15
Competence in Functional Safety
Functional safety of globe valves, rotary plug valves, ball valves and butterfly valves
5.3 Ball valve requirements Responsibility
Note for ball valves that higher initial breakaway torques arise as the differential pressure
of the process medium rises, requiring higher actuator torques.
Manufacturer
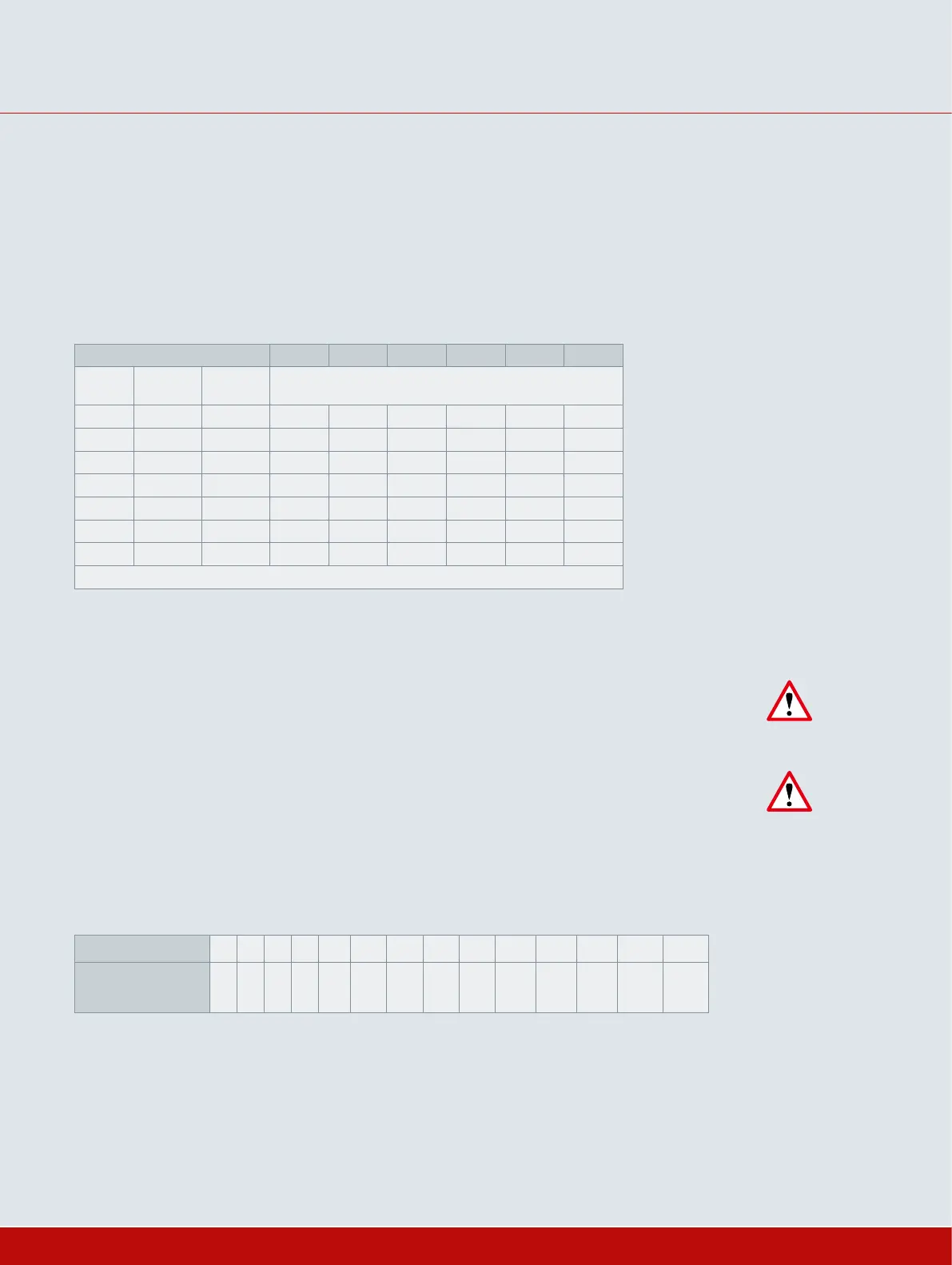
Differential pressure ∆p (bar) 0 3 6 10 16 40
DN
M
dmax
(Nm)
M
d
(Nm) M
dl
(Nm)
15 60 3 5 5 5 8 9 11
25 240 5 10 10 10 14 18 28
40 450 10 20 20 20 26 35 52
50 450 15 30 30 33 36 42 73
80 750 25 60 60 66 72 86 144
100 750 40 90 90 105 120 140 251
150 3160 60 120 120 160 210 290 450
Max. permissible torque, required torques and initial breakaway torques
Example: Torque specifications for a ball valve
Media, especially degreasing, swelling and fibrous media, may affect the torque.
The operating conditions, e.g. switching interval and the medium temperature, have
an effect on the torques.
The mounting of the valve and actuator is of vital importance.
The permissible torques for the ball valve shaft, shaft adapter and bridge have been
verified by the manufacturer. As a result, the max. torque of the actuator (air or spring
torque) must not exceed these torques under any circumstances.
The corresponding specifications in accordance with DIN EN ISO 5211/DIN EN 15081
(NAMUR Recommendation NE 14) must be observed
Operator
Manufacturer
Flange type
F03 F04 F05 F07 F10 F12 F14 F16 F25 F30 F35 F40 F48 F60
Maximum torque of the
attachment flanges (Nm)
32 63 125 250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000 16000 32000 63000 125000 250000
Maximum torque of the attachment flanges according to DIN EN ISO 5211

 Loading...
Loading...