Glossary
active function readout
Area at left of screen that displays the active function and its state. The active function is
determined by the last completed programming command or key function.
active marker
Marker which can be repositioned by programming commands or front-panel controls.
active trace
Trace that is being updated (swept) with incoming signal information. Only traces A, B,and
C can be active.
See
trace
.
address
,
HP-IB
See
HP-IB
and
address
map
.
address
,
HP-MSIB
See
address
map
.
address map
A modular measurement system consists of instruments. Instruments can be stand-alone
instruments, such as the HP 70004A color display, or can consist of one or more modules
which are plugged into a mainframe or display.
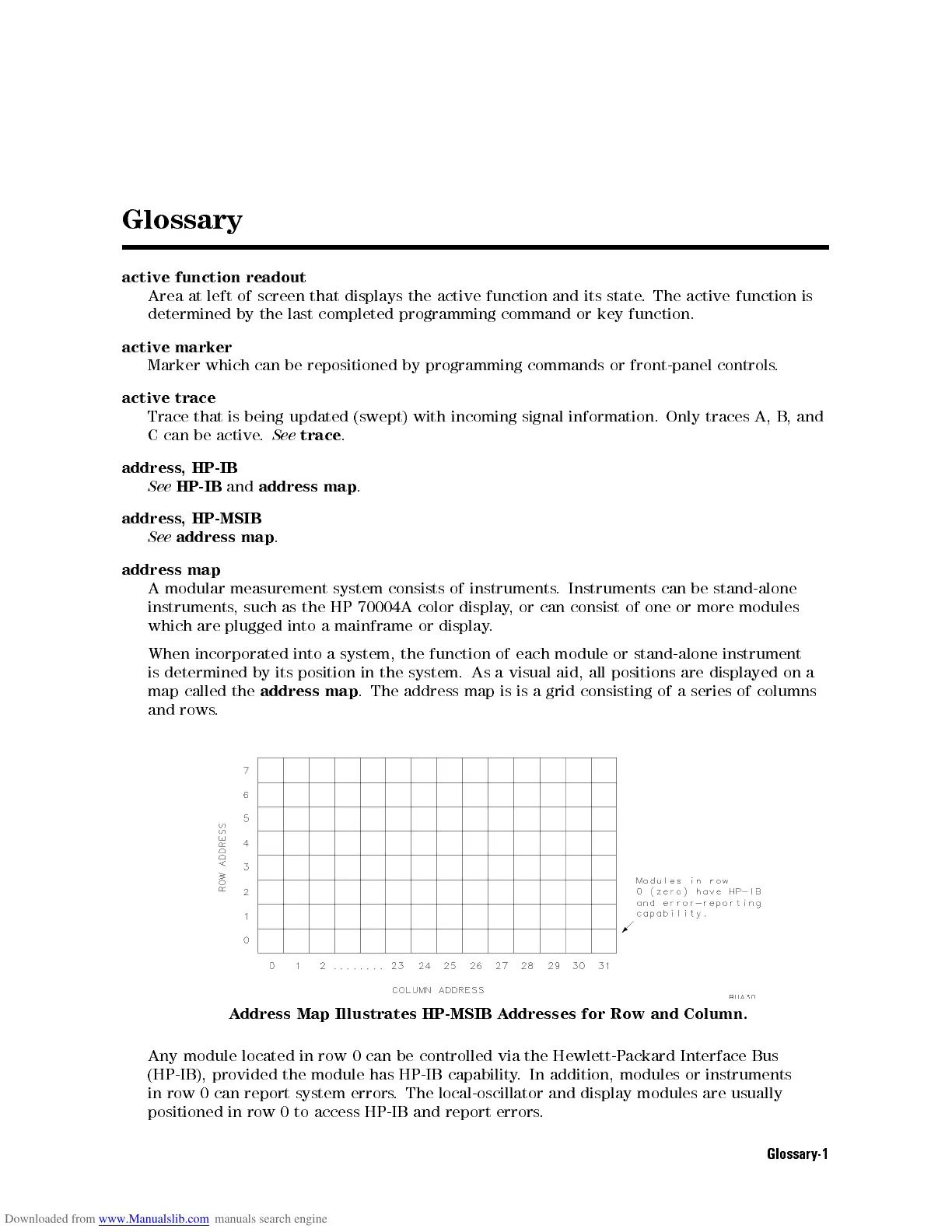
When incorporated into a system, the function of each module or stand-alone instrument
is determined by its position in the system. As a visual aid, all positions are displayed on a
map called the
address map
. The address map is is a grid consisting of a series of columns
and rows.
Address Map Illustrates HP-MSIB Addresses for Row and Column.
Any module located in row 0 can be controlled via the Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus
(HP-IB), provided the module has HP-IB capability. In addition, modules or instruments
in row 0 can report system errors. The local-oscillator and display modules are usually
positioned in row 0 to access HP-IB and report errors.
Glossary-1

 Loading...
Loading...