NAT_S615
Entry ID: 109744660, V1.1, 08/2017
Siemens AG All rights reserved
Process flow (active connection establishment from PC to CPU):
The additional subnet 172.16.1.0/24 is used by the SCALANCE S615. The
SCALANCE S615 uses NETMAP for the address translation. With NETMAP,
complete subnets can be translated to a different subnet. The addresses are
translated one to one.
For the example, this results in the following translations:
Table 2-2
Via routing, the PC accesses the IP address 172.16.1.20 as the destination, for
example.
Using the definition in its NAT table, the SCALANCE S615 replaces the destination
IP address to 192.168.2.20 and sends the packet to CPU1.
The source IP address (in this document: 192.168.1.10) is not changed; from the
CPU’s perspective, the packet is from a non-local subnet.
That is why the CPU requires an additional entry for the gateway (IP address of the
SCALANCE S615 for VLAN1).
In all reply packets from the CPU to the PC, the source IP address 192.168.2.x is
automatically replaced with 172.16.1.x.
Advantages
The advantage of the NAT table is that, due to the use of additional addresses per
CPU, all ports can be forwarded or used. The one-to-one address translation
simplifies the NAT configuration, since there is only one line necessary in the NAT
table.
Disadvantages
The disadvantage is that only active connection establishment from the PC to the
CPU is possible. The route to the virtual subnet needs to be known. The virtual
NAT IP addresses cannot be accessed directly.
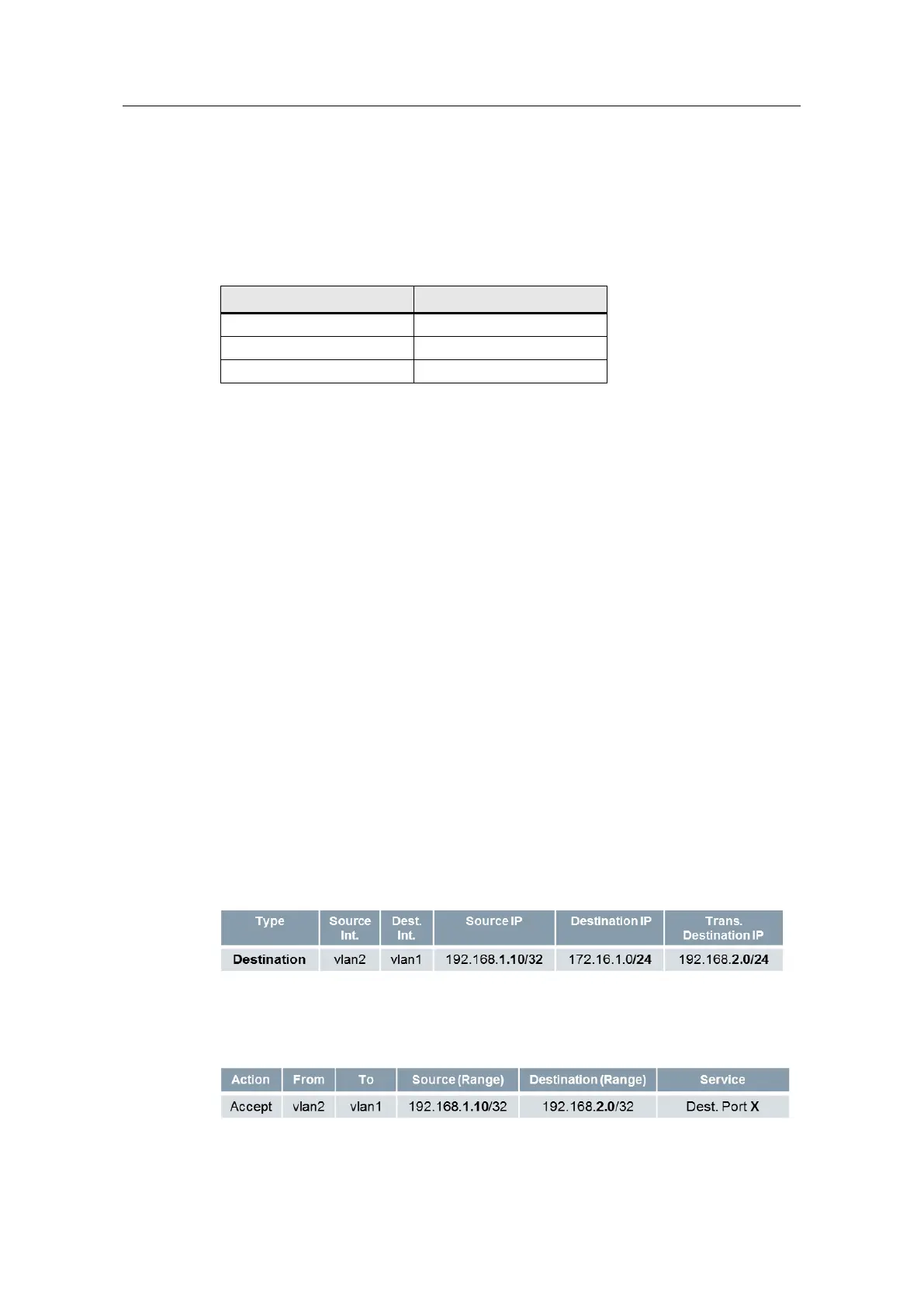
NAT and firewall rules
The NAT table of the SCALANCE S615 translates packets from 172.16.1.0/24 with
the destination IP address to VLAN 1. The translation is done one-to-one.
Figure 2-2:
The firewall must allow communication between the PC (VLAN2) and the
automation devices (VLAN1).
Figure 2- :

 Loading...
Loading...











