3
SEQUENCE PROGRAM CONFIGURATION AND
EXECUTION CONDITIONS
3.9 Numeric Values which can be Used in Sequence Programs
3.9.4 Real numbers (floating decimal point data)
3
- 80
1
Overview
2
Performance
Specification
3
Sequence Program
Configuration and
Execution Conditions
4
I/O Nunber Assignment
5
Memories and Files
Handled by CPU Module
6
Functions
7
Communication with
Intelligent Function
Module
8
Parameters
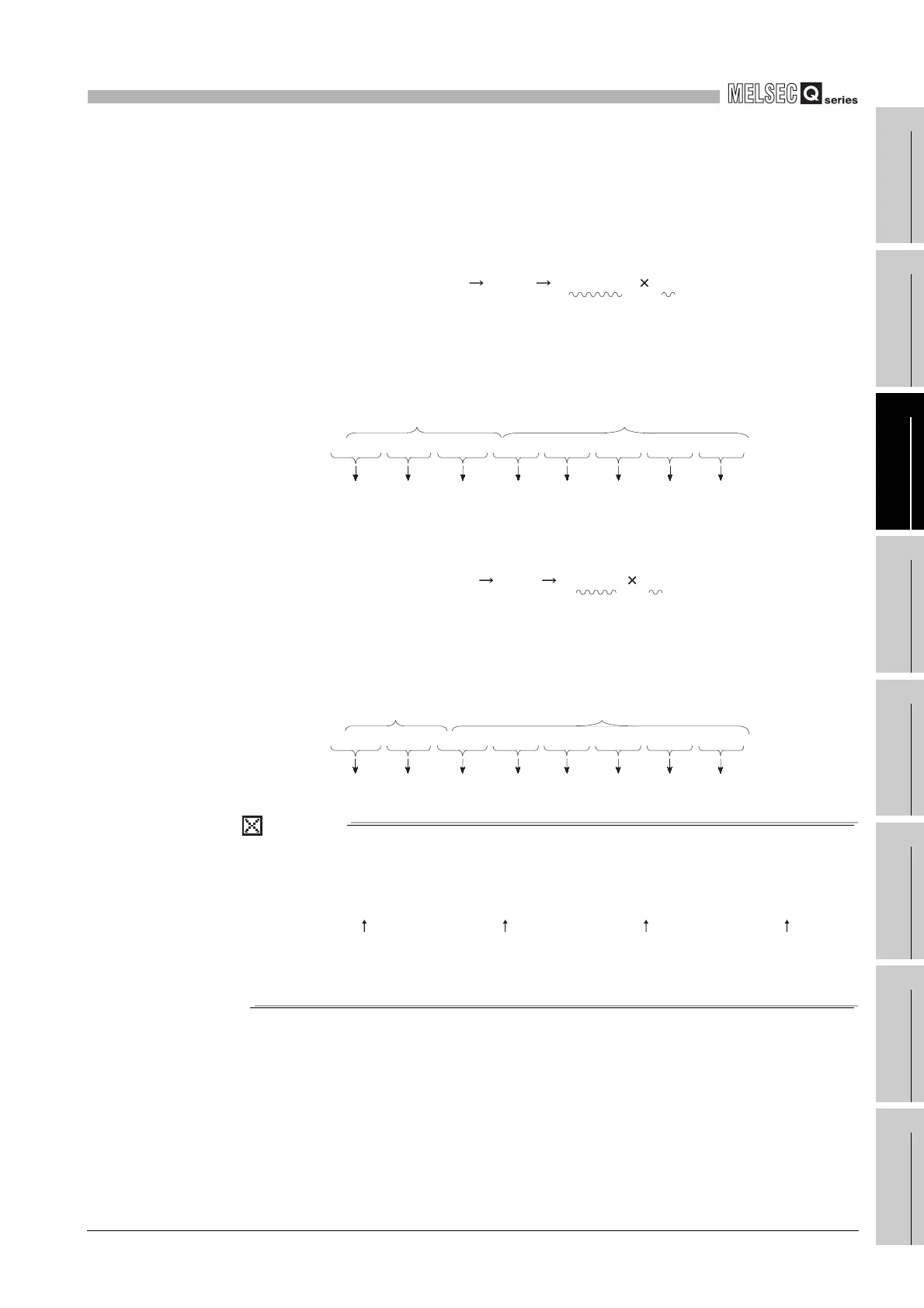
(3) Calculation examples
Calculation examples are shown below (the nnnnn "X" indicates an X-system data
expression).
(a) Storing "10"
Sign Positive to 0
Exponent part 3 to 82
H
to (10000010)
2
Mantissa (010 00000 00000 00000 00000)
2
Therefore, the data expression will be 41200000
H
, as shown below.
(b) Storing "0.75"
Sign Positive to 0
Exponent part -1 to 7E
H
to (01111110)
2
Mantissa (100 00000 00000 00000 00000)
2
Therefore, the data expression will be 3F400000
H
, as shown below.
POINT
In binary notation, the portion of the value following the decimal point is calculated
as follows:
(0.1101)
2
=2
-1
+2
-2
+2
-4
=0.5+0.25+0.0625=(0.8125)
10
0.1 1 0 1
This bit expresses2
-1
This bit expresses2
-2
This bit expresses2
-3
This bit expresses2
-4
(10)10 (1010)2 (1.01000..... 2
3
)2
Sign Exponent part Mantissa
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
41 2 00000
(0.75)10 (0.11)2 (1.100..... 2
-1
)2
Sign Exponent part Mantissa
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3F4 00000

 Loading...
Loading...











