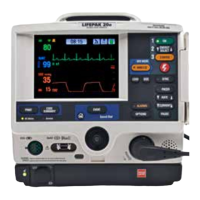
Shock Advisory System
LIFEPAK 1000 Defibrillator Operating Instructions B-5
©2018 Physio-Control, Inc.
MOTION DETECTION
The Shock Advisory System detects patient motion independent of ECG analysis. MOTION
DETECTION can be set up to be ON or OFF. For more information, see “Changing Setup
Options” in the LIFEPAK 1000 Defibrillator Operating Instructions.
A number of activities can create motion, including CPR, rescuer movement, patient movement,
and vehicle movement. If variations in the transthoracic impedance signal exceed a maximum
limit, the Shock Advisory System determines that patient motion of some kind is present. If
motion is detected, the ECG analysis is inhibited. The operator is advised by a voice prompt.
After 10 seconds, if motion is still present, the motion alert stops and the analysis always
proceeds to completion. This limits the delay in therapy in situations where it may not be
possible to stop the motion. However, the rescuer should remove the source of motion
whenever possible to minimize the chance of artifact in the ECG.
There are two reasons why ECG analysis is inhibited when the motion alert occurs, and why the
rescuer should remove the source of the motion whenever possible:
• Such motion may cause artifact in the ECG signal. This artifact may occasionally cause the
Shock Advisory System to reach an incorrect decision.
• The motion may be caused by a rescuer’s interventions. To reduce the risk of inadvertently
shocking a rescuer, the motion alert prompts the rescuer to move away from the patient. This
will stop the motion and ECG analysis will proceed.
DEFINITIONS AND REFERENCES
A true positive (A) is a correct classification of a shockable rhythm. A true negative (D) is a
correct classifications of all rhythms for which a shock is not indicated. A false positive (B) is an
organized or perfusing rhythm or asystole that has been incorrectly classified as a shockable
rhythm. A false negative (C) is a VF or VT associated with cardiac arrest that has been
incorrectly classified as non-shockable.
The sensitivity of the device for shockable rhythms is A/(A+C). The true predictive value is
expressed as A/(A+B). The specificity of the device for non-shockable rhythms is D/(B+D). The
false positive rate is expressed as B/(B+D).
3
1 Kerber RE, et al, "Automatic External Defibrillators for Public Access Defibrillation: Recommendations for Specifying
and Reporting Arrhythmia Analysis Algorithm Performance, Incorporating New Waveforms, and Enhancing Safety: A
Statement for Health Professionals from the American Heart Association Task Force on Automatic External
Defibrillation", Subcommittee on AED Safety and Efficacy. Circulation, 1997: Vol. 95: 1677-1682.
2 Clause 201.7.9.3.103, "Essential Performance data of the Rhythm Recognition Detector," International Electrotechnical
Association, IEC 60601-2-4, Medical Electrical Equipment – Part 2-4: Particular Requirements for the Basic Safety and
Essential Performance of Cardiac Defibrillators: 2010
3 Quoted from clause 201.107, "Requirements for Rhythm Recognition Detector," International Electrotechnical
Association, IEC 60601-2-4, Medical Electrical Equipment – Part 2-4: Particular Requirements for the Basic Safety and
Essential Performance of Cardiac Defibrillators: 2010.
 Loading...
Loading...