12
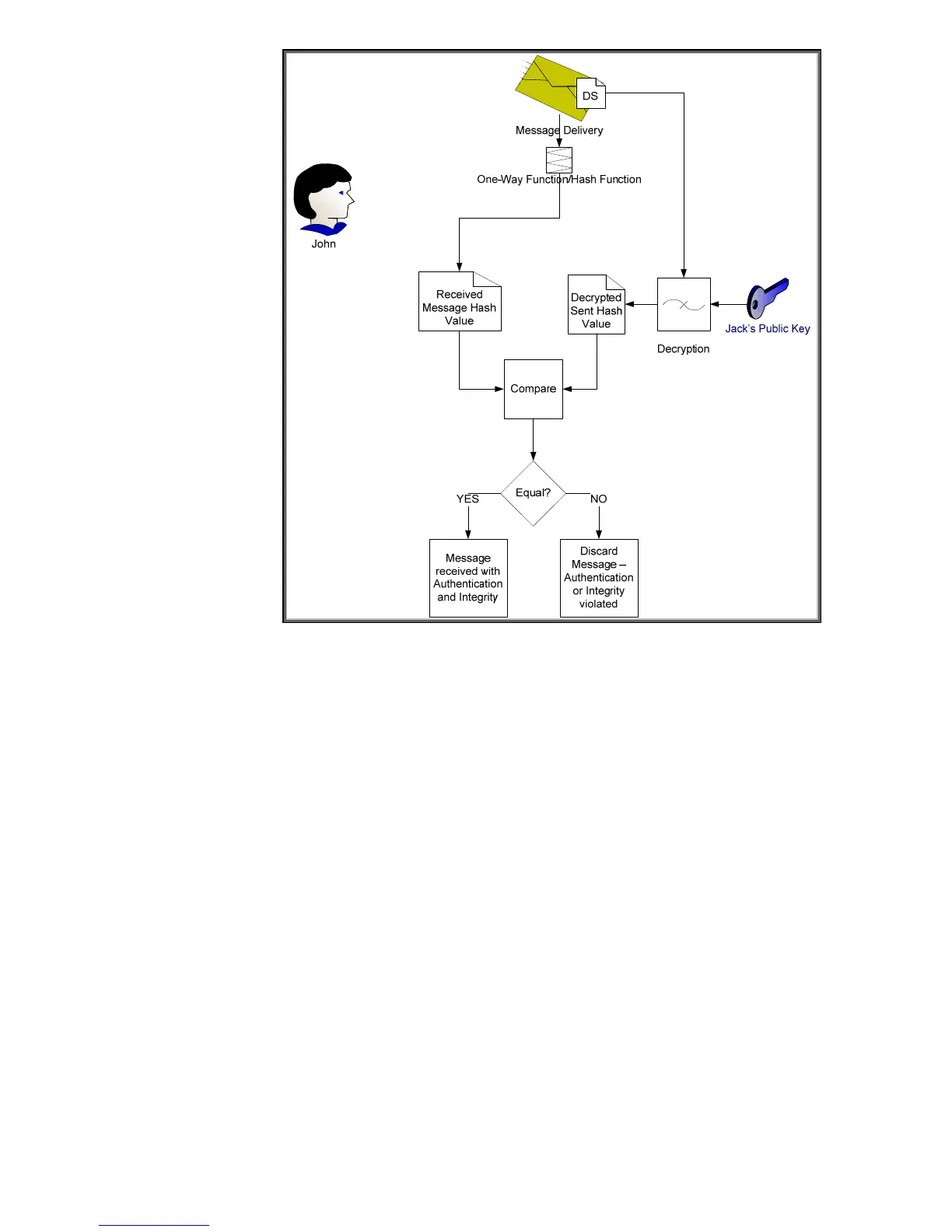
Figure 13 – Digital Signature Verification
Here we see how John uses Jack’s public key to verify the message. Jack’s public key is the only key
that can decrypt the digital signature and obtain the hash value of the message that Jack calculated
before sending the message. Because the hash was encrypted with Jack’s private key, which no one
should know but Jack, John can be sure that Jack was the one that sent it.
We still have a problem – How does John know that Jack’s public key really belongs to the person
that he knows as “Jack”? There are many people in the world named “Jack” – how does John know
it isn’t one of them? We still need a trusted third party to provide Jack’s public key in a format John
can trust and we probably need Jack to provide a little more identity information too. Here is where
the Certificate Authority comes into play. Refer to Figure 14 – Certificate Authority.
 Loading...
Loading...











