B504
B504 Page 4 840D/828D SINUMERIK Operate
Notes
Section 3
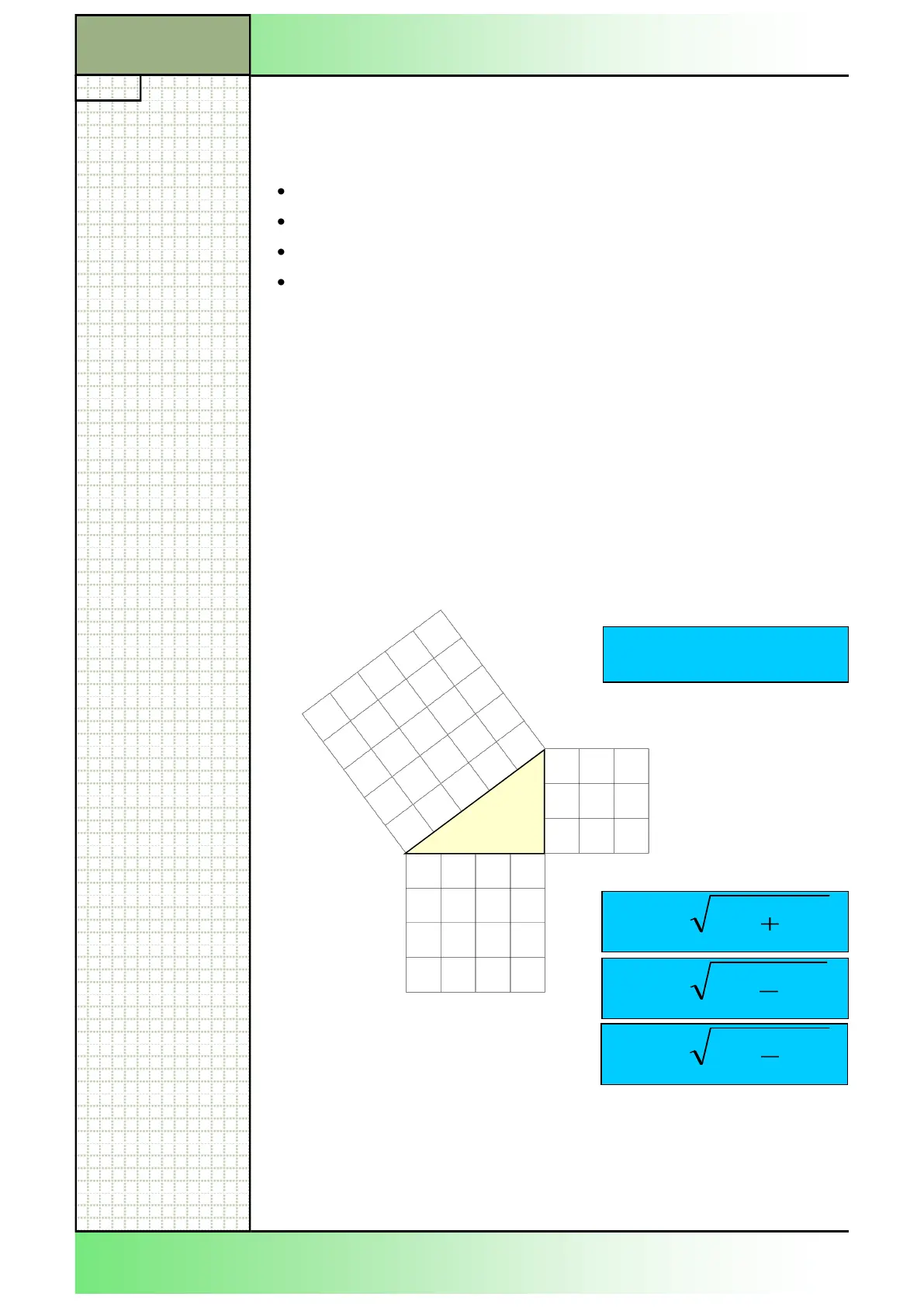
The Pythagorean theorem
In a right-angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse (the side
opposite the right angle), c, is equal to the sum of the squares
of the other two sides, b and a - that is: a² + b² = c².
The right angled triangle has a special meaning in geometry, since the
sides of such a triangle exhibit a definite relationship to one another.
The various sides of the right angled triangle are named specifically:
The longest line opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
The two other lines, which form the right angle, are called cathetus.
The side opposite an angle is called the opposite side.
The bounding side of the angle is called the adjacent side.
Pythagorean theorem :
In case of a right angled triangle the missing length of a side can be calcu-
lated if the length of the other two sides is known. For this the Pythagorean
theorem is used.
c²= a² + b²
By suitable rearrangement of
the equations the respective
sides can be calculated.
3x3=9
4x4=16
5x5=25
16+9=25
a =
c =
b =
a
b
c
 Loading...
Loading...























