6V&12V Serials
0605
| Working principle
The chemical reaction-taking place in lead acid battery is as follows:
Following side reaction ① takes place in ordinary lead acid battery:
This side reaction makes water loss gradually and distilled water need to be added regularly to keep
the battery operate normally.
Thus there is a path existing between the positive and the negative for O2 recombination. Also
special alloy grid is chosen to increase over-potential of hydrogen evolution on the negative plate,
which minimize generation of Hydrogen. The reactions are as follows:
So it is possible to build EOS series battery in sealed structure.
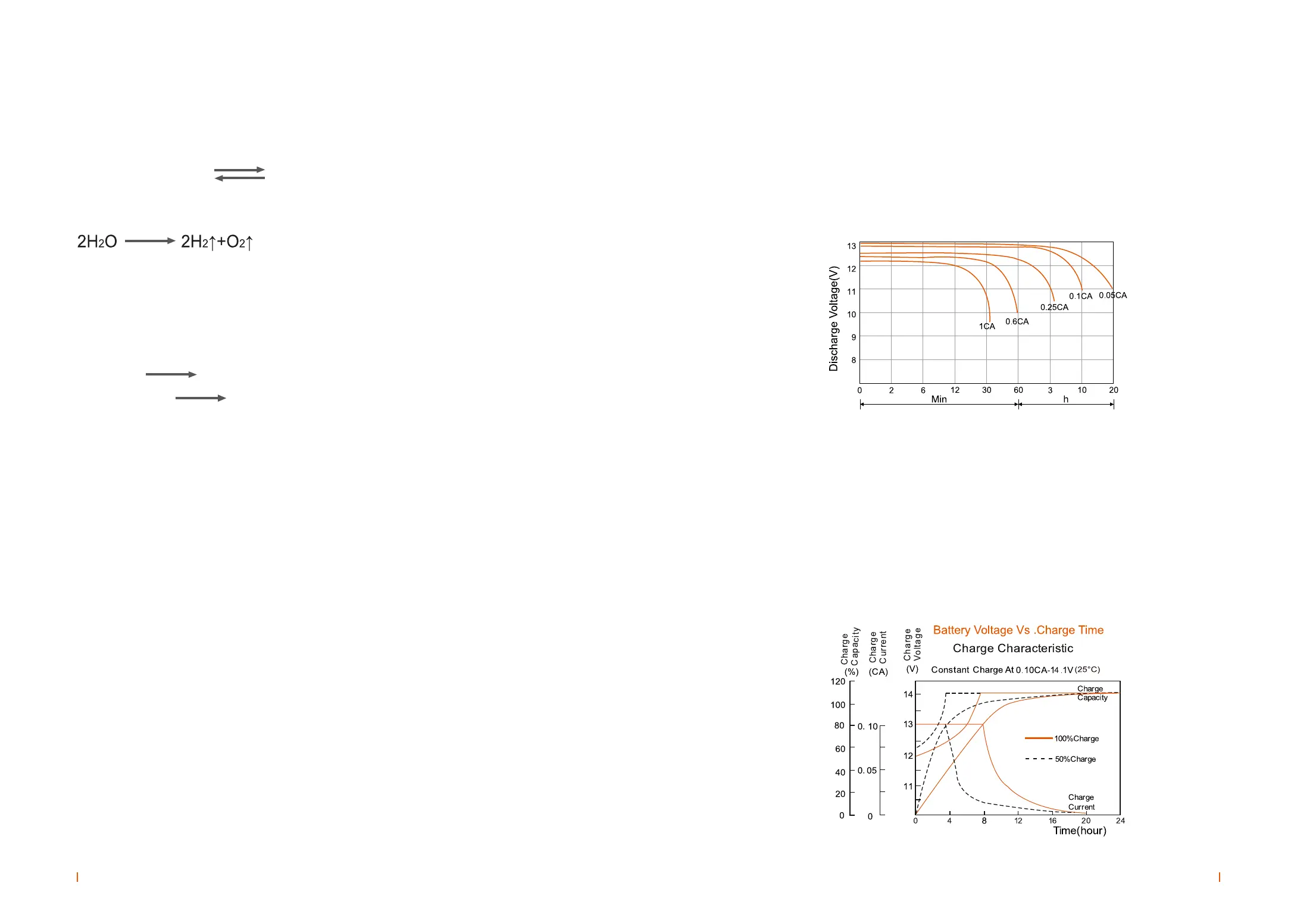
Figure 2-2 is the battery charging characteristics curve of 6V & 12V series battery with constant
voltage and limited current (0.1C
10
A current, voltage limit 2.35V/cell), fully discharged battery charges
for 24 hours, and the charge power up to 105%. The dotted line is the 50% charge curve.
Pb+PbO2+2H2SO4 2PbSO4+2H2O
Discharge
Charge
2Pb +O
2
2PbO
PbO+ H2SO4
PbSO4 +H2O
①
②
③
| Discharge performance
1$68(,6"9'.8"+"6%$+,:%,6'
.8"<%$+'1B4D=E
Fig.2-1 the terminal voltage vs discharge time curves at different current at 25°C
Note:
■ Discharge current is larger, the actual discharge capacity is much less.
■ Discharge end voltage is varying with discharge current, voltage should not lower than specied value.
Terminal Voltage(V) Vs.Discharge Time (25°C,77°F)
| Charge Performance
Fig.2-2 the battery voltage vs charge time curves at 25°C
 Loading...
Loading...