7
.
Working Principle
Working
conditions
Pilot valve
Pressure
conditions
Operation description
Internal construction/Cylinder actuation circuit
(Meter-out control) example
Low
Speed
air supply
ON
P
S
> P
A
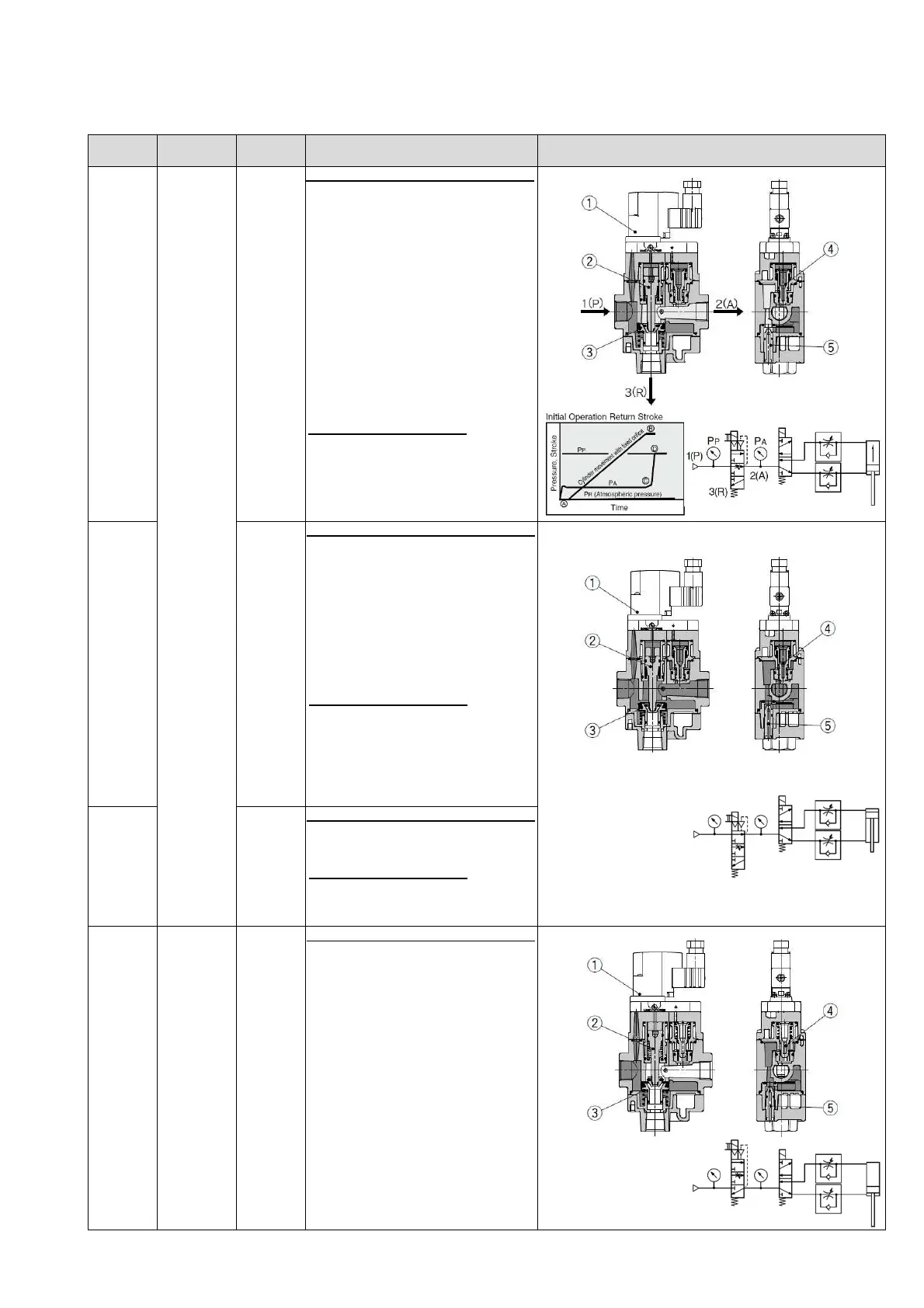
Operation description of the soft start-up valve
When the pilot valve ① is energized or
turned ON manually, the spool ② is
pushed down due to the pilot air and
gets into contact with the valve ③,
closing the flow passage to port 3 (R). At
this time, force that pushed the valve ③
≧ force that pushed down the spool ②
Therefore, the flow passage from the
valve ③ to port 2 (A) is still closed.
Furthermore, the piston ④ is pushed
down due to the pilot air, and the flow
passage from the needle ⑤ to port 2
(A) opens.
And then, the air pressure whose flow
rate is adjusted by the needle ⑤ flows
to port 2 (A).
Description of cylinder actuation
The meter-in control of the needle ⑤
slowly moves the cylinder from A to B.
P
P
: Inlet pressure
P
A
: Outlet pressure
High
Speed
air supply
P
S
≦P
A
Operation description of the soft start-up valve
When the outlet side is filled with
pressure supplied from the needle ⑤,
P
A
increased. When P
A
exceeds the
specified pressure, the force that
pushed up the valve ③ becomes
smaller than t
he force that pushed down
the spool ②. Then, the valve ③ is
pushed down, opening the flow
passage, and pressure is supplied to
port 2 (A).
Description of cylinder actuation
When P
S
< P
A
after the cylinder reaches
B, the mail calve fully opens and P
A
increase rapidly as shown C to D and
becomes the same pressure as P
P
.
P
S
:
Pressure for switching to rapid air supply
Normal
operation
P
S
≒P
A
Operation description of the soft start-up valve
The valve ③ holds the fully open
condition.
Description of cylinder actuation
The cylinder operation is controlled by a
meter-out circuit on the cylinder side.
Exhaust
OFF
-
Operation description of the soft start-up valve
When the pilot valve ① is turned OFF,
the pilot air of the spool ②
from the pilot valve ①, and the spool ②
and valve ③ are returned upward due
to the spring. This opens the flow
passage to the port 3 (R), exhausting
the air pressure on the port 2 (A)
side.
The pilot air of the piston ④ is also
exhausted from the pilot valve ①, and
the piston ④ is returned upward due to
the spring, closing the flow passage
from needle ⑤.
-25-
 Loading...
Loading...