Cycle and response times of the S7-1500R/H redundant system
5.4 Response time of R/H CPUs
Cycle and response times
Function Manual, 10/2018, A5E03461504-AD
67
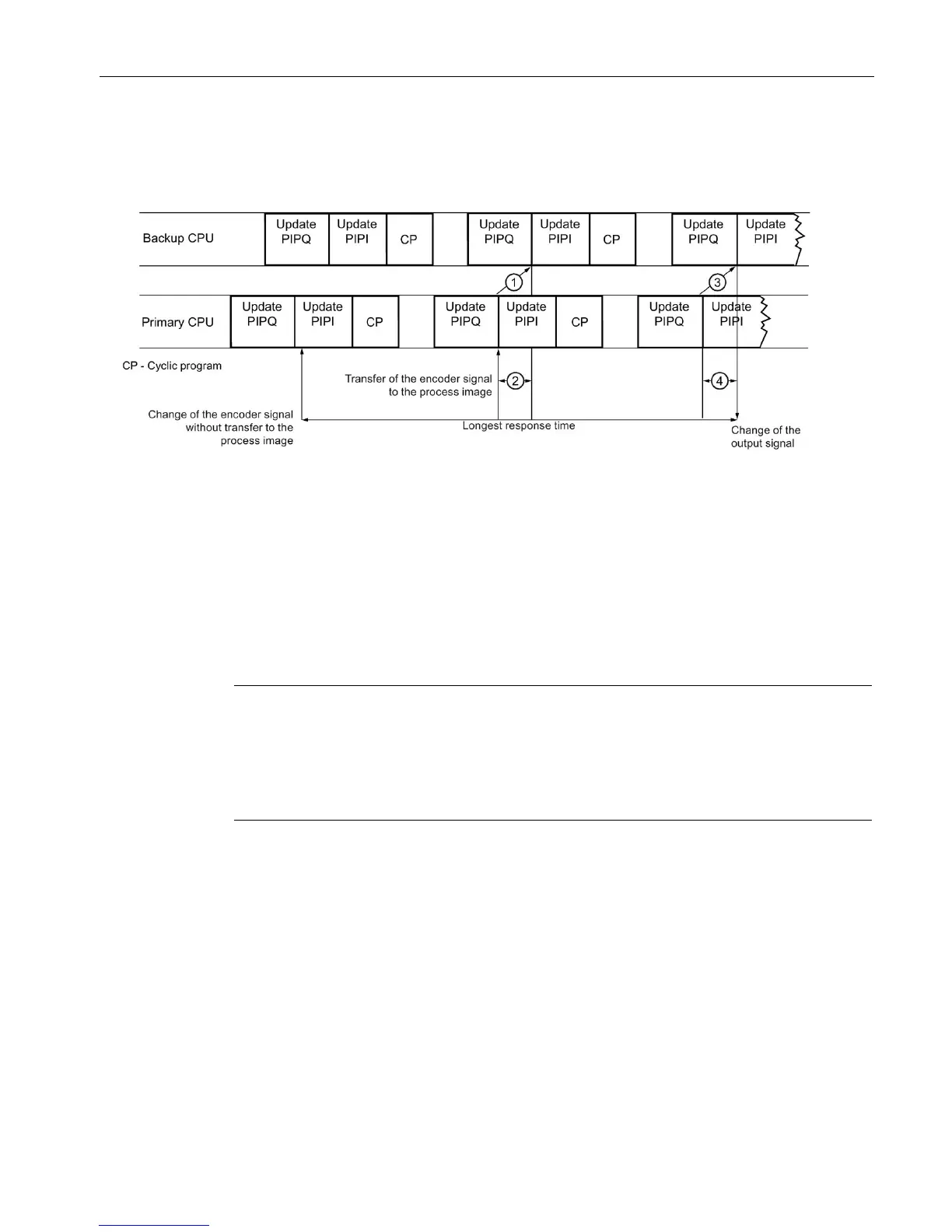
In the figure below, the process image has already been updated by the time of the signal
change. It therefore takes one cycle until the system detects the change and sets the input in
the process image. The output signal is changed after an additional cycle.
Synchronization of the encoder signal change in the backup CPU
Time lag of the backup CPU to the primary CPU
Synchronization of the output signal change in the backup CPU
Time lag of the backup CPU to the primary CPU until actual output of the signal change to the IO devices in the
Figure 5-7 Longest response time
The cycle times include the time lag. The time lag of the backup CPU to the primary CPU
depends on the synchronization load. The synchronization load results from the data to be
synchronized in the user program and in the communication.
Note
Effect of the time lag
The synchronization and transfer of the changes requires computing time. The time lag
therefore affects both CPUs (from the primary CPU to the backup CPU and from the backup
CPU to the primary CPU). The slower the CPU and the slower and longer
synchronization connection, the greater the time lag.

 Loading...
Loading...











