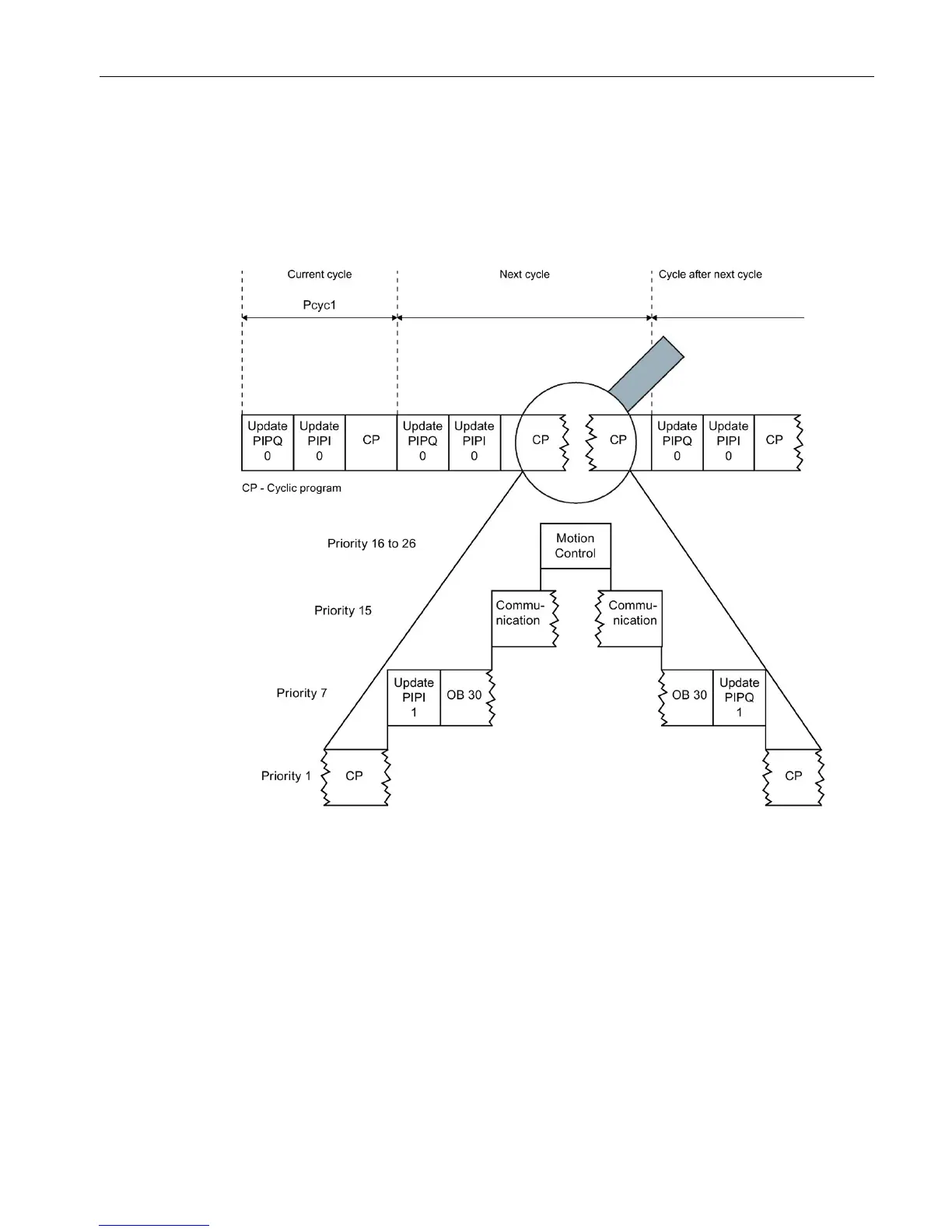
The figure below shows the different cycle times T
cyc1
and T
cyc2
using an example.
Because the cyclic program is interrupted by a cyclic interrupt OB in this example (for
example: OB 30), the cycle time T
cyc2
is greater than T
cyc1
. The cyclic interrupt OB in turn is
interrupted by Motion Control functions and communication.
Figure 3-3 Possible causes of differing cycle times

 Loading...
Loading...











