Refer to the following sections for more information about cRIO controller pulse-width
measurement options:
• Single Pulse-Width Measurement
• Implicit Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
• Sample Clocked Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
Single Pulse-Width Measurement
With single pulse-width measurement, the counter counts the number of edges on the Source
input while the Gate input remains active. When the Gate input goes inactive, the counter
stores the count in the FIFO and ignores other edges on the Gate and Source inputs. Software
then reads the stored count.
The following figure shows an example of a single pulse-width measurement.
Figure 53. Single Pulse-Width Measurement
SOURCE
GATE
Counter Value
Latched Value
10
2
2
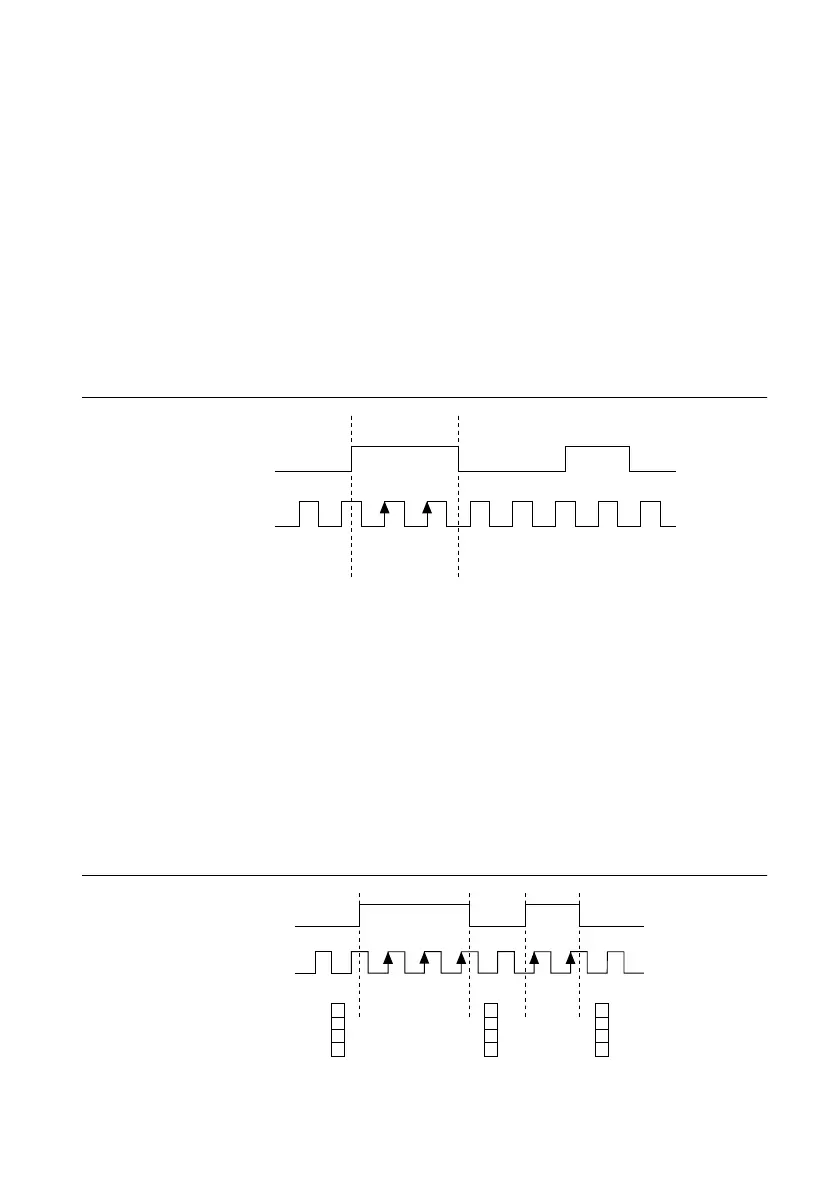
Implicit Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
An implicit buffered pulse-width measurement is similar to single pulse-width measurement,
but buffered pulse-width measurement takes measurements over multiple pulses.
The counter counts the number of edges on the Source input while the Gate input remains
active. On each trailing edge of the Gate signal, the counter stores the count in the counter
FIFO. The sampled values will be transferred to host memory using a high-speed data stream.
The following figure shows an example of an implicit buffered pulse-width measurement.
Figure 54. Implicit Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
SOURCE
GATE
Counter Value
Buffer
10 3
3 2
212
3
3
2
80 | ni.com | cRIO-904x User Manual

 Loading...
Loading...