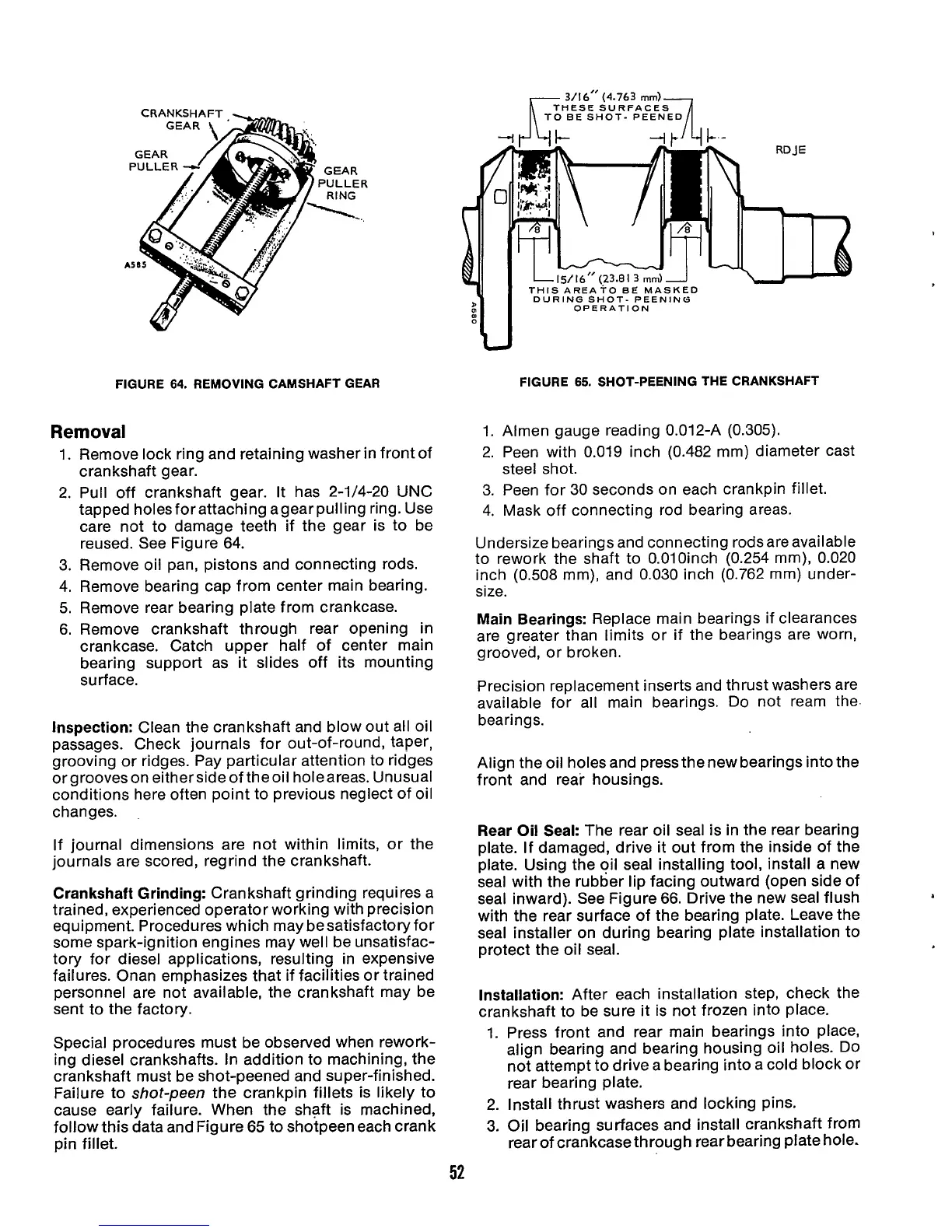
FIGURE
64.
REMOVING CAMSHAFT GEAR
Removal
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Remove lock ring and retaining washer in front of
crankshaft gear.
Pull off crankshaft gear. It has 2-1/4-20 UNC
tapped holesfor attaching agear pulling ring. Use
care not to damage teeth if the gear is to be
reused. See Figure 64.
Remove oil pan, pistons and connecting rods.
Remove bearing cap from center main bearing.
Remove rear bearing plate from crankcase.
Remove crankshaft through rear opening
in
crankcase. Catch upper half of center main
bearing support as
it
slides off its mounting
surface.
Inspection:
Clean the crankshaft and blow out all oil
passages. Check journals for out-of-round, taper,
grooving or ridges. Pay particular attention to ridges
orgrooveson eitherside of theoil holeareas. Unusual
conditions here often point to previous neglect of oil
changes.
.
If journal dimensions are not within limits, or the
journals are scored, regrind the crankshaft.
Crankshaft Grinding:
Crankshaft grinding requires a
trained, experienced operator working with precision
equipment. Procedures which may besatisfactory for
some spark-ignition engines may well be unsatisfac-
tory for diesel applications, resulting in expensive
failures. Onan emphasizes that if facilities or trained
personnel are not available, the crankshaft may be
sent to the factory.
Special procedures must be observed when rework-
ing diesel crankshafts.
In
addition to machining, the
crankshaft must be shot-peened and super-finished.
Failure to
shot-peen
the crankpin fillets is likely to
cause early failure. When the shaft is machined,
follow this data and Figure
65
to shotpeen each crank
pin fillet.
3/16’’
(4.763
mrn)
~\HEs~
TO
BE
SHOT- SURFACES PEENA
II
I
L!z&ZZ~J.%
,TO
EE
MASKED
-
._.
.-
1
I
THIS
AREA
DURING
SHOT-
PEENINU
OPERATION
U
FIGURE
65.
SHOT-PEENING THE CRANKSHAFT
1. Almen gauge reading 0.012-A
(0.305).
2. Peen with 0.019 inch (0.482 mm) diameter cast
3.
Peen for
30
seconds on each crankpin fillet.
4. Mask off connecting rod bearing areas.
steel shot.
Undersize bearings and connecting rodsare available
to rework the shaft to 0.010inch (0.254 mm), 0.020
inch (0.508 mm), and
0.030
inch (0.762 mm) under-
size.
Main Bearings:
Replace main bearings if clearances
are greater than limits or if the bearings are worn,
grooved, or broken.
Precision replacement inserts and thrust washers are
available for all main bearings.
Do
not ream the
bearings.
Align the oil holes and press the new bearings into the
front and rear housings.
Rear
Oil
Seal:
The rear oil seal is in the rear bearing
plate. If damaged, drive it out from the inside of the
plate. Using the oil seal installing tool, install a new
seal with the rubber lip facing outward (open side of
seal inward). See Figure 66. Drive the new seal flush
with the rear surface of the bearing plate. Leave the
seal installer on during bearing plate installation to
protect the oil seal.
Installation:
After each installation step, check the
crankshaft to be sure it is not frozen into place.
1.
Press front and rear main bearings into place,
align bearing and bearing housing oil holes. Do
not attempt to drive a bearing into a cold block or
rear bearing plate.
2. Install thrust washers and locking pins.
3.
Oil bearing surfaces and install crankshaft from
rear of crankcase through rear bearing plate hole.
52

 Loading...
Loading...