223Section 12 Paralleling System InformationTP-6953 7/19
12.6.4 Load Sharing
Load Sharing Parameters are found under the Real
Power Load Sharing heading in SiteTecht and under
the Generator Info -> Paralleling Operation -> Sharing
Setup menu on the user interface of the controller.
Real Load Sharing
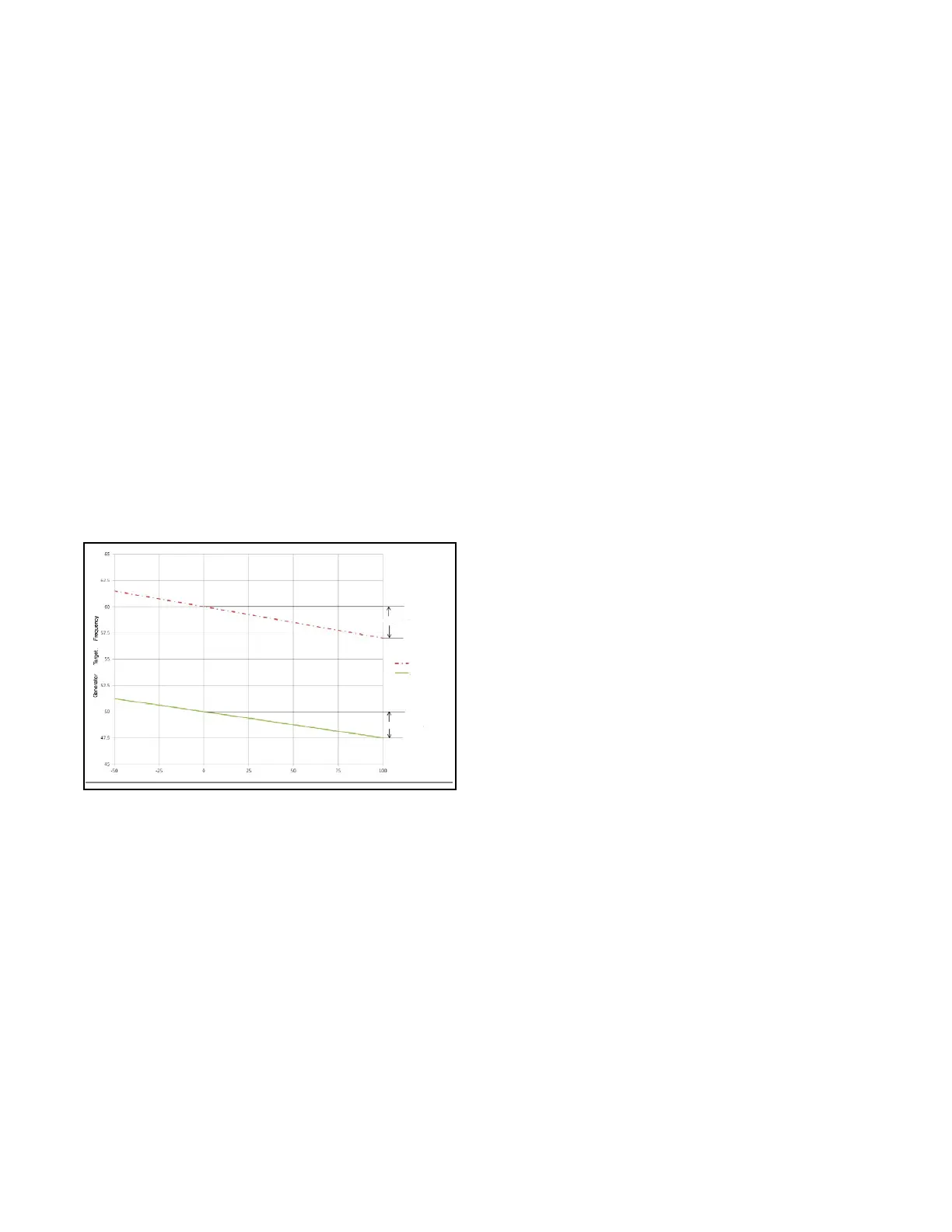
D Real Power Droop Slope
This controls the rate at which the target speed of the
engine decreases with increasing load. Real Power
Droop is intended to permit generators to share load
in paralleled applications when there is no
communication between the generator controllers.
SeeFigure12-6.
If the load on a given generator increases, the target
speed will decrease, resulting in a decrease in
throttle, causing a decrease in load. The remaining
load will be supplied by other generators in the
paralleling system, which will cause their target speed
to decrease slightly. The generator system will share
load relatively evenly if they operate in droop mode,
but the system frequency will vary with load.
3Hz (5%) @ 100%
5% Droop @ 60Hz
5% Droop @ 50Hz
2.5Hz (5%) @ 100%
Generator Load (% of rated capacity)
Range: 0.0% – 10.0%
Default: 1.0%
Figure 12 -6 Real Power Droop Slope
D Real Power Sharing Proportional Gain
The Real Power Sharing Proportional Gain
determines the contribution of the real power sharing
proportional term to the speed bias. The proportional
term is directly related to the difference between the
average percent electrical loading of all gens on the
bus and the percent electrical loading of this
individual generator. The proportional term increases
the speed bias when the average bus load is greater
than the generator load.
Range: 0.01 – 100.00
Default: 1.00
D Real Power Sharing Integral Gain
The Real Power Sharing Integral Gain determines
the contribution of the real power sharing integral
term to the speed bias. The integral term ramps at a
rate directly related to the difference between the
average percent electrical loading of all gens on the
bus and the percent electrical loading of this
individual generator. The integral term ramps the
speed bias up when the average bus load is greater
than the generator load.
Range: 0.01 – 100.00
Default: 1.00
D Real Power Sharing Derivative Gain
The Real Power Sharing Derivative Gain determines
the contribution of the real power sharing derivative
term to the speed bias. The derivative term is directly
related to the rate of change in the difference between
the average percent electrical loading of all gens on
the bus and the percent electrical loading of this
individual generator. The derivative term increases
the speed bias when the difference between the
average bus load and the average generator load
increases.
Range: 0.01 – 100.00
Default: 1.00
D Torque Sharing Proportional Gain
The Torque Sharing Proportional Gain determines
the contribution of the torque sharing proportional
term to the speed bias. The proportional term is
directly related to the difference between the average
percent mechanical loading of all gens on the bus and
the percent mechanical loading of this individual
generator. The proportional term increases the speed
bias when the average bus load is greater than the
generator load.
Range: 0.01 – 100.00
Default: 1.00
D Torque Sharing Integral Gain
The Torque Sharing Integral Gain determines the
contribution of the torque sharing integral term to the
speed bias. The integral term ramps at a rate directly
related to the difference between the average percent
mechanical loading of all gens on the bus and the
percent mechanical loading of this individual
generator. The integral term ramps the speed bias up
when the average bus load is greater than the
generator load.
Range: 0.01 – 100.00
Default: 1.00

 Loading...
Loading...