Cable and Wire Length
Guidelines
Table 4 defines cable length guidelines for the various
wire sizes that may be used for wiring low-voltage (<30V)
input and outputs.
Table 4: Cable Length Guidelines for Recommended Wire Sizes for Low-Voltage (<30V) Inputs and Outputs
AssumptionsMaximum Cable
Length and Type
Wire Size/Gauge and TypeGuideline
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on cable and the connected input
or output device, you may have to define an
offset in the setup software for the input or
output point.
457 m (1,500 ft) twisted
wire
1.5 mm
2
(18 AWG) stranded copper
A
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
107 m (350 ft) twisted wireN/A (24 AWG) stranded copper
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on cable and the connected input
or output device, you may have to define an
offset in the setup software for the input or
output point.
229 m (750 ft) twisted wire
1.5 mm
2
(18 AWG) stranded copper
B
137 m (450 ft) twisted wire0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
91 m (300 ft) twisted wire0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
61 m (200 ft) twisted wireN/A (24 AWG) stranded copper
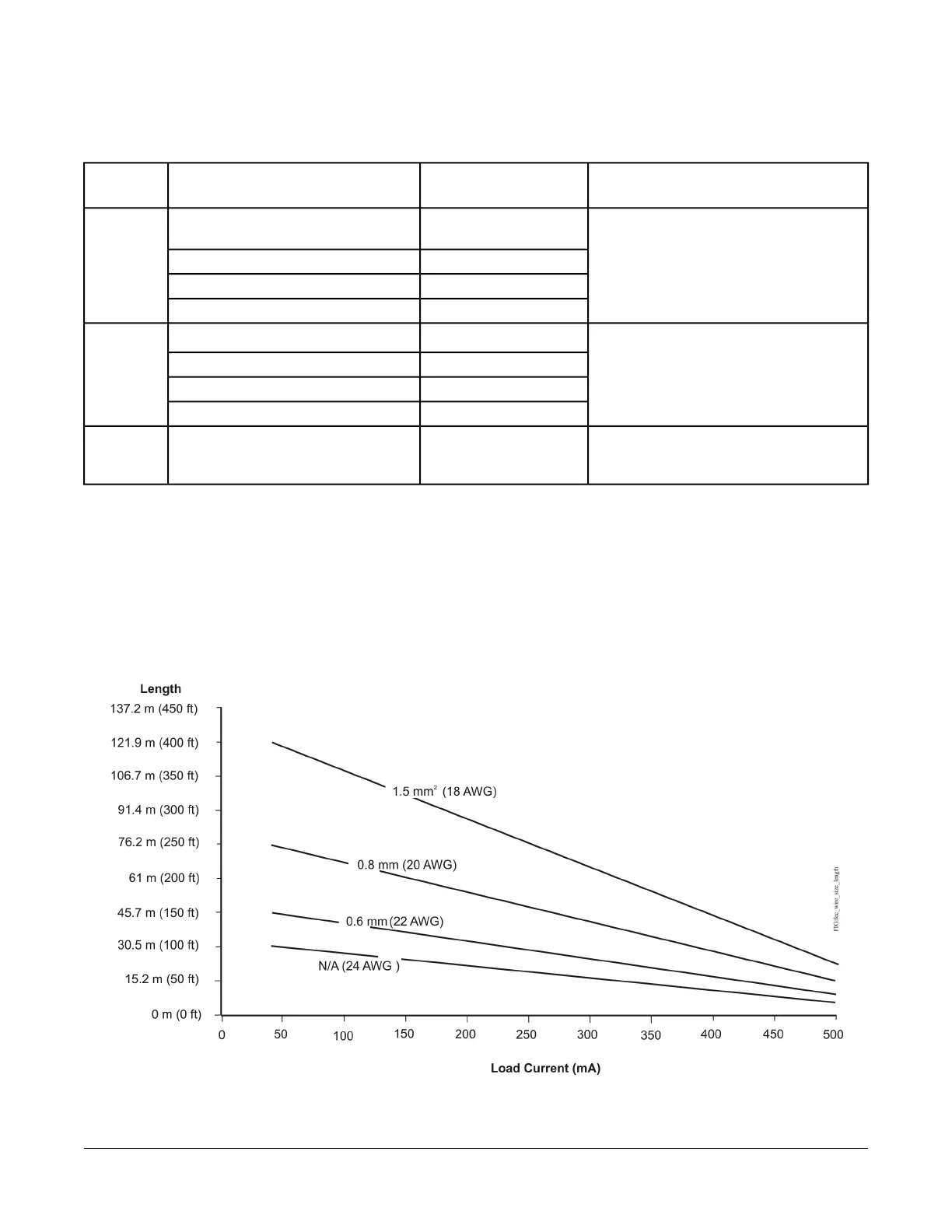
N/A
See Figure 8 to determine
cable length. Use twisted
wire cable.
See Figure 8 to select wire size/gauge.
Use stranded copper wire.
C
Maximum Cable Length versus
Load Current
Use Figure 8 to estimate the maximum cable length
relative to the wire size and the load current (in mA) when
wiring inputs and outputs.
Note: Figure 8 applies to low-voltage (<30V) inputs and
outputs only.
Figure 8: Maximum Wire Length for Low-Voltage (<30V) Inputs and Outputs by Current and Wire Size
15FX-PCX47 Expansion Input/Output Module Installation Instructions

 Loading...
Loading...