NAT_S615
Entry ID: 109744660, V1.1, 08/2017
Siemens AG All rights reserved
2.2 Web server access via NAPT
Starting situation
The PC is to be able to access the CPU’s web server without a gateway.
The destination port is not defined and can be changed when establishing the
connection.
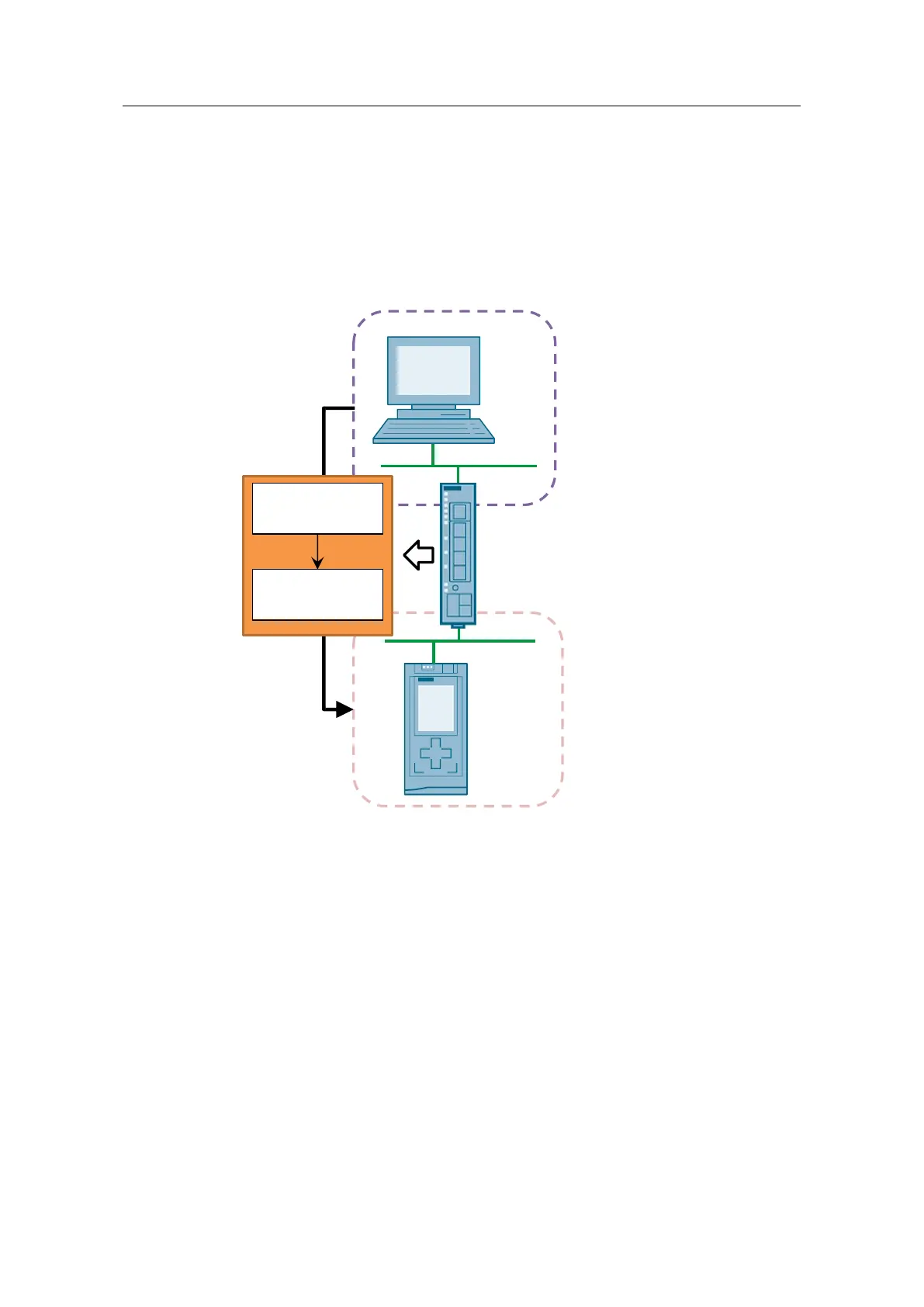
Figure 2-3
VLAN2: 192.168.1.0/24
VLAN1: 192.168.2.0/24
CPU:
192.168.2.20
Gateway:
192.168.2.1
PC:
192.168.1.10
Gateway:
None
192.168.2.1
192.168.1.1
SRC IP: 192.168.1.10
DST IP: 192.168.1.1
DST Port: 8080
SRC IP: 192.168.1.10
DST IP: 192.168.2.20
DST Port: 80
NAPT Table
Requirements
For network separation, the SCALANCE S615 has two VLANs with different
network IDs. As a result, the device has a separate IP address for each VLAN
(in this document: VLAN1: 192.168.2.1 and VLAN2: 192.168.1.1).
In addition, a NAPT table is defined in the SCALANCE S615 to translate the PC’s
message frames to a different IP address.
For the CPU’s reply packets to find their way to VLAN2, the IP address of the
SCALANCE S615 (VLAN1) must be entered in the CPU as the gateway.
Process flow (active connection establishment from PC to CPU)
Instead of the IP address of the CPU, 192.168.2.20, the PC accesses the local IP
address of the SCALANCE S615 (192.168.1.1), including a port, as the
destination.
Using the definition in its NAPT table, the SCALANCE S615 replaces the
destination IP address and optionally a port and sends the packet to the CPU.

 Loading...
Loading...











