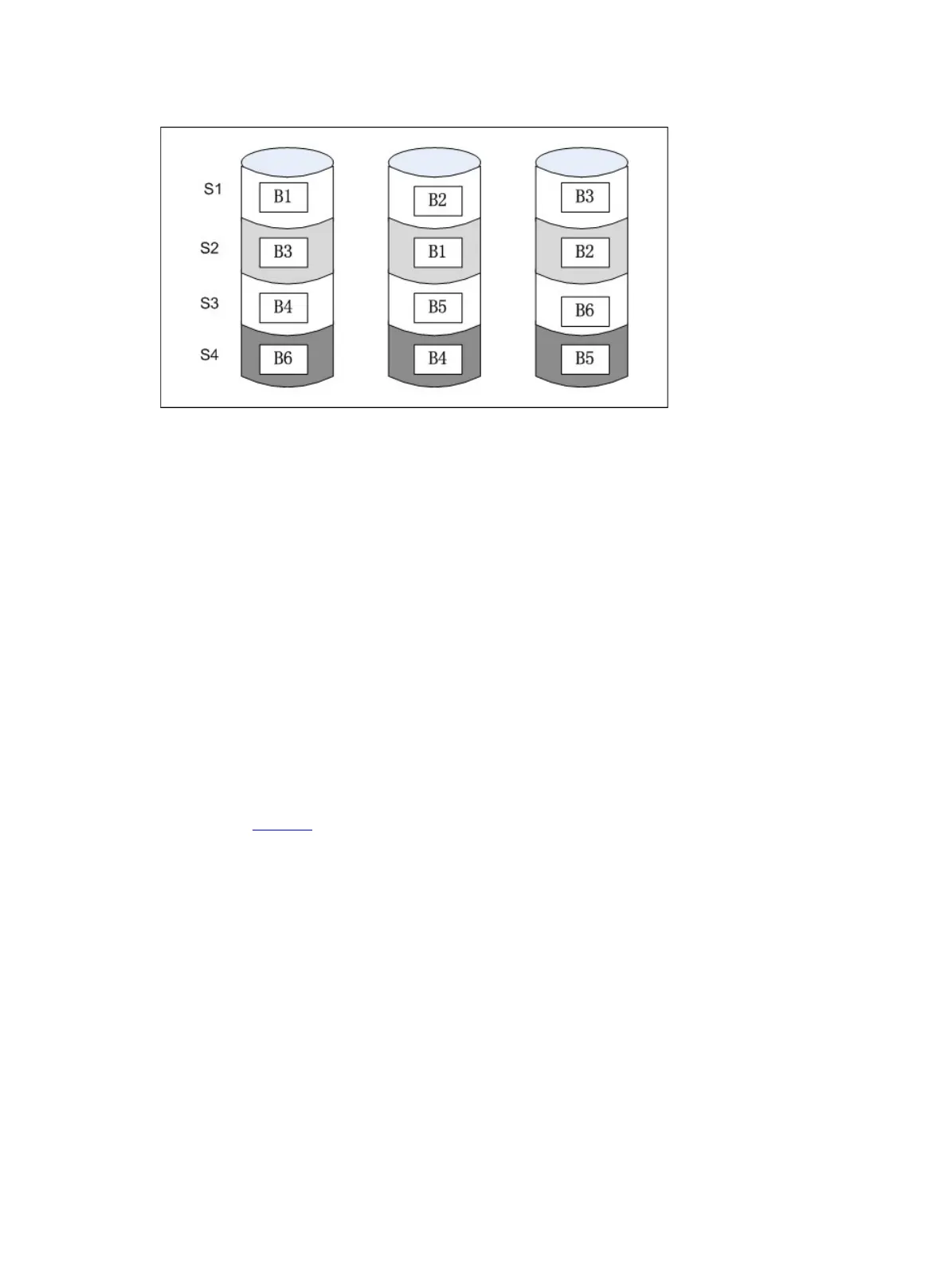
Figure 7 RAID 1E
Application scenarios
RAID 1E is useful when high performance and data protection are more important than the cost of
physical drives.
Advantages
Has higher read performance than RAID 1 and mirrors data for an odd number of drives.
No data is lost as long as no failed drive is mirrored to another failed drive.
Up to half of the physical drives in the array can fail.
Disadvantages
This method is expensive as it needs many drives for fault tolerance.
Only half of the total drive capacity is usable for data storage.
Has lower security performance than RAID 10 when the same even number of drives are used
to create the array.
RAID 5
As shown in Figure 8, in RAID 5 configuration, data protection is provided by parity data (denoted
by P
x,y
). This parity data is calculated stripe by stripe from the user data that is written to all other
blocks within that stripe. The blocks of parity data are distributed evenly over every physical drive
within the logical drive.

 Loading...
Loading...