MFJ-935C High-Efficiency Magnetic Loop Tuner Instruction & Technical Manual
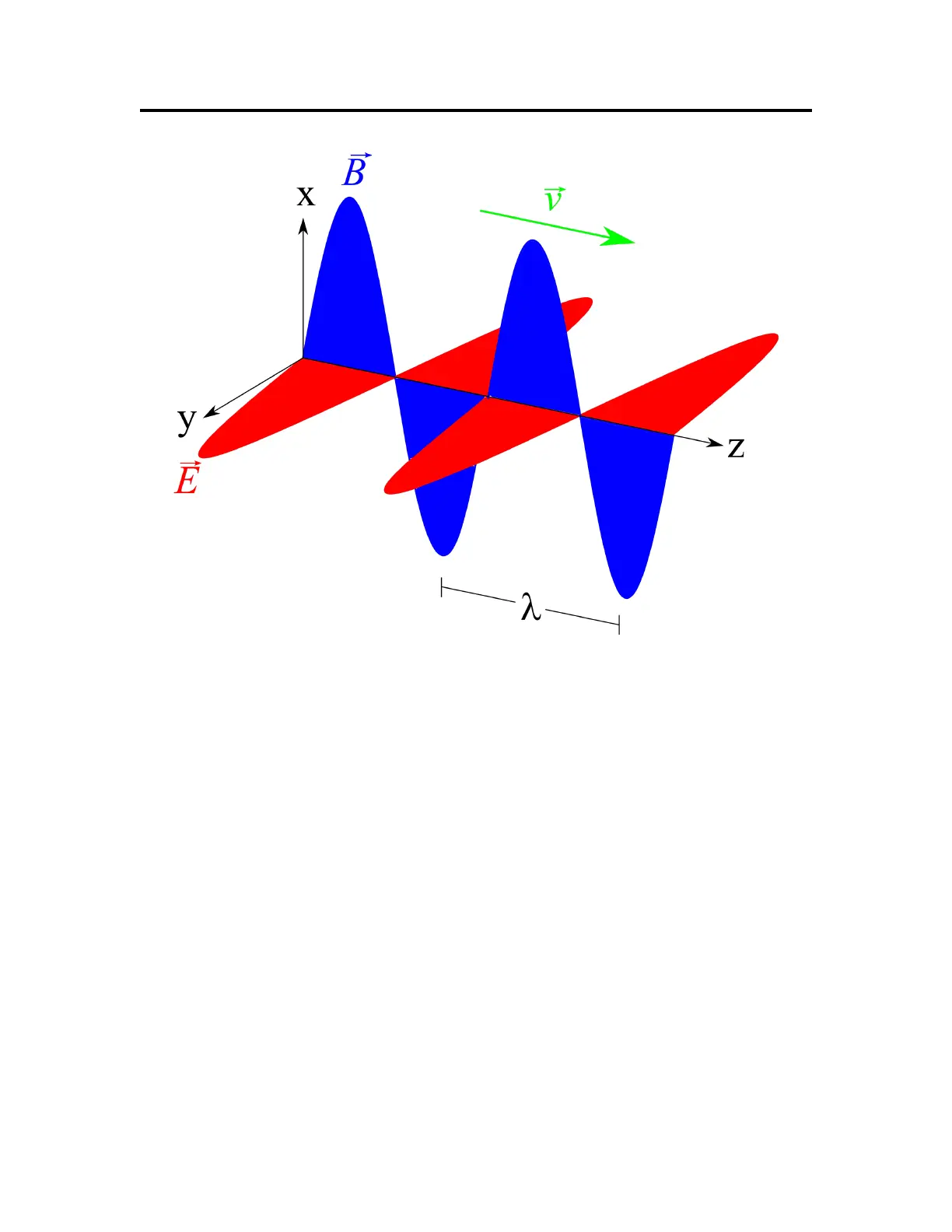
Figure 1: An Electromagnetic Plane Wave
Electromagnetic waves travel through space at the speed of light. Wavelength and frequency are
inversely related by a simple equation: frequency × wavelength = the speed of light, or fλ = c.
Since the speed of light is a fundamental constant, High Frequency (HF) electromagnetic waves
have short wavelengths, and Low-Frequency (LF) waves have long wavelengths. The frequency
bands used for amateur radio transmissions are usually characterized by their approximate
corresponding wavelengths, such as 12, 15, 17, 20 meters, et cetera.
The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 2) includes all of the various energies of electromagnetic
radiation ranging from extremely low frequency (ELF) ranges (with very long wavelengths) to all
the way up to x rays and γ rays, which have very high frequencies and correspondingly short
wavelengths. In between these extremes lie radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible
light and ultraviolet radiation. The RF part of the electromagnetic spectrum can generally be
defined as that part of the spectrum where electromagnetic waves have frequencies that range from
about 3 kilohertz (kHz) to 300 gigahertz (GHz).
-2-
 Loading...
Loading...