75
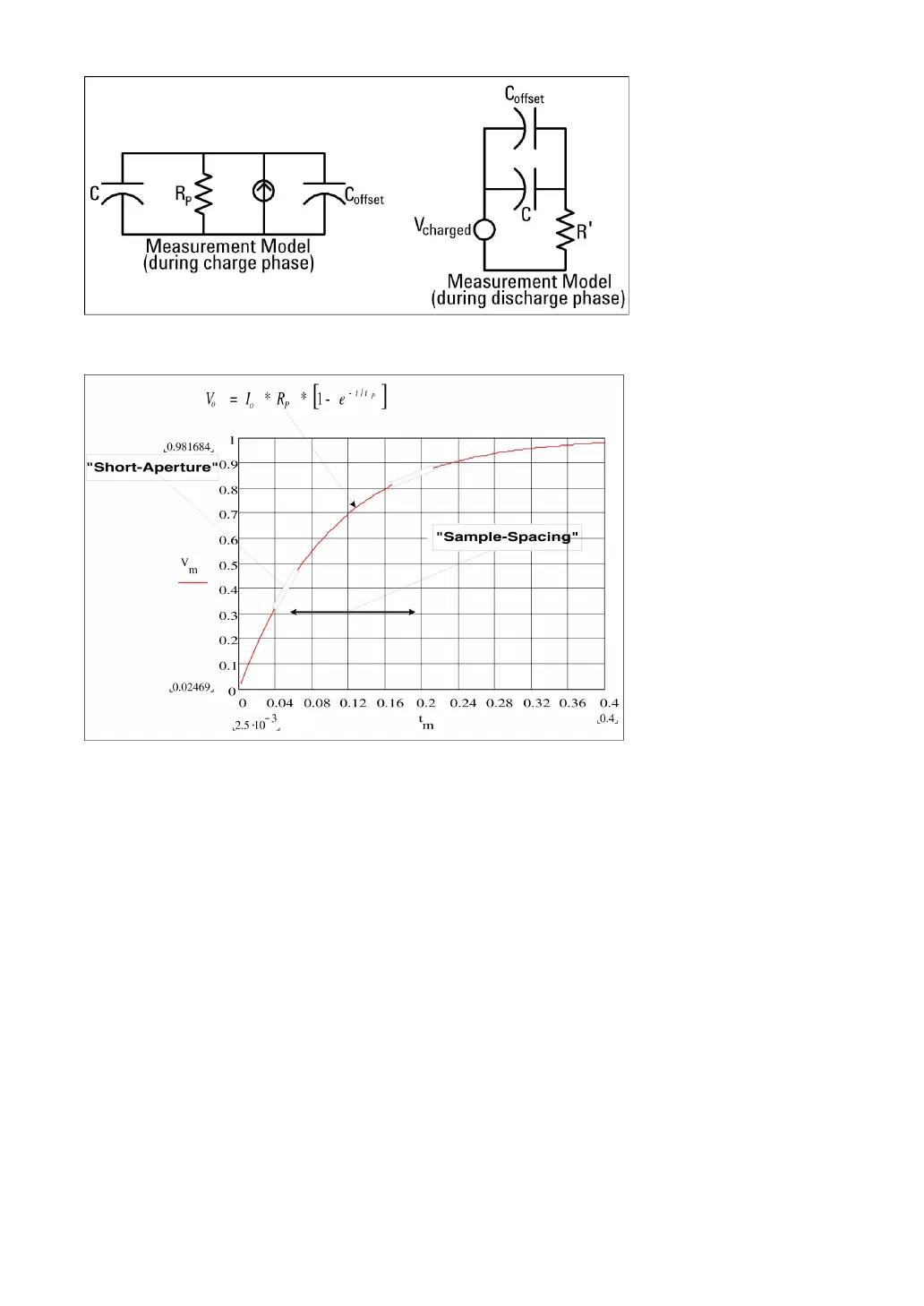
The response curve during charging is shown as follows:
The capacitance is calculated by measuring the voltage change (DV) that occurs during
the "short aperture" period (Dt). The measurement was repeated at two different time
periods during which the exponential rise occurred. The algorithm extracts data from these
four points and calculates the exact capacitance value by linearizing the exponential rise
that occurs during the "short aperture" period.
The measurement cycle consists of two parts: the charging stage (as shown in the figure)
and the discharge stage. The time constant in the discharge stage is larger because of the
protective resistor in the measuring loop. The time constant plays an important role in the
resulting read rate (measurement time). To minimize noise and increase reading accuracy,
the increment time (or "sampling time") and the width of the "short aperture" vary with the
range.
For maximum accuracy, a zeroing measurement should be performed using an open
probe to eliminate capacitance in the test lead prior to connecting the probe to the
capacitor under test.
Precautions for capacitance measurement

 Loading...
Loading...