-TCSCAN Scanner Card User's Manual Section 3:
2001-TCSCAN-900-01 Rev. A / April 2018 3-15
Reference junction sensor
Operating temperature is the primary factor in determining reference junction accuracy. Using the
2001-TCSCAN in the 18 °C to 28 °C range, maximum sensor performance is achieved. The
2001-TCSCAN may also be used over 0 °C to 18 °C and 28 °C to 50 °C with reduced accuracy.
Path isolation
Path isolation is the equivalent impedance between any two test paths in a measurement system.
Theoretically, the path isolation should be infinite, but the actual resistance and distributed
capacitance of cables and connectors results in less than infinite path isolation values for these
devices.
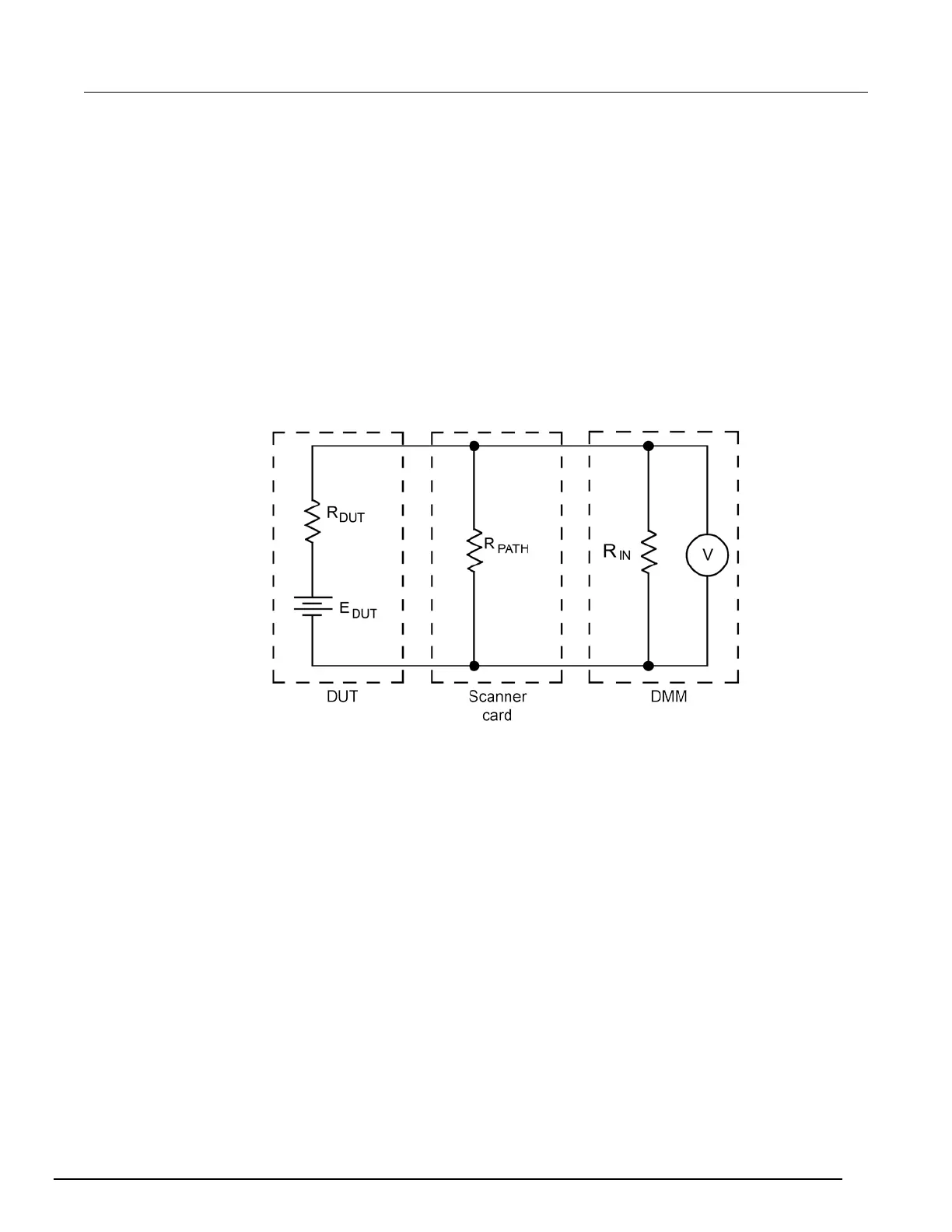
Figure 23: Path isolation resistance
R
DUT
= source resistance of the DUT
E
DUT
= source EMF of the DUT
R
PATH
= path isolation of resistance
R
IN
= input resistance of the multimeter
Path isolation resistance forms a signal path that is in parallel with the equivalent resistance of the
DUT, as shown in the figure above. For low-to-medium device resistance values, path isolation
resistance is seldom a consideration; however, it may seriously degrade measurement accuracy
when testing high-impedance devices. For example, the voltage measured across such a device can
be substantially attenuated by the voltage divider action of the device source resistance and path
isolation resistance, as shown in the previous figure. Also, leakage currents can be generated
through these resistances by voltage sources in the system.
 Loading...
Loading...