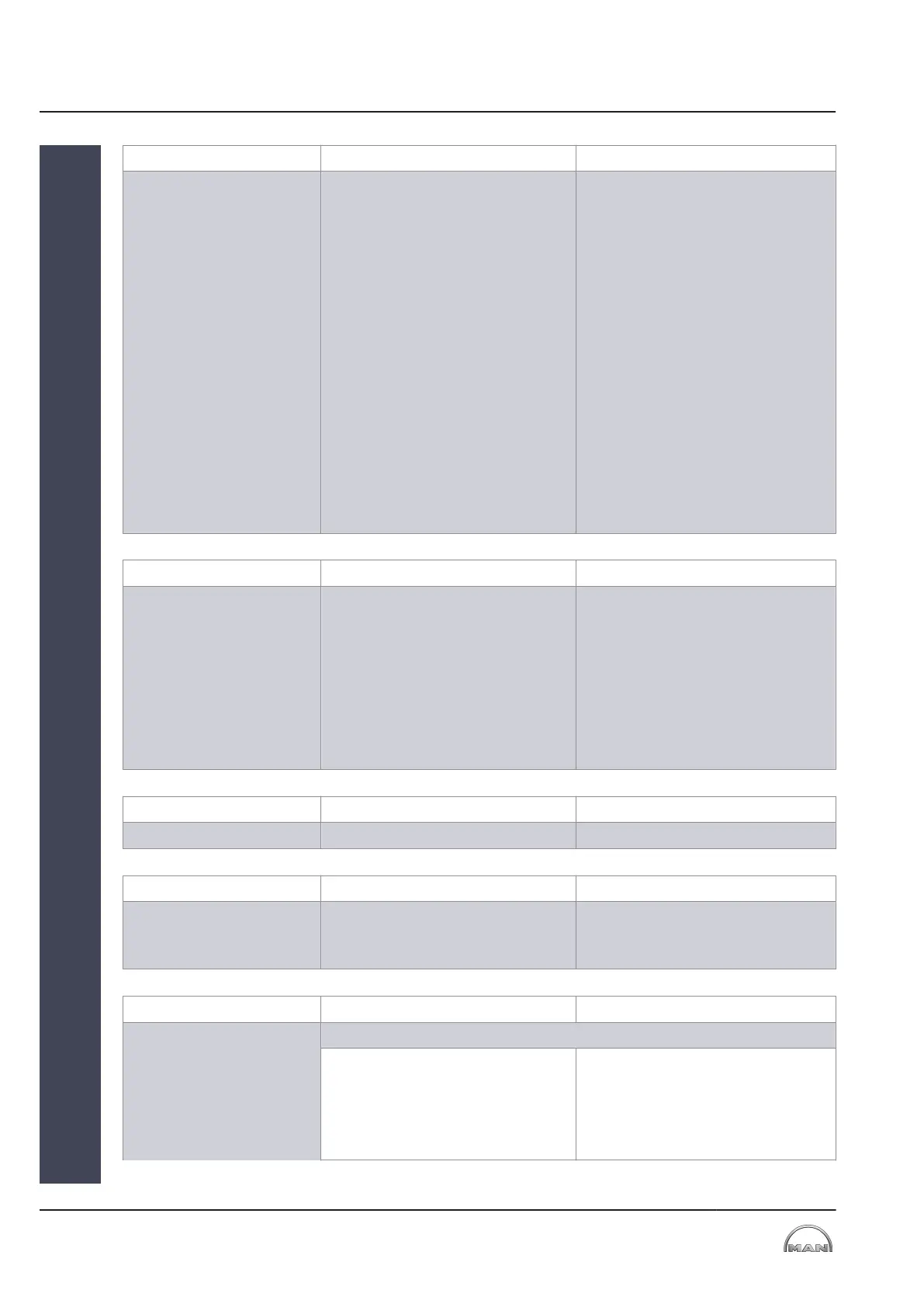
Application Functional principle Effect
4-stroke diesel engine
▪ VTA closes at partial load
▪ Compensation of ambient tem-
perature influences on charge
pressure
▪ Closing on acceleration
▪ Compensation of extracted gas
flows (e.g. for power turbine
applications, see “Power tur-
bine” line)
▪
Plants with EGR
4)
:
Charge air pressure kept con-
stant when EGR rate is modified
▪
HAM
5)
applications:
Increased water content at par-
tial load.
4) Exhaust gas recirculation
5) Humid air motor
▪ Reduced fuel consumption at
partial load
▪ Increased NOx emissions ⇨
With appropriate rating within the
limit values or constant cycle val-
ues, similar to 2-stroke
▪ Reduction of exhaust gas tem-
peratures at partial load
▪ Elimination of blow-off valves
▪ Improved load application behav-
ior
▪ Reduction of soot emissions in
the case of low load and load
application
▪ Additional improvement of partial
load performance by shifting the
maximum efficiency towards a
lower engine load
Table 2: VTA range of applications on 4-stroke diesel engine
Application Functional principle Effect
Gas-powered engine
▪ VTA opens at partial load
▪ Compensation of ambient tem-
perature influences on charge
pressure
▪ Closing on load application to
prevent overgreasing
▪ Variation of the charge pressure
to adapt to changing gas quali-
ties
▪ Reduced fuel consumption due
to increased turbocharging effi-
ciency compared with blow-off
valves or throttle
▪ Elimination of blow-off valves/
throttle
Table 3: VTA range of applications on gas-powered engine
Application Functional principle Effect
Dual-fuel engine See gas-powered and diesel engine See gas-powered and diesel engine
Table 4: VTA range of applications on dual-fuel engine
Application Functional principle Effect
Test engine
▪ Adaptation of the charge air
pressure to changing engine
parameters
▪ Elimination of conversions
▪ Infinitely adjustable setting of the
charge air pressure
Table 5: VTA range of applications on test engine
Application Functional principle Effect
Power turbine 1. VTA only on power turbine
▪ “Closing” of the VTA to throttle
the power turbine output
▪ Increased turbocharging effi-
ciency at a given power turbine
output, compared with power
turbine control by means of con-
trol flaps, due to elimination of
pressure losses
1 Adjustable turbine nozzle ring (VTA)
1.1 Range of applications
2013-12-04 - de
1
MAN Diesel & Turbo
6 (38)
EN-US
 Loading...
Loading...